Bipolar Disorder Type I Prognosis
Bipolar I disorder is a highly persistent illness with 40-50 percent of people experiencing another episode of mania within two years of their first episode. Even 40 percent of those treated with lithium considered the gold standard treatment for bipolar disorder type I go on to have a continuing illness. Additionally, suicide is a real risk with approximately 25-50 percent of people attempting suicide and about 11 percent completing suicide.
While that may sound bleak, many people with bipolar disorder type I do go on to lead happy and productive lives in the community. Medication adherence, therapy, and routine can all go a long way to making that happen.
Rarer Types Of Bipolar Disorder
There are two other types of the disorder that are less common than bipolar I and II. Cyclothymic disorder involves changes in mood and shifts similar to bipolar I and II, but the shifts are often less dramatic in nature. A person with cyclothymic disorder can often function normally without medication, though it may be hard. Over time, a persons changes in mood may develop into a diagnosis of bipolar I or II.
Bipolar disorder not otherwise specified is a general category for a person who only has some symptoms of bipolar disorder. These symptoms are not enough to make a diagnosis of one of the other three types.
While bipolar disorder can be difficult to diagnose, once its identified, it can be treated.
Being Engaged In Many Activities At Once
During a manic episode, you may be restlessly searching for ways to work off extra energy. This symptom is often described as “multitasking on steroids.” People often take on many projects or experience a burst in productivity that is beyond what they would normally accomplish during a set period of time.
Recommended Reading: Does Celine Dion Have An Eating Disorder
What Is The Outlook
Bipolar disorder isnt curable. But with proper treatment and support from family and friends, you can manage your symptoms and maintain your quality of life.
Its important that you follow your doctors instructions regarding medications and other lifestyle choices. This includes:
Including your friends and family members in your care can be especially helpful.
Its also helpful to learn as much as you can about bipolar disorder. The more you know about the condition, the more in control you may feel as you adjust to life after diagnosis.
You may be able to repair strained relationships. Educating others about bipolar disorder may make them more understanding of hurtful events from the past.
Treatments For Bipolar Disorder

The high and low phases of bipolar disorder are often so extreme that they interfere with everyday life.
But there are several options for;treating bipolar disorder that can make a difference.
They aim to control the effects of an episode and help someone with bipolar disorder live life as normally as possible.
The following treatment options are available:
- medicine to prevent episodes of mania and depression;;these are known as mood stabilisers, and you take them every day on a long-term basis
- medicine to treat the main symptoms of depression and mania when they happen
- learning to recognise the triggers and signs of an episode of depression or mania
- psychological treatment;;such as talking therapy, which can help you deal with depression, and provides advice about how to improve your relationships
- lifestyle advice;;such as doing regular exercise, planning activities you enjoy that give you a sense of achievement, as well as advice on;improving your diet and getting more sleep
It’s thought using a combination of different treatment methods is the best way to control bipolar disorder.
Help and advice for people with a long-term condition or their carers;is also available;from charities, support groups and associations.
This includes self-help and learning to;deal with the practical aspects of a long-term condition.
You May Like: Can Depression Make You Lose Your Appetite
What Are The Treatments For Bipolar Ii Disorder
Hypomania often masquerades as happiness and relentless optimism. When hypomania is not causing unhealthy behavior, it often may go unnoticed and therefore remain untreated. This is in contrast to full mania, which by definition causes problems in functioning and requires treatment with medications and possibly hospitalizations.
People with bipolar II disorder can benefit from preventive drugs that level out moods over the long term. These prevent the negative consequences of hypomania, and also help to prevent episodes of depression.
Mood Stabilizers
Lithium : This simple metal in pill form is highly effective at controlling mood swings in bipolar disorder. Lithium has been used for more than 60 years to treat bipolar disorder. Lithium can take weeks to work fully, making it better for long-term treatment than for acute hypomanic episodes. Blood levels of lithium and other laboratory tests must be monitored periodically to avoid side effects.
Carbamazepine : This antiseizure drug has been used to treat mania since the 1970s. It’s possible value for treating bipolar depression, or preventing future highs and lows, is less well-established. Blood tests to monitor liver functioning and white blood cell counts also are periodically necessary.
Valproate : This antiseizure drug also works to level out moods. It has a more rapid onset of action than lithium, and it can also be used “off label” for prevention of highs and lows.
Antipsychotics
Benzodiazepines
How Is Bipolar Disorder Diagnosed
To diagnose bipolar disorder, your health care provider may use many tools:
- A physical exam
- A medical history, which will include asking about your symptoms, lifetime history, experiences, and family history
- Medical tests to rule out other conditions
- A mental health evaluation. Your provider may do the evaluation or may refer you to a mental health specialist to get one.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Phobia Of Bees
Statistical Methods And Measurement Caveats
National Comorbidity Survey Replication
Diagnostic Assessment and Population:
- The NCS-R is a nationally representative, face-to-face, household survey conducted between February 2001 and April 2003 with a response rate of 70.9%. DSM-IV mental disorders were assessed using a modified version of the fully structured World Health Organization Composite International Diagnostic Interview , a fully structured lay-administered diagnostic interview that generates both International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, and DSM-IV diagnoses. The DSM-IV criteria were used here. The Sheehan Disability Scale assessed disability in work role performance, household maintenance, social life, and intimate relationships on a 010 scale. Participants for the main interview totaled 9,282 English-speaking, non-institutionalized, civilian respondents. Bipolar disorder was assessed in a subsample of 5,692 adults. The NCS-R was led by Harvard University
Survey Non-response:
- In 2001-2002, non-response was 29.1% of primary respondents and 19.6% of secondary respondents.
- Reasons for non-response to interviewing include: refusal to participate ; respondent was reluctant- too busy but did not refuse ; circumstantial, such as intellectual developmental disability or overseas work assignment ; and household units that were never contacted .;
- For more information, see;PMID: 15297905;and the NIMH NCS-R study page.
National Comorbidity Survey Adolescent Supplement
Diagnostic Assessment and Population:
What Are The Symptoms Of Bipolar Ii Disorder
During a hypomanic episode, elevated mood can manifest itself as either euphoria or as irritability.
Symptoms during hypomanic episodes include:
- Flying suddenly from one idea to the next
- Having exaggerated self confidence
- Rapid, “pressured” and loud speech
- Increased energy, with hyperactivity and a decreased need for sleep
People experiencing hypomanic episodes are often quite pleasant to be around. They can often seem like the “life of the party” — making jokes, taking an intense interest in other people and activities, and infecting others with their positive mood.
What’s so bad about that, you might ask? Hypomania can also lead to erratic and unhealthy behavior. Hypomanic episodes can sometimes progress onward to full manias that affect a person’s ability to function . In mania, people might spend money they don’t have, seek out sex with people they normally wouldn’t, and engage in other impulsive or risky behaviors with the potential for dangerous consequences.
The vast majority of people with bipolar II disorder experience more time with depressive than hypomanic symptoms. Depressions can occur soon after hypomania subsides, or much later. Some people cycle back and forth between hypomania and depression, while others have long periods of normal mood in between episodes.
Untreated, an episode of hypomania can last anywhere from a few days to several months. Most commonly, symptoms continue for a few weeks to a few months.
Read Also: Phobia Of Bees
What Is A Manic Episode
A manic episode is characterized by a sustained period of abnormally elevated or irritable mood, intense energy, racing thoughts, and other extreme and exaggerated behaviors. People can also experience psychosis, including hallucinations and delusions, which indicate a separation from reality.
The symptoms of mania can last for a week or more and manic episodes may be interspersed within periods of;depression;during which you may experience fatigue, sadness, and hopelessness. While manic episodes are most common in people with bipolar disorder, there are other causes for these extreme changes in behavior and mood.;
Symptoms That Lead To A Diagnosis
If youre suffering from any kind of mental health disorder, its important that you identify and understand your symptoms in order for our doctors to correctly diagnose you. Bipolar disorder consists of both manic and depressive episodes that create an unstable mood.;
Mania can be extreme changes in mood, or you can have hypomania which is typically less severe. Symptoms of mania include:
Difficulty sleeping Extreme energy Increased self-esteem Difficulty concentrating Racing thoughts
On the opposite end of the spectrum, depression can change your emotional highs to hopeless lows. If you have bipolar disorder with depression, symptoms you may experience include:
Fatigue Sadness Decreased energy Overeating or loss of appetite Suicidal thoughts
Our team at Boston MindCare take a detailed history to decipher your symptoms and give you a definitive diagnosis. With that, we can also form a customized treatment plan for you.
Also Check: What Phobia Is Weather Related
Living With Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a chronic mental illness. That means youll live and cope with it for the rest of your life. However, that doesnt mean you cant live a happy, healthy life.
Treatment can help you manage your changes in mood and cope with your symptoms. To get the most out of treatment, you may want to create a care team to help you. In addition to your primary doctor, you may want to find a psychiatrist and psychologist. Through talk therapy, these doctors can help you cope with symptoms of bipolar disorder that medication cant help.
You may also want to seek out a supportive community. Finding other people whore also living with this disorder can give you a group of people you can rely on and turn to for help.
Finding treatments that work for you requires perseverance. Likewise, you need to have patience with yourself as you learn to manage bipolar disorder and anticipate your changes in mood. Together with your care team, youll find ways to maintain a normal, happy, healthy life.
What Is A Bipolar Disorder

Bipolar disorder is a mental condition when people start having constant mood swings and pretend to be some other personality. The personality of the other side of people is completely different. Despite this authentic definition, no exact meaning of bipolar disorder is identified.
Bipolar disorder can be caused due to the combined effect of atmospheric, genetic, chemical changes in the bodies of people. These changes may cause some disturbance in your mental health and lead you towards getting affected with bipolar disorder.
Even if this disorder is very disturbing for an individuals personality, it may also be some good things that can cause behavioral as well as personality changes in the patient.
Read Also: Eating Disorders Essay Outline
Manic & Hypomanic Episode Symptoms
Both manic and hypomanic episodes include three or more of the below symptoms:
- Talking much more than usual;
- Racing thoughts
- Feeling the need for less sleep
- Feeling abnormally upbeat, jumpy or wired
- Increased activity levels, energy or agitation
- Inflated sense of well-being and self-confidence;
- Poor decision-making and increased impulsive behavior
Bipolar Disorder In Teens
Angst-filled behavior is nothing new to the average parent of a teenager. The shifts in hormones, plus the life changes that come with puberty, can make even the most well-behaved teen seem a little upset or overly emotional from time to time. However, some teenage changes in mood may be the result of a more serious condition, such as bipolar disorder.
A bipolar disorder diagnosis is most common during the late teens and early adult years. For teenagers, the more common symptoms of a manic episode include:
- being very happy
- taking part in risky behaviors
- abusing substances
- thinking about sex more than usual
- becoming overly sexual or sexually active
- having trouble sleeping but not showing signs of fatigue or being tired
- having a very short temper
- having trouble staying focused, or being easily distracted
For teenagers, the more common symptoms of a depressive episode include:
- sleeping a lot or too little
- eating too much or too little
- feeling very sad and showing little excitability
- withdrawing from activities and friends
- thinking about death and suicide
Recommended Reading: Can Depression Make You Lose Your Appetite
What Causes Bipolar Disorder
Scientists dont know what causes bipolar disorder. Abnormal physical characteristics of the brain or an imbalance in certain brain chemicals may be among the main causes.
As with many medical conditions, bipolar disorder tends to run in families. If you have a parent or sibling with bipolar disorder, your risk of developing it is higher. The search continues for the genes which may be responsible for bipolar disorder.
Researchers also believe that severe stress, drug or alcohol abuse, or severely upsetting experiences may trigger bipolar disorder. These experiences can include childhood abuse or the death of a loved one.
Bipolar Disorder Causes And Risks
While the exact causes of bipolar disorder are unknown, there are a few factors that play a role, including:
- Genetics Bipolar disorder is more common in people who have a first-degree relative with the condition, such as a parent or sibling, and researchers continue to search for the genes that are involved in causing bipolar disorder. But just because you have family members with a history of bipolar disorder, does not mean that you will develop it. Most people who have bipolar disorder in their family history will never actually develop this mental health disorder.
- Brain structure There are biological differences for those that have the disorder, including physical changes to their brains. Any abnormalities in the structure or functions of your brain may increase the risk for bipolar disorder.
- Environmental factors Beyond your own biology and family history, environmental can contribute too.;
- Other Extreme stress, traumatic experiences, and physical illnesses can also influence who develops bipolar disorder.;
You May Like: Is Celine Dion Anorexic
Bipolar Disorder Risk Factors
When someone develops bipolar disorder, it usually starts when they’re in late adolescence or young adulthood. Rarely, it can happen earlier in childhood. Bipolar disorder can run in families.
Men and women are equally likely to get it. Women are somewhat more likely than men to go through “rapid cycling,” which is having four or more distinct mood episodes within a year. Women also tend to spend more time depressed than men with bipolar disorder.
Bipolar disorder usually develops later in life for women, and theyâre more likely to have bipolar disorder II and be affected by seasonal mood changes.
A combination of medical and mental issues is also more common in women. Those medical issues can include thyroid disease, migraine, and anxiety disorders.
Some things that make you more likely to have bipolar disorder include:
-
Having a family member with bipolar disorder
-
Going through a time of high stress or trauma
-
Drug or alcohol abuse
-
Certain health conditions
Many people with the condition abuse alcohol or other drugs when manic or depressed. People with bipolar disorder are more likely to have seasonal depression, co-existing anxiety disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Is Bipolar Disorder Hereditary
Bipolar disorder can be passed from parent to child. Research has identified a strong genetic link in people with the disorder. If you have a relative with the disorder, your chances of also developing it are four to six times higher than people without a family history of the condition.
However, this doesnt mean that everyone with relatives who have the disorder will develop it. In addition, not everyone with bipolar disorder has a family history of the disease.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Phobia For Bees
Dont Let Yourself Be Alone And Isolated:
The worst thing that a person does when he is identified with a bipolar disorder is he/she isolates themselves completely. This is very bad because this isolation will only open up doors to your bipolar personality. So, dont try to keep yourself alone or isolated in an attempt to keep your loved ones away from your other personality.
All the above measures can be taken when you are suspected of having bipolar disorder. However, emotional support means a lot in such a phase, and having your loved ones around you will help you a lot.
What Is Bipolar Disorder Definition Symptoms And Treatment
Bipolar disorder is a serious mental illness that is hard to accurately describe in a sentence or two. That is because it is a nuanced illness with so many people experiencing it in so many ways. That said, the overarching principles of bipolar disorder is that it is a chronic, lifelong mental illness that remains a challenging struggle for those who have it.
Bipolar disorder is also sometimes called manic depressive illness.
Also Check: What Is A Phobia Of Spoons Called
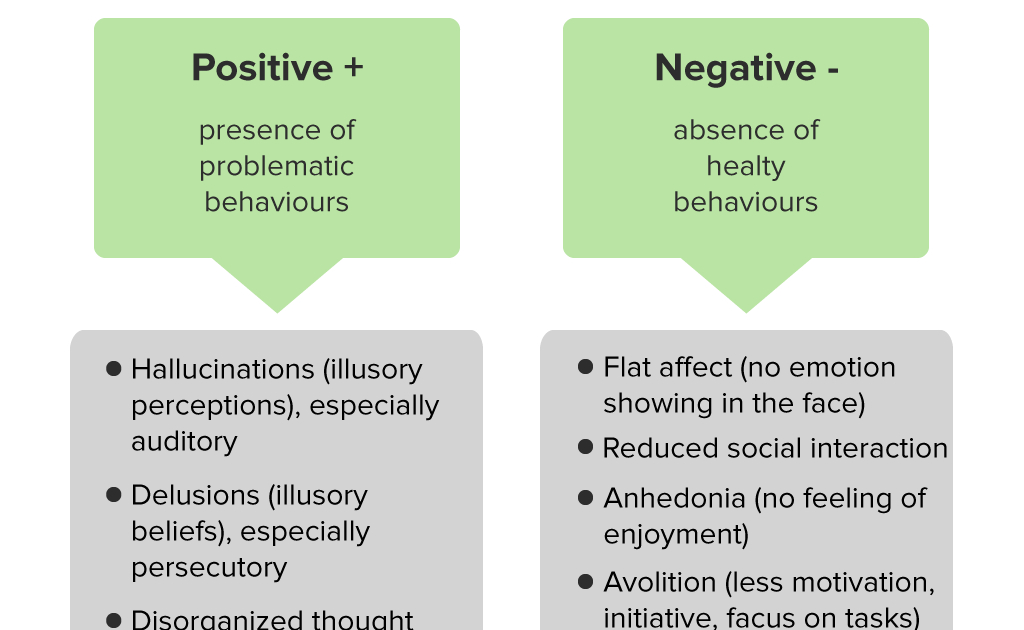
What Are The Symptoms Of Bipolar I Disorder
During a manic episode in someone with bipolar disorder, elevated mood can manifest itself as either euphoria or as irritability.
Abnormal behavior during manic episodes includes:
- Flying suddenly from one idea to the next
- Rapid, “pressured” , and loud speech
- Increased energy, with hyperactivity and a decreased need for sleep
- Inflated self-image
- Substance abuse
People in manic episodes may spend money far beyond their means, have sex with people they wouldn’t otherwise, or pursue grandiose, unrealistic plans. In severe manic episodes, a person loses touch with reality. They may become delusional and behave bizarrely.
Untreated, an episode of mania can last anywhere from a few days to several months. Most commonly, symptoms continue for a few weeks to a few months. Depression may follow shortly after, or not appear for weeks or months.
Many people with bipolar I disorder experience long periods without symptoms in between episodes. A minority has rapid-cycling symptoms of mania and depression, in which they may have distinct periods of mania or depression four or more times within a year. People can also have mood episodes with “mixed features,” in which manic and depressive symptoms occur simultaneously, or may alternate from one pole to the other within the same day.