Chemical Changes In The Brain
A series of complex interrelated chemicals in the brain, called neurotransmitters, are responsible for sending signals between brain cells.
Low levels or imbalances of these chemicals are believed to play a role in the development of schizophrenia and other mental health conditions.
Dopamine, in particular, seems to play a role in the development of schizophrenia.
Researchers have found evidence that dopamine causes an overstimulation of the brain in people with schizophrenia. It may account for some of the symptoms of the condition.
Glutamate is another chemical thats been linked to schizophrenia. Evidence has pointed toward its involvement. However, there are a number of limitations to this research.
Complications before and during birth may increase the likelihood a person will develop mental health disorders, including schizophrenia.
These complications include:
Because of the ethics involved in studying pregnant women, many of the studies that have looked at the connection between prenatal complications and schizophrenia have been on animals.
Women with schizophrenia are at an increased risk for complications during pregnancy.
Its unclear if their children are at an increased likelihood for developing the condition because of genetics, pregnancy complications, or a combination of the two.
Schizophrenia: What You Should Know About This Psychological Illness
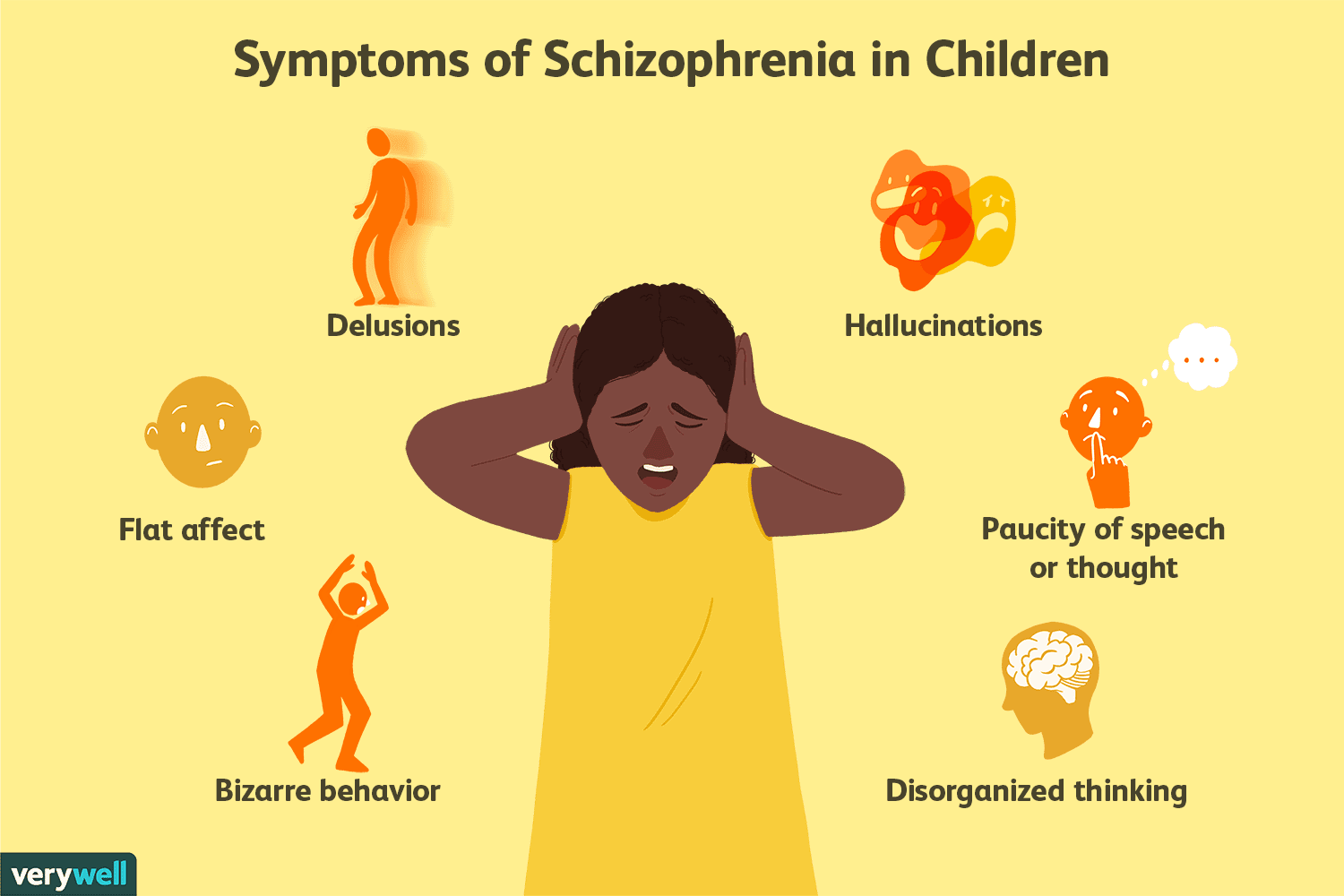
Schizophrenia is a chronic, severe, and disabling brain disorder. It affects about 1% of the population over the course of their lifetime. Symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, social withdrawal, difficulty with thinking and concentration, and inappropriate or bizarre behavior.
This complex mental health condition is characterized by a wide variety of symptoms that are often hard to diagnose. The effects can be so debilitating that they interfere with everyday life. There are treatments available for schizophrenia that can help reduce or manage symptoms. Its important to know what it is so you can share it with friends or family if someone you love has it.
When To See A Healthcare Provider
As schizophrenia usually develops gradually, it can be difficult to pinpoint when changes in behavior start or know whether they are something to worry about. Identifying that you are experiencing a pattern of concerning behaviors can be a sign you should consult with a professional.
Symptoms may intensify in the run-up to an acute episode of psychosis in schizophrenia. The warning signs include:
- A worrying drop in grades or job performance
- New difficulty thinking clearly or concentrating
- Suspiciousness of or uneasiness with others
- Withdrawing socially, spending a lot more time alone than usual
- Unusual, overly intense new ideas, strange feelings, or having no feelings at all
- Difficulty telling reality from fantasy
- Confused speech or trouble communicating
While these changes might not be concerning by themselves, if you or a loved one are experiencing a number of these symptoms, you should contact a mental health professional. It can be difficult for those with schizophrenia to want to get help, especially if they are experiencing symptoms such as paranoia.
If you or your loved one is thinking of or talking about harming themselves, contact someone who can help right away. You can call the toll-free, 24-hour National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 800-237-8255.
If you require immediate emergency care, call 911 for emergency services or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
You May Like: Four Subtypes Of Schizophrenia
Family Education And Support
Educational programs for family members, significant others, and friends offer instruction about schizophrenia symptoms and treatments, and strategies for assisting the person with the illness. Increasing key supporters understanding of psychotic symptoms, treatment options, and the course of recovery can lessen their distress, bolster coping and empowerment, and strengthen their capacity to offer effective assistance. Family-based services may be provided on an individual basis or through multi-family workshops and support groups. For more information about family-based services in your area, you can visit the family education and support groups page on the National Alliance on Mental Illness website.
Can Schizophrenia Be Treated
Yes. The main types of treatment are counseling and medicines to lessen or stop psychotic symptoms. Medicines will control psychotic symptoms in most people. In milder cases of schizophrenia, medications may not be needed. Medicines can:
- Lessen or stop hallucinations
- Help the person tell the difference between hallucinations and the real world
- Lessen or stop false beliefs
- Lessen feelings of confusion
- Help the person think more clearly
Lessening of these symptoms can help the person resume his or her normal lifestyle and activities. Medicines for schizophrenia need to be taken regularly, even after symptoms are gone. Some people with schizophrenia will stop taking their medicine because they believe the medicine is no longer needed, or they dislike the medication’s side effects. Psychotic symptoms often return when medication is stopped. Do not stop taking medicine without the advice of your healthcare provider.
Discuss any concerns you have about side effects with your healthcare provider.
Also Check: Can Anxiety Cause High Blood Sugar
The 10 Most Common Signs Of Schizophrenia
Hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking and behaviors knowing these signs and what they look like can be a good step toward the right treatment plan.
Schizophrenia is a chronic mental health condition that affects a persons behaviors, thoughts, and feelings.
The condition is one of the top 15 leading causes of disability in the world. Its usually diagnosed between the ages of 16 and 30, after a person has experienced their first psychotic episode. Its rare for a young child to have schizophrenia.
But symptoms of schizophrenia develop slowly over time. You may begin to see signs in early teen years, such as:
- experiencing a significant drop in grades or job performance
- suddenly having trouble thinking clearly or concentrating
- becoming suspicious of others or having paranoid thoughts
- spending more and more time alone
- having new passionate ideas that seem strange to others
- having strange feelings or seeming like they experience no feelings at all
- having less or no interest in how they look
- finding it difficult to tell the difference between whats real and whats not real
- being unable to speak clearly or struggling to communicate with others
Symptoms usually fall into one of three categories:
People with schizophrenia have a variety of symptoms that can range in severity. The 10 most common ones are:
Cognitive Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
Cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia have to do with the way a person thinks. Although cognitive symptoms are not used to diagnose schizophrenia, some are fairly common with the condition, such as:
- Difficulty maintaining attention – The inability to maintain focused attention makes people with schizophrenia seem spacey or out of it.
- Memory problems – Schizophrenia often affects working memory, which is the kind of memory you use to keep things in your head for active processing, like the digits of a phone number youre about to dial.
- Difficulty planning and structuring activities – Caused by reduced executive function. Executive function is a set of mental processes that allows us to identify the steps needed to complete a task and then execute them in a proper order. Executive function also allows us to suppress our response to distractions in order to get something done.
- Lack of insight – People with schizophrenia have a specific cognitive blind spot that prevents them from understanding that they are ill. This means that loved ones and caregivers should remain as vigilant as possible to help the patient maintain the routines of treatment in order to control symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Prodromal Stage Schizophrenia
Risk Factors For Schizophrenia
Different factors combine to heighten the risk of schizophrenia, says Dr. Bowers:
- Genetics: Having a relative with schizophrenia or one who displays schizophrenic behaviors increases risk.
- Life stressors: Extreme poverty homelessness traumatic events early in life early isolation or deprivation or a constant fight for survival heighten risk.
- Hallucinogens: The use of crystal meth, LSD, PCP or psilocybin mushrooms increases risk in the vulnerable.
How Common Is Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is more common than most people think. About 1 in 200 of the people in the United States will develop schizophrenia over the course of their lives. It’s also important to know that schizophrenia has many different symptoms and can show up in many different ways.
Schizophrenia is not the same as a “split personality.” A split personality is another type of mental illness. Split personality is much less common than schizophrenia.
Recommended Reading: Can Anxiety Cause Burning Skin
Parkinsons Disease And Lewy Body Dementia
is linked with for their similar hallucinatory symptoms. The symptoms strike during the evening in any part of the visual field, and are rarely polymodal. The segue into hallucination may begin with illusions where sensory perception is greatly distorted, but no novel sensory information is present. These typically last for several minutes, during which time the subject may be either conscious and normal or drowsy/inaccessible. Insight into these hallucinations is usually preserved and is usually reduced. Parkinsonâs disease is usually associated with a degraded pars compacta, but recent evidence suggests that PD affects a number of sites in the brain. Some places of noted degradation include the median , the parts of the , and the neurons in the and nuclei of the .
This type of hallucination is usually experienced during the recovery from a comatose state. The migraine coma can last for up to two days, and a state of depression is sometimes . The hallucinations occur during states of full consciousness, and insight into the hallucinatory nature of the images is preserved. It has been noted that ataxic lesions accompany the migraine coma.
Read Also: Define Aerophobia
Increased Precautions We’re Taking In Response To Covid
As updates on the impact of COVID-19 continue to be released, we want to take a moment to inform you of the heightened preventative measures we have put in place at Covington Behavioral Health Hospital to keep our patients, their families, and our employees safe. All efforts are guided by and in adherence to the recommendations distributed by the CDC.
Please note that for the safety of our patients, their families, and our staff, there are certain restrictions in place regarding on-site visitation at Covington Behavioral Health Hospital.
- These restrictions have been implemented in compliance with updated corporate and state regulations to further reduce the risks associated with COVID-19.
- Options for telehealth visitation are continuously evaluated so that our patients can remain connected to their loved ones.
- Alternate methods of communication for other services may be offered when deemed clinically appropriate.
For specific information regarding these changes and limitations, please contact us directly.
CDC updates are consistently monitored to ensure that all guidance followed is based on the latest information released.
The safety of our patients, their families, and our employees is our top priority, and we will remain steadfast in our efforts to reduce any risk associated with COVID-19.
The CDC has provided a list of easy tips that can help prevent the spread of the coronavirus.
For detailed information on COVID-19, please visit the CDC website HERE.
Don’t Miss: Can Anxiety Cause Low Blood Sugar
Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
The negative symptoms of schizophrenia can often appear several years before somebody experiences their first acute schizophrenic episode.
These initial negative symptoms are often referred to as the prodromal period of schizophrenia.
Symptoms during the prodromal period usually appear gradually and slowly get worse.
They include the person becoming more socially withdrawn and increasingly not caring about their appearance and personal hygiene.
It can be difficult to tell whether the symptoms are part of the development of schizophrenia or caused by something else.
Negative symptoms experienced by people living with schizophrenia include:
- losing interest and motivation in life and activities, including relationships and sex
- lack of concentration, not wanting to leave the house, and changes in sleeping patterns
- being less likely to initiate conversations and feeling uncomfortable with people, or feeling there’s nothing to say
The negative symptoms of schizophrenia can often lead to relationship problems with friends and family as they can sometimes be mistaken for deliberate laziness or rudeness.
How Is Schizophrenia Treated
There are different types of treatment available. Medical professionals should work with you to find the right treatment for you. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommends that you should be offered a combination of medication and talking therapies.
People who live with schizophrenia can respond to treatment differently.
For many treatment helps to reduce symptoms to help make daily life easier. You may find that you need to continue with treatment to keep well. For every 5 people with schizophrenia:
- 1 will get better within 5 years of their first obvious symptoms.
- 3 will get better but will have times when they get worse again.
- 1 will have troublesome symptoms for long periods of time.
What medication should I be offered?
Your doctor may offer you medication known as an antipsychotic. These reduce the symptoms of schizophrenia, but dont cure the illness. Your healthcare professionals should work with you to help choose a medication. If you want, your carer can also help you make the decision. Doctors should explain the benefits and side effects of each drug.
In the past, some antipsychotics had negative side effects. Some people find that the side effects of newer antipsychotic drugs are easier to manage.
Your medication should be reviewed at least once a year.
What type of psychosocial treatment will I be offered?
Family intervention is where you and your family work with mental health professionals to help to manage relationships.
Recommended Reading: Whats The Fear Of Throwing Up
What Are The Types Of Schizophrenia
There are different types of schizophrenia. The International Classification of Diseases manual describes them as below.
Paranoid schizophrenia
- Pranks, giggling and health complaints.
- Usually diagnosed in adolescents or young adults.
Catatonic schizophrenia
- Unusual movements, often switching between being very active and very still.
- You may not talk at all.
Simple schizophrenia
- Negative symptoms are prominent early and get worse quickly.
- Positive symptoms are rare.
Undifferentiated schizophrenia
Your diagnosis may have some signs of paranoid, hebephrenic or catatonic schizophrenia, but doesnt obviously fit into one of these types alone.
Residual schizophrenia
This type of schizophrenia is diagnosed in the later stages of schizophrenia. You may be diagnosed with this if you have a history of schizophrenia but only continue to experience negative symptoms.
Other schizophrenia
There are other types of schizophrenia according to the ICD-10, such as.
- Cenesthopathic schizophrenia. This is where people experience unusual bodily sensations.
- Schizophreniform. Schizophreniform disorder is a type of psychotic illness with symptoms similar to those of schizophrenia. But symptoms last for a short period.
Unspecified schizophrenia
Symptoms meet the general conditions for a diagnosis, but do not fit in to any of the above categories.
Easily Stay On Top Of The Latest Nutrition Research
Become an Examine Member to get access to the latest research. Get 150+ studies summarized for you across 25 different categories every month.
Members also have access to the Examine Study Database of 400+ supplements and their effects on 600+ health outcomes, as well as in-depth research analyses. Understand the whole body of nutrition and supplement evidence at a glance.
Also Check: Audrey Hepburn Eating Disorder
What Causes Schizophrenia
Nobody knows exactly what causes schizophrenia, it is likely to be the result of several factors. For example:
- Stress. Some people can develop the illness as a result of a stressful event, such as the death of a loved one or the loss of a job.
- Genetics. You are more likely to develop schizophrenia if you have a close relation with the illness.
- Brain damage. This is usually damage that has stopped your brain from growing normally when your mother was pregnant. Or during birth.
- Drugs and alcohol. Research has shown that stronger forms of cannabis increase your risk of developing schizophrenia.
- A difficult childhood. If you were deprived, or abused, as a child this can increase your risk of developing a mental illness. Including schizophrenia.
There is research to suggest that may be an association between menopause and schizophrenia. This may be due to the hormonal changes during this stage of life for women.
You can find more information about:
- Does mental illness run in families? by clicking here.
- Drugs, alcohol and mental health by clicking here.
- Cannabis and mental health by clicking here.
What Is The Outlook
- In most cases there are recurring episodes of symptoms . Most people in this group live relatively independently with varying amounts of support. The frequency and duration of each relapse can vary. Some people recover completely between relapses. Some people improve between relapses but never quite fully recover. Treatment often prevents relapses, or limits their number and severity.
- In some cases, there is only one episode of symptoms that lasts a few weeks or so. This is followed by a complete recovery, or substantial improvement without any further relapses. It is difficult to give an exact figure as to how often this occurs. Perhaps 2 in 10 cases or fewer.
- Up to 2 in 10 people with schizophrenia are not helped much by treatment and need long-term dependent care. For some, this is in secure accommodation.
- Depression is a common complication of schizophrenia.
- It is thought that up to a third of people with schizophrenia misuse alcohol and/or illegal drugs. Helping or treating such people can be difficult.
- About 1 in 10 people with schizophrenia end their own life.
The outlook is thought to be better if:
Newer medicines and better psychological treatments give hope that the outlook is improving.
You May Like: Feretrophobia Define
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
If symptoms are present, your doctor will perform a complete medical history and physical examination. Although there are no laboratory tests to specifically diagnose schizophrenia, the doctor might use various diagnostic tests â such as MRI or CT scans or blood tests â to rule out physical illness as the cause of your symptoms.
If the doctor finds no physical reason for the symptoms, he or she might refer the person to a psychiatrist or psychologist, healthcare professionals who are specially trained to diagnose and treat mental illnesses. Psychiatrists and psychologists use specially designed interview and assessment tools to evaluate a person for schizophrenia. The doctor or therapist bases his or her diagnosis on the personâs report of symptoms, and his or her observation of the personâs attitude and behavior.
The doctor or therapist then determines if the personâs symptoms point to a specific disorder as outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , which is published by the American Psychiatric Association and is the standard reference book for recognized mental illnesses. According to the DSM-5, a diagnosis of schizophrenia is made if a person has two or more core symptoms, one of which must be hallucinations, delusions, or disorganized speech for at least one month. The other core symptoms are gross disorganization and diminished emotional expression. Other DSM-5 criteria for a diagnosis of schizophrenia include: