Balance Your Blood Sugar And Avoid Stimulants
Your intake of sugar, refined carbohydrates, caffeine, alcohol and cigarettes, as well as stimulant drugs, all affect the ability to keep ones blood sugar level balanced. On top of this common antipsychotic medication may also further disturb blood sugar control. Stimulant drugs, from amphetamines to cocaine, can induce schizophrenia. The incidence of blood sugar problems and diabetes is also much higher in those with schizophrenia.
Therefore it is strongly advisable to reduce, as much as possible, your intake of sugar, refined carbohydrates, caffeine and stimulant drugs and eat a low glycemic load diet.
What Neurotransmitters Are Involved In Schizophrenia
DOPAMINE
Two brain chemicals may interact to contribute to the development of psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia, according to a new study. The results suggest abnormal levels of the neurotransmitter glutamate may lead to changes in the levels of another neurotransmitter, dopamine, causing the transition into psychosis.
Beside above, what is the chemical imbalance in schizophrenia? Chemistry: Scientists believe that people with schizophrenia have an imbalance of the brain chemicals or neurotransmitters: dopamine, glutamate and serotonin. These neurotransmitters allow nerve cells in the brain to send messages to each other.
In respect to this, what is the role of dopamine in schizophrenia?
Dopamine gets a lot of attention in brain research because its been linked to addiction. It also plays a role in other psychiatric and movement disorders, like Parkinsons disease. In schizophrenia, dopamine is tied to hallucinations and delusions.
What does serotonin do in schizophrenia?
Moreover, serotonin has been implicated in a variety of behaviors and somatic functions that are disturbed in schizophrenia .
Studies On The Glutamatergic Systems
The ability of phencyclidine, a glutamate receptor ion channel blocker, to induce or exacerbate a schizophrenic-like psychoses, has been central to the hypotheses that changed glutamatergic function is involved in the pathology of schizophrenia. This has led to an extensive investigation of glutamatergic markers in postmortem CNS tissue from subjects with schizophrenia. There are two major families of glutamate receptors. One family is a group of ionotropic glutamate receptors made up of the N-methyl-d-aspartate , the -amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid and the kainate receptors. All these receptors are made up of a combination of specific subunits, which assemble in the membrane to form cation conductance channels. The other family of receptors are known as the metabotropic receptors and are G-protein coupled receptors.
In contrast to studies in the thalamus and hippocampus, it has been reported that neither AMPA receptor radioligand binding nor levels of mRNA for AMPA receptor subunits are altered in the frontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. However, levels of mRNA for the NR1, gluR1, gluR7, and KA1 subunits of glutamate receptors have been reported as being decreased in the cortex of schizophrenic subjects not receiving antipsychotic drugs within six months of death. Significantly, in this study decreased levels of mRNA for subunits of the glutamate receptors were not observed in subjects who were receiving antipsychotic drugs up until death.
Also Check: What Is The Phobia Of Death Called
What Occurs In The Brain
| The picture below showsmagnetic resonance image brain scans of a pair of twins:one with schizophrenia, one without schizophrenia. Notice that theventricles are larger in the twin withschizophrenia. |
A reduced size of the hippocampus, increased size of the basal ganglia,and abnormalities in the prefrontal cortex are seen in some people withschizophrenia. However, these changes are not seen in all people withschizophrenia and they may occur in people without this disorder.
Drugs That Influence Neurotransmitters
Perhaps the greatest practical application for the discovery and detailed understanding of how neurotransmitters function has been the development of drugs that impact chemical transmission. These drugs are capable of changing the effects of neurotransmitters, which can alleviate the symptoms of some diseases.
- Agonists vs Antagonists: Some drugs are known as agonists and function by increasing the effects of specific neurotransmitters. Other drugs and referred to as antagonists and act to block the effects of neurotransmission.
- Direct vs Indirect Effects:These neuro-acting drugs can be further broken down based on whether they have a direct or indirect effect. Those that have a direct effect work by mimicking the neurotransmitters because they are very similar in chemical structure. Those that have an indirect impact work by acting on the synaptic receptors.
Drugs that can influence neurotransmission include medications used to treat illness including depression and anxiety, such as SSRIs, tricyclic antidepressants, and benzodiazepines.
Illicit drugs such as heroin, cocaine, and marijuana also have an effect on neurotransmission. Heroin acts as a direct-acting agonist, mimicking the brains natural opioids enough to stimulate their associated receptors. Cocaine is an example of an indirect-acting drug that influences the transmission of dopamine.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Also Check: How To Treat Severe Anxiety And Panic Attacks
Neurotransmitters And T Gondii
For more than 40 years, it has been known that neurotransmitters are involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. An excess of dopamine has been widely suspected, and along with genetics, dopamine-excess has been one of the most thoroughly researched theories. Despite hundreds of research projects, however, relatively few abnormalities in the dopamine system have ever been identified in individuals with schizophrenia. In recent years, more research attention has been focused on other neurotransmitters, especially glutamate and GABA.
Origin of interest in dopamine and T. gondii
Toxoplasma gondii has the ability to make dopamine
Effects of changing levels of dopamine on behavior induced by T. gondii infection
Joanne Webster and her colleagues at Oxford infected rats with T. gondii, then treated them with haloperidol, an antipsychotic known to block dopamine. The effect of the haloperidol was to reverse the behavioral effects of T. gondii. They speculated that possible explanatory mechanisms include the ability of haloperidol to inhibit T. gondii replication and to reduce, directly and indirectly, dopamine levels.5
In other publications, Flegr et al. have speculated that dopamine is the missing link between schizophrenia and toxoplasmosis, specifically suggesting that dopamine is increased by activated cytokines as a consequence of infection.7
Effects of T. gondii infection on GABA, glutamate and other neurotransmitters
Effect of T. gondii on endogenous retroviruses
Neural Circuits And Dopamineglutamate Interactions
The evidence discussed above suggests that, while the dopamine hypothesis can account for the positive symptoms of psychosis, it is less clear whether it can fully account for negative and cognitive symptoms. Similarly, while glutamatergic models of psychosis are able to replicate a wide range of symptoms of psychosis, they do not directly account for the finding of increased presynaptic striatal dopamine function, nor the clinical effectiveness of dopamine antagonists. This suggests that dysfunction in both systems contributes to the pathophysiology of schizophrenia, and highlights the need to understand how these two systems may interact.
Much research has investigated dopamineglutamate relationships in humans using pharmacological challenges. Amphetamine administration has been shown to increase cortical glutamate levels, as measured using 1HMRS220, but dopamine antagonists do not have consistent effects on glutamate levels as measured using 1HMRS221. Several, but not all, PET studies have found that ketamine administration is associated with striatal dopamine release222. While glutamatergic dysfunction may encourage dopaminergic disinhibition, it is clear that this is not the only route to symptoms, given that dopamine antagonists do not entirely ameliorate the effects of NMDA antagonists223.
Read Also: How To Handle Panic Attacks
Other Neurotransmitters In Schizophrenia
Clozapine, which is the most effective medication available for treating the symptoms of Schizophrenia, is a very weak blocker of the D2 dopamine receptors. This suggests that there must be other neurotransmitter systems that are also involved in causing Schizophrenia, though so far not much is known about what are these other factors.
One neurotransmitter that has gotten increased attention in recent years for its role in Schizophrenia in glutamate, which targets NMDA receptors in the brain. Phencyclidine and Ketamine are two drugs that block the actions of glutamate at the NMDA receptor, and these drugs can cause both the positive and negative symptoms of Schizophrenia in people who do not have the condition. Increasing the actions of glutamate by using high doses of precursor molecules that are metabolized into glutamate, such as D-serine, glycine and D-cycloserine, show promise in helping to improve the negative symptoms of Schizophrenia.
Read Also: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Does Too Much Dopamine Cause Schizophrenia
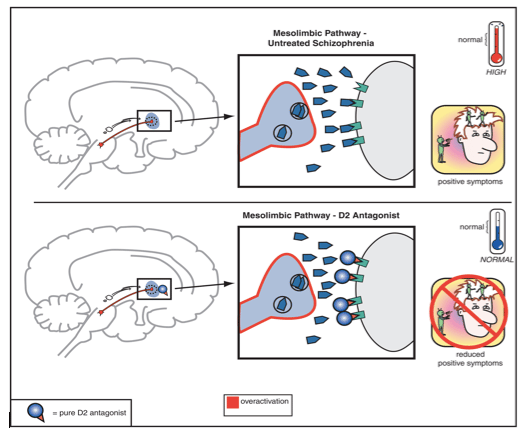
Increased activity of the mesolimbic pathway is related to positive symptoms of schizophrenia . This means that increasing the activity of dopamine receptors in this brain system could theoretically reduce delusions and hallucinations.
A closely related idea is that by blocking post-synaptic dopamine receptors, scientists can reduce the psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia.
As mentioned previously, this is what most modern medications do: they block post-synaptic dopamine receptors in order to reduce psychotic symptoms. Unfortunately, when scientists block all available dopamine receptors they also produce a number of debilitating side effects such as extrapyramidal symptoms and tardive dyskinesia.
Recommended Reading: How To Snap Someone Out Of A Panic Attack
Integrating The Dopamine And Glutamate Hypotheses
Whilst the evidence for the involvement of presynaptic dopamine dysfunction in the majority of cases of schizophrenia is compelling, dopamine dysfunction is most clearly linked to psychotic symptoms and the evidence for dopamines involvement in the negative and cognitive symptoms is much less clear-cut . In this respect glutamate models involving NMDA receptor blockade appear to be better able account for the range and nature of these aspects of schizophrenia . A combination of both NMDA hypofunction and presynaptic dopamine dysfunction may therefore provide the best explanation of all the clinical aspects of schizophrenia.
Interactions between glutamatergic and dopaminergic pathways
Whilst the studies discussed above provide evidence that dopamine dysregulation in schizophrenia could be secondary to glutamatergic dysfunction, they do not identify the specific brain circuits or regions involved. The prefrontal cortex and hippocampus have both been suggested as potential sites as both regulate midbrain dopamine neurons via glutamatergic projections to the midbrain .
Hippocampus
Prefrontal cortex
Whilst there are data linking altered frontal function to striatal presynaptic dopamine dysfunction in patients and at risk subjects , we are not aware of any studies investigating the relationship between frontal glutamate to striatal dopamine dysfunction in patients.
Challenging Longstanding Assumptions And Moving Forward
Clozapine, discovered in the 1960s, remains the most effective antipsychotic medication, although its use is restricted due to its side effect profile. This stagnation in drug development for schizophrenia highlights a key weakness in schizophrenia research a lack of effective bi-directional translation between basic and clinical research. The fact that the current methods of testing for psychotic symptoms in rodents are now misaligned with recent clinical evidence indicates a need to advance how positive symptoms are examined in animal models. We have proposed a combination of behavioural tests in rodents that are sensitive to dysfunction at the primary site of dopaminergic neurobiology observed in schizophrenia. There will never be a perfect model for psychosis in rodents, but it is critical that we acknowledge the limitations of current methods so that an active dialogue is established.
You May Like: Are Panic Attacks Bad For You
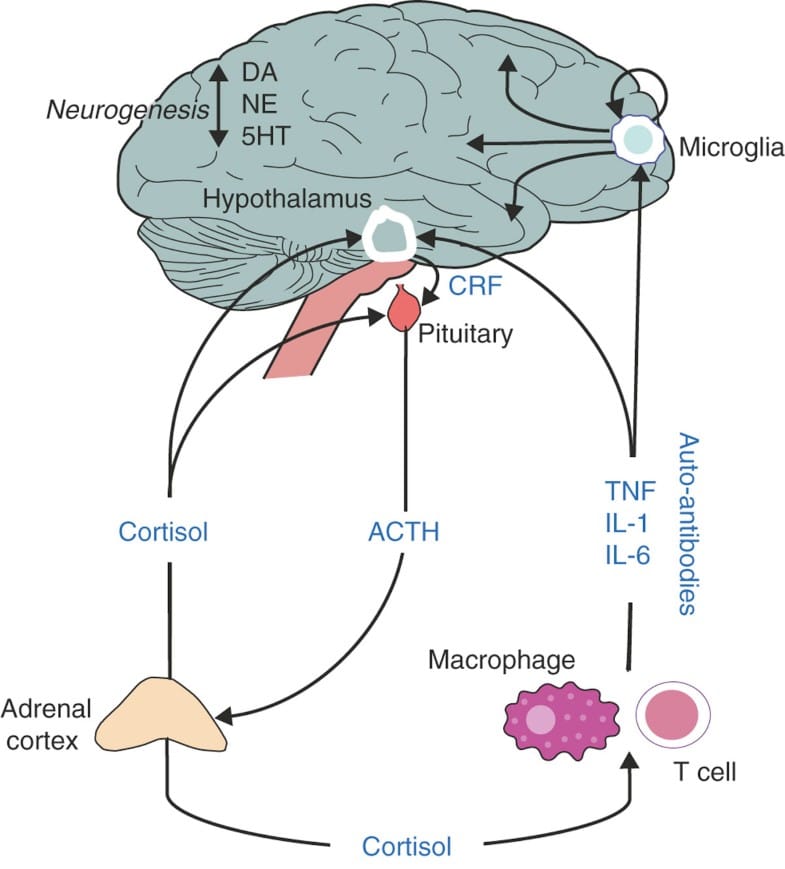
Brain Chemicals And Depression
Researchers have suggested that for some people, having too little of certain substances in the brain could contribute to depression. Restoring the balance of brain chemicals could help alleviate symptomswhich is where the different classes of antidepressant medications may come in.
Even with the help of medications that balance specific neurotransmitters in the brain, depression is a highly complex condition to treat. What proves to be an effective treatment for one person with depression may not work for someone else. Even something that has worked well for someone in the past may become less effective over time, or even stop working, for reasons researchers are still trying to understand.
Researchers continue to try to understand the mechanisms of depression, including brain chemicals, in hopes of finding explanations for these complexities and developing more effective treatments. Depression is a multi-faceted condition, but having an awareness of brain chemistry can be useful for medical and mental health professionals, researchers, and many people who have depression.
Depression Discussion Guide
Dont Miss: Schizophrenia Physiology
Negative And Cognitive Symptoms
The negative symptoms of schizophrenia can include:
- apathy or disinterest in daily activities
- limited emotional expression
- trouble with planning or following through with plans
- low energy levels
- behavioral and social skills training
- supported employment
Theres currently no cure for schizophrenia, but it can be successfully managed. Its a chronic condition that requires treatment over the course of a persons lifetime.
Researchers continue to investigate the role of dopamine in schizophrenia. This is not only important in further understanding the causes of schizophrenia itself, but also in improving treatment.
Current antipsychotic drugs are mostly effective for positive symptoms. Even then, some cases of schizophrenia can be resistant to these drugs. Further, antipsychotic drugs can come with significant side effects, particularly when theyre used long term.
Understanding how dopamine and other neurotransmitters affect schizophrenia can
Read Also: What Factors Contribute To Schizophrenia
An Overview Of Neurotransmitters And Mental Health During Brain Awareness Week
Brain Awareness Week is March 12-18. The annual event focuses attention on the importance of the brain and the work of partner organizations around the world. Activities run the gamut from exhibitions about the brain to brain-themed lectures to open house events at neuroscience labs. There are also special displays at libraries and community gathering places, classroom workshops and other events. The goal is to engage people of all ages and provide information on this most important of organs and one we too often take for granted. Its also an excellent time for providers of mental health services to share insights on how the workings of the brain affect mental health.
Treatment Implications Of The Dopamine Hypothesis
The dopamine hypothesis has important treatment implications. The vast majority of current antipsychotic medications target dopamine, and this makes sense given that these drugs were discovered through serendipitous observations of their effect on schizophrenia.
The most important dopamine-affecting medications are the typical antipsychotics, which increase post-synaptic receptor stimulation by blocking dopamine receptors. Unfortunately, these medications produce a number of debilitating side effects, most notably extrapyramidal symptoms like tardive dyskinesia. Newer second-generation antipsychotics have fewer side effects, but none are perfect.
Treatment with dopamine agonists is a third possibility suggested by the dopamine hypothesis. Dopamine agonists stimulate post-synaptic dopamine receptors directly, and as such, they can be used to treat schizophrenia without producing EPS.
You May Like: Can A Lcsw Diagnose Ptsd
Challenges In Diagnosing Schizophrenia
Psychiatric symptoms exist on continua from normal to pathological, meaning the threshold for diagnosis of schizophrenia in clinical practice can be challenging. The clinical diagnosis of schizophrenia relies heavily on the positive symptoms associated with a prolonged psychotic episode. However, a relatively high percentage of the general population report delusional experiences or hallucinations in their lifetime,,, but for most people these are transient. Psychotic symptoms are also not specific to a particular mental disorder. The clinical efficacy of antipsychotic drugs is heavily correlated with their ability to block subcortical dopamine D2 receptors, , suggesting dopamine signalling is important. In spite of this, no consistent relationship between D2 receptors and the pathophysiology of schizophrenia has emerged, . In contrast, the clinical evidence points towards presynaptic dopamine dysfunction as a mediator of psychosis in schizophrenia.
The Relationship Between Schizophrenia And Dopamine
Schizophrenia is a debilitating mental disorder with a multitude of symptoms. These can range from disorganized speech and behavior to delusions and hallucinations. Some individuals are more disabled by the disorder than others, but most people with this disorder require lifelong treatment and care.
Current research suggests that schizophrenia is a neurodevelopmental disorder with an important dopamine component.Four decades of research have focused on the role of dopamine in schizophrenia, and it seems clear that excesses or deficiencies in dopamine can lead to symptoms of schizophrenia.
You May Like: How To Calm Bipolar Rage
Indirect Evidence For Dopamine Dysfunction In Schizophrenia
Animal models
Rodent models of schizophrenia are useful for investigating molecular mechanisms that may be of pathophysiological relevance, and for testing novel therapeutic interventions.
One well characterized model of dopaminergic hyperactivity involves administering repeated doses of amphetamine. This has been shown to induce events that are also observed in individuals with schizophrenia, such as reduced prepulse inhibition, stereotyped behaviours, and impaired cognitive flexibility and attention6. Given that amphetamine results in dopamine release, and that the above effects can be ameliorated with the administration of dopamine antagonists, this provides indirect evidence for a role of dopamine in behaviour thought to be a proxy for psychotic symptoms.
Another example is that of mice genetically modified to overexpress dopamine D2 receptors in the striatum, which also display a wide range of schizophrenialike behaviours7. Similarly, transgenic insertion of tyrosine hydroxylase and guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrase 1 into the substantia nigra in early adolescence increases dopamine synthesis capacity, and has been associated with a schizophrenialike behavioural phenotype8.
In summary, multiple methods have been used to induce increased striatal dopamine signalling in animal models, and these consistently produce behaviours analogous to those observed in individuals with schizophrenia.
Cerebrospinal fluid and postmortem studies
Summary of indirect findings
Examples Of Important Neurotransmitter Actions
As explained above, the only direct action of a neurotransmitter is to activate a receptor. Therefore, the effects of a neurotransmitter system depend on the connections of the neurons that use the transmitter, and the chemical properties of the receptors that the transmitter binds to.
Here are a few examples of important neurotransmitter actions:
Read Also: Definition Of Phobia
Read Also: Did Robin Williams Have Depression
The Role Of Key Neurotransmitters
The three neurotransmitters implicated in depression are:
There are other neurotransmitters that can send messages in the brain, including glutamate, GABA, and acetylcholine. Researchers are still learning about the role these brain chemicals play in depression and other conditions, such as Alzheimers and fibromyalgia.