Economic Depression: Causes Examples Effects Possible Solutions
What it is: An economic depression is a prolonged period of decline in economic activity, worse than a recession. A recession occurs when economic growth falls for two consecutive quarters and can last up to three years, such as in the 2007-2009 recession. In periods of depreciation, real GDP falls by more than 10% and lasts for 3 years or more.
How Does A Recession Affect Me
You may lose your job during a recession, as unemployment levels rise. Not only are you more likely to lose your current job, it becomes much harder to find a job replacement since more people are out of work. People who keep their jobs may see cuts to pay and benefits, and struggle to negotiate future pay raises.
Investments in stocks, bonds, real estate and other assets can lose money in a recession, reducing your savings and upsetting your plans for retirement. Even worse, if you cant pay your bills due to job loss, you may face the prospect of losing your home and other property.
Business owners make fewer sales during a recession, and may even be forced into bankruptcy. The government tries to support businesses during these tough times, like with the PPP during the coronavirus crisis, but its hard to keep everyone afloat during a severe downturn.
With more people unable to pay their bills during a recession, lenders tighten standards for mortgages, car loans and other types of financing. You need a better credit score or a larger down payment to qualify for a loan that would be the case during more normal economic times.
Even if you plan ahead to prepare for a recession, it can be a frightening experience. If theres any silver lining, its that recessions do not last forever. Even the Great Depression eventually ended, and when it did, it was followed by the arguably the strongest period of economic growth in U.S. history.
Reduction In Purchasing Across The Board
With people’s investments worthless, their savings diminished or depleted, and credit tight to nonexistent, spending by consumers and companies alike ground to a standstill. As a result, workers were laid off en masse. In a chain reaction, as people lost their jobs, they were unable to keep up with paying for items they had bought through installment plans repossessions and evictions were commonplace. More and more unsold inventory began to accumulate. The unemployment rate rose above 25%, which meant even less spending to help alleviate the economic situation.
Don’t Miss: Pristiq Anxiety Side Effects
What Caused The Depression Of 1890
CausescausesPanic of 1893economy
. Regarding this, what caused the 1890s depression in Australia?
Banks flourished and factory jobs multiplied. But then 1890 hit along with a drought that sent the Land Down Under spiraling into an economic depression. With a decreased demand for wool , public works projects fell like dominoes and banks closed their doors.
what was happening in the world in the 1890s? The 1890s was the ten-year period from the years 1890 to 1899. In the United States, the 1890s were marked by a severe economic depression sparked by the Panic of 1893, as well as several strikes in the industrial workforce. The decade saw much of the development of the automobile.
Likewise, what caused the economic depression in Europe in the 1870s?
American inflation, rampant speculative investments , the demonetization of silver in Germany and the United States, ripples from economic dislocation in Europe resulting from the Franco-Prussian War , major property losses in the Chicago and Boston fires, and other
What caused the economic depression in the late 1800s?
The primary cause of the price depression in the United States was the tight monetary policy that the United States followed to get back to the gold standard after the Civil War.
Genes’ Effect On Mood And Depression

Every part of your body, including your brain, is controlled by genes. Genes make proteins that are involved in biological processes. Throughout life, different genes turn on and off, so that in the best case they make the right proteins at the right time. But if the genes get it wrong, they can alter your biology in a way that results in your mood becoming unstable. In a person who is genetically vulnerable to depression, any stress can then push this system off balance.
Mood is affected by dozens of genes, and as our genetic endowments differ, so do our depressions. The hope is that as researchers pinpoint the genes involved in mood disorders and better understand their functions, depression treatment can become more individualized and more successful. Patients would receive the best medication for their type of depression.
Another goal of gene research, of course, is to understand how, exactly, biology makes certain people vulnerable to depression. For example, several genes influence the stress response, leaving us more or less likely to become depressed in response to trouble.
The evidence for other types of depression is more subtle, but it is real. A person who has a first-degree relative who suffered major depression has an increase in risk for the condition of 1.5% to 3% over normal.
Read Also: Is Tequila A Stimulant Or Depressant
What Were The Long Term Effects Of The Great Depression On Families
The Depression had a powerful impact on family life. It forced couples to delay marriage and drove the birthrate below the replacement level for the first time in American history. The divorce rate fell, for the simple reason that many couples could not afford to maintain separate households or pay legal fees.
Great Depression Ends And World War Ii Begins
With Roosevelts decision to support Britain and France in the struggle against Germany and the other Axis Powers, defense manufacturing geared up, producing more and more private sector jobs.
The Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in December 1941 led to Americas entry into World War II, and the nations factories went back in full production mode.
This expanding industrial production, as well as widespread conscription beginning in 1942, reduced the unemployment rate to below its pre-Depression level. The Great Depression had ended at last, and the United States turned its attention to the global conflict of World War II.
Access hundreds of hours of historical video, commercial free, with HISTORY Vault. Start your free trial today.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
Entrepreneurial Activity: Business Formation And Expansion
Aside from the general downturn in investment activity, recessionsand particularly ones that involve a credit crunch as the current one doescan hamper small business formation and entrepreneurial activity.
From a long-run perspective, new business formation is important because of the links between innovation, R& D, and new start-ups. New businesses are often formed to develop, implement, and market new technologies. To take one example, Kirchhoff et al. examines the link between university-based R& D activity and new business creation and finds that university R& D expenditures are significantly related to new firm formations in the same . Thus delays in new business formation may mean delays in the development and adoption of new technologies, causing long-run damage to the economy.7
There are several ways recessions can slow business formation and expansion. First, to state the obvious, new businesses need new customers. An economic slowdown means that there is less spending overall therefore, people looking to start a new business may decide to delay ventures until demand returns to normal levels. Second, new businesses need new investors and creditors. Lower incomes and wealth levels may mean that new business will find it more difficult to find individual investors, and credit constraints may limit borrowing from private banks.
Rise Of Fascism In Germany Essay
Introduction This investigation examines to what extent the economic failures of the Weimar republic led to the rise of fascism in Germany, especially in regards to the importance of the hyperinflation of 1923 and the Dawes plan in conjunction with the Great Depression. Beginning with the end of World War I and the Treaty of Versailles, which set the foundation for the economic failure of the Weimar Republic, it will demonstrate the impact of other nations on Germanys economy. However, it will also address internal factors which caused continuous inflation and only postponed the inevitable failure of the economy.
Also Check: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
What Triggers A Depression
A series of factors can cause an economy and production to contract severely. In the case of the Great Depression, questionable monetary policy took the blame.
After the stock market crashed in 1929, the Federal Reserve continued to hike interest ratesdefending thegold standard took priority over pumping money into the economy to encourage spending. Those actions triggered massive deflation. Prices declined by about 10% each year and consumers, mindful that the prices for goods and services would continue to fall, refrained from making purchases.
Effects Of The Great Depression
When Franklin D. Roosevelt became President in 1933, he almost immediately started pushing through Congress a series of programs and projects called the New Deal. How much the New Deal actually alleviated the depression is a matter of some debate throughout the decade, production remained low and unemployment high.
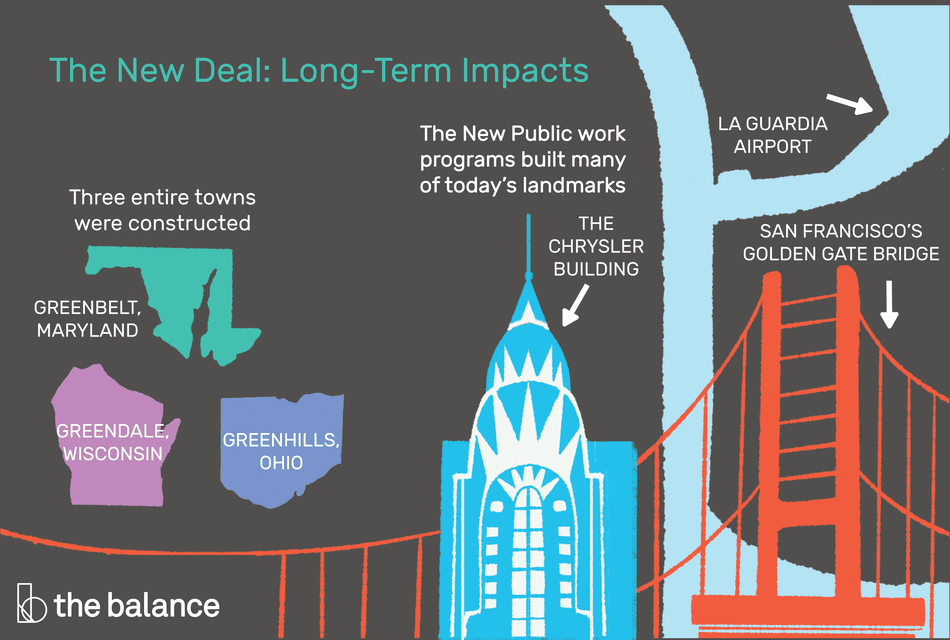
But the New Deal did more than attempt to stabilize the economy, provide relief to jobless Americans and create previously unheard of safety net programs, as well as regulate the private sector. It also reshaped the role of government, with programs that are now part of the fabric of American society.
Among the New Deal’s accomplishments:
- Worker protections, like the National Labor Relations Act, which legitimized unions, collective bargaining, and other employee rights
- Public works programs, aimed at providing employment via construction projects a win-win for society and individuals
- Individual safety nets, such as the Social Security Act of 1935, which created the pension system still with us today, and unemployment insurance
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Schizophrenia Permanently
What Causes An Economic Depression
Who are the experts?Our certified Educators are real professors, teachers, and scholars who use their academic expertise to tackle your toughest questions. Educators go through a rigorous application process, and every answer they submit is reviewed by our in-house editorial team.
An economic depression is caused by a massive slowdown of business activity. This slowdown causes a decrease in a nation’s gross national production and helps to begin an adverse psychological belief in the consumer that is enhanced by a rise in prices and unemployment, and a decrease or lack of…
Is It Safe To Keep All Your Money In One Bank
insures the money you put into savings accounts, checking accounts certificates of deposit and money market deposit accounts up to a maximum of $250,000. If you put all of your money into these kinds of accounts at one bank and the total exceeds the $250,000 limit, the excess isnÄôt safe because it is not insured.
You May Like: How To Handle Eating Disorders
Th Century Japan Analysis
Nevertheless, this new tax reform harmed the farmers, since they had to pay the same amount of taxes even if they had a bad harvest and they had to put the lower princes on their sellings as a consequence of the deflation. Meiji leaders focused their efforts in transforming the economy to an industrial one, where was promoted technological industrialization by importing new machinery and develop equipments. Old factories were bought by new private businessmen, helping the economy growth. Nonetheless, Japanese workers also helped the economy as well, women and men under very poor working environment, worked to produce many goods for exportation. This labor played a key role to pay for the new utilities and machinery to keep up with the quick industrialization Japan
Disparities In Wealth And Income
Economists such as Waddill Catchings, William Trufant Foster, Rexford Tugwell, Adolph Berle , popularized a theory that had some influence on Franklin D. Roosevelt. This theory held that the economy produced more goods than consumers could purchase, because the consumers did not have enough income. According to this view, in the 1920s wages had increased at a lower rate than productivity growth, which had been high. Most of the benefit of the increased productivity went into profits, which went into the stock market bubble rather than into consumer purchases. Thus workers did not have enough income to absorb the large amount of capacity that had been added.
According to this view, the root cause of the Great Depression was a global overinvestment while the level of wages and earnings from independent businesses fell short of creating enough purchasing power. It was argued that government should intervene by an increased taxation of the rich to help make income more equal. With the increased revenue the government could create public works to increase employment and ‘kick start’ the economy. In the USA the economic policies had been quite the opposite until 1932. The Revenue Act of 1932 and public works programmes introduced in Hoover’s last year as president and taken up by Roosevelt, created some redistribution of purchasing power.
Also Check: Can Being Dehydrated Cause Anxiety
A Constrained Presidential Response
President Herbert Hoover’s response to the economic crisis was tardy. A believer in minimal government intervention, he considered direct public relief character-weakening. He did eventually start spending and launched lending and public works projects. Still, according to many economists, it was too little, too late.
What Is The Difference Between A Recession And A Depression
Great question. Unfortunately, there isnt a standard answer, although there is a well-known joke economists like to tell regarding the difference between the two. But, lets come back to that later.
Recession
Lets start by defining a recession. As I mentioned, there are several commonly used definitions of a recession. For example, journalists often describe a recession as two consecutive quarters of declines in quarterly real gross domestic product .
The definition used by economists differs. Economists use monthly business cycle peaks and troughs designated by the National Bureau of Economic Research to define periods of expansion and contractions. The NBER website lists the peaks and troughs in economic activity starting with the December 1854 trough. The website also defines a recession as:
A recession is a significant decline in economic activity spread across the economy, lasting more than a few months, normally visible in real GDP, real income, employment, industrial production, and wholesale-retail sales. A recession begins just after the economy reaches a peak of activity and ends as the economy reaches its trough. Between trough and peak, the economy is in an expansion. Expansion is the normal state of the economy most recessions are brief and they have been rare in recent decades.
Depression
Degree of Severity
Chart 1: Annual growth rate of Real GDP
When your neighbor loses their job, its a recession. When you lose your job, thats a depression!
References
Don’t Miss: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
Economic Scarring: The Long
Report September 30, 2009
Executive summary
Economic recessions are often portrayed as short-term events. However, as a substantial body of economic literature shows, the consequences of high unemployment, falling incomes, and reduced economic activity can have lasting consequences. For example, job loss and falling incomes can force families to delay or forgo a college education for their children. Frozen credit markets and depressed consumer spending can stop the creation of otherwise vibrant small businesses. Larger companies may delay or reduce spending on R& D.
In each of these cases, an economic recession can lead to scarringthat is, long-lasting damage to individuals economic situations and the economy more broadly. This report examines some of the evidence demonstrating the long-run consequences of recessions. Findings include:
There is also substantial evidence that economic outcomes are passed across generations. As such, economic hardships for parents will mean more economic hurdles for their children. While it is often said that deficits can cause transfers of wealth from future generations of taxpayers to the present, this cost must also be compared with the economic consequences of recessions that are also passed to future generations.
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act passed earlier this year included tax cuts, transfers to state governments, and direct spending. The Obama administration has projected that the package would create or save
Diagnosing An Economic Depression
We define a recession as two consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth. In other words, if the economy has been shrinking for at least six months, we have a recession.
Determining what an economic depression is, however, is not so clear. Very few sources tell us exactly what a depression is. They all say the same: A depression is more severe and longer-lasting than a recession.
In a 2008 article about the definition of depression in the Economist titled Diagnosing Depression, the author writes:
So how severe does this current slump have to get before it warrants the D word?
The author searched on the Internet and found two principal criteria for distinguishing an economic depression from a recession:
- GDP must shrink by at least 10% .
- The economic downturn must last longer than three years.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
How Photos From The Battle Of Antietam Revealed The American Civil Wars Horrors
Roosevelt took immediate action to address the countrys economic woes, first announcing a four-day bank holiday during which all banks would close so that Congress could pass reform legislation and reopen those banks determined to be sound. He also began addressing the public directly over the radio in a series of talks, and these so-called fireside chats went a long way towards restoring public confidence.
During Roosevelts first 100 days in office, his administration passed legislation that aimed to stabilize industrial and agricultural production, create jobs and stimulate recovery.
In addition, Roosevelt sought to reform the financial system, creating the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation to protect depositors accounts and the Securities and Exchange Commission to regulate the stock market and prevent abuses of the kind that led to the 1929 crash.