What If I See These Signs In A Friend Or Family Memberhow Can I Help
It can be hard to be with someone who is behaving oddly or not like themselves. If you are concerned for a friend or family member its important to tell a responsible person. Talk to your health care provider and another trusted adult, such as a parent or other family member, a religious leader, or a teacher.
How Can I Talk To My Health Care Provider
If you are concerned about your own thoughts and/or feelings the best thing you can do is bring it up with your health care provider or talk to a mental health counselor or therapist. This might feel scary, especially if you are unsure of what you have been experiencing, and thats okay. Try to remind yourself that your health care provider is there to help. Some ways to bring it up are by saying Ive been feeling really strange lately and I dont really know whats going on or I sometimes feel like my mind is playing tricks on me. Your doctor will be able to have a deeper conversation with you to help figure out if what youre experiencing is normal or if there are things you can do to make it better.
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
People with schizophrenia should do the following to help care for themselves and manage their condition:
- Take medications as prescribed. One of the most critical things a person with schizophrenia can do to help themselves is to take their medications. If you have schizophrenia, you should not stop your medication without talking to your healthcare provider. Sudden stopping of medication often speeds up the return of psychosis symptoms. Side effects are common with antipsychotics. However, there are many antipsychotic medications, so its often possible to work with your healthcare provider to find one that both works well for you and has minimal or no side effects.
- See your healthcare provider as recommended. Your healthcare provider will set up a schedule for you to see them. These visits are especially important to help with managing your condition.
- Dont ignore or avoid symptoms. Schizophrenia is more likely to respond and have a good outcome with early diagnosis and treatment.
- Avoid alcohol and recreational drug use. Alcohol and drug use can make schizophrenia symptoms worse and can lead to other issues. This includes using prescription medications in a way other than prescribed.
- Consider seeking support. Organizations such as the National Alliance on Mental Illness can offer resources and information that can help.
Recommended Reading: Is An Anxiety Attack The Same As A Panic Attack
Find A Qualified Therapist
“Medication is always emphasized, but it’s only one piece of the puzzle,” Jewell says. Itâs important to find a therapist who specializes in schizophrenia, especially when someone doesnât want treatment.
“Patients don’t understand that they’ve been sick or what has to be done about it. This makes it hard to keep them motivated to stay in treatment. Counseling can help.”
Effective therapy teaches patients and families about the illness — “what can make it worse, what can make it better, and how to deal with hallucinations,â Jewell says.
For example, therapy can help patients learn to ignore voices they hear. Counseling should also address substance abuse and social withdrawal, which are common problems for people with schizophrenia.
What Myths Are There About Schizophrenia
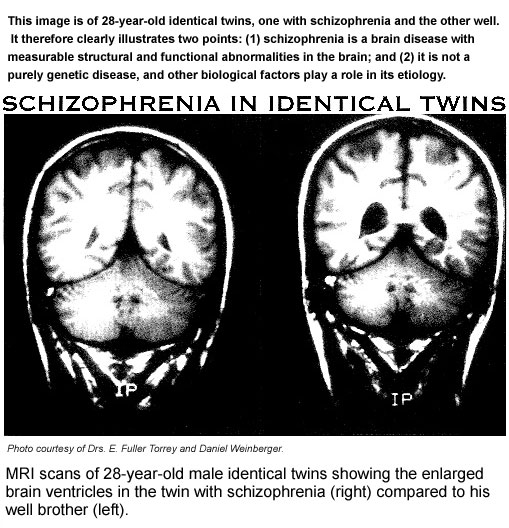
There are some myths or mistaken beliefs about schizophrenia which come from the media. For example,
- Schizophrenia means someone has a split personality
This is not the case. The mistake may come from the fact that the name ‘schizophrenia’ comes from two Greek words meaning ‘split’ and ‘mind’.
- People who live with schizophrenia are dangerous
Those who live with schizophrenia arent usually dangerous. People who live with schizophrenia are far more likely to be harmed by other people than harm others.
There is a higher risk of violent behaviour from those who live with schizophrenia. But, as with people who dont live with schizophrenia, much of the risk is linked to the use of street drugs or alcohol.
Sometimes people who live with schizophrenia commit violent crimes. The media often report them in a way which emphasises the persons mental health diagnosis. This can create fear and stigma in the general public. But it should be remembered that:
- violent crimes are also committed by people who dont live with schizophrenia,
- its often later found that the person was failed or neglected by the mental health system, and
- the crime might have been prevented if the person had received the care and support they needed.
So, its not right to say that schizophrenia equals dangerous.
Don’t Miss: How Do People With Schizophrenia Act
What Is Schizophrenia Or Paranoid Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a challenging brain disorder that often makes it difficult to distinguish between what is real and unreal, to think clearly, manage emotions, relate to others, and function normally. It affects the way a person behaves, thinks, and sees the world.
The most common form is paranoid schizophrenia, or schizophrenia with paranoia as its often called. People with paranoid schizophrenia have an altered perception of reality. They may see or hear things that dont exist, speak in confusing ways, believe that others are trying to harm them, or feel like theyre being constantly watched. This can cause relationship problems, disrupt normal daily activities like bathing, eating, or running errands, and lead to alcohol and drug abuse in an attempt to self-medicate.
Many people with schizophrenia withdraw from the outside world, act out in confusion and fear, and are at an increased risk of attempting suicide, especially during psychotic episodes, periods of depression, and in the first six months after starting treatment.
Take any suicidal thoughts or talk very seriously
If you or someone you care about is suicidal, call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline in the U.S. at 1-800-273-TALK, visit IASP or Suicide.org to find a helpline in your country, or read Suicide Prevention.
Risk Factors For Schizophrenia
Different factors combine to heighten the risk of schizophrenia, says Dr. Bowers:
- Genetics: Having a relative with schizophrenia or one who displays schizophrenic behaviors increases risk.
- Life stressors: Extreme poverty homelessness traumatic events early in life early isolation or deprivation or a constant fight for survival heighten risk.
- Hallucinogens: The use of crystal meth, LSD, PCP or psilocybin mushrooms increases risk in the vulnerable.
Also Check: Can Anxiety Cause A Heart Attack
What If I Am Not Happy With My Treatment
If you are not happy with your treatment you can:
- talk to your doctor about your treatment options,
- ask for a second opinion,
- get an advocate to help you speak to your doctor,
- contact Patient Advice and Liaison Service and see whether they can help, or
- make a complaint.
There is more information about these options below.
Treatment options
You should first speak to your doctor about your treatment. Explain why you are not happy with it. You could ask what other treatments you could try.
Tell your doctor if there is a type of treatment that you would like to try. Doctors should listen to your preference. If you are not given this treatment, ask your doctor to explain why it is not suitable for you.
Second opinion
A second opinion means that you would like a different doctor to give their opinion about what treatment you should have. You can also ask for a second opinion if you disagree with your diagnosis.
You dont have a right to a second opinion. But your doctor should listen to your reason for wanting a second opinion.
Advocacy
An advocate is independent from the mental health service. They are free to use. They can be useful if you find it difficult to get your views heard.
There are different types of advocates available. Community advocates can support you to get a health professional to listen to your concerns. And help you to get the treatment that you would like.
The Patient Advice and Liaison Service
Complaints
You can find out more about:
Early Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
Because early treatment is thought to be most effective for schizophrenia, researchers are continually looking for ways to detect it before symptoms fully develop.
Hallucinations and delusions are the hallmark symptoms of psychosis and must be present for a diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Although psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations or delusions are the most common aspects that present in schizophrenia, there are several symptoms involved. People with schizophrenia experience:
- Positive symptoms: The appearance of things that should not be there, like hallucinations, delusions, and thought disorder .
- Negative symptoms: The absence of things that should be there, like loss of motivation, disinterest or lack of enjoyment in daily activities, social withdrawal, difficulty showing emotions, and difficulty functioning normally.
- Cognitive symptoms: Problems with attention, concentration, and memory.
Assessment of these symptoms is typically how schizophrenia is diagnosed, but the discovery of brain differences in people with schizophrenia could potentially mean an earlier diagnosis and more effective treatment.
While schizophrenia is usually diagnosed in the late teens to early thirties, subtle changes in cognition and social relationships may be noticeable before the actual diagnosis, even during adolescence. Often these early symptoms are apparent years before a person is diagnosed with schizophrenia.
Some of these early symptoms include:
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Ptsd Anxiety
What Should I Know About Psychosis
-
Anyone can have a psychotic episode.
-
Psychosis does not discriminate across cultures, races, or social classes.
-
At this time it is still unknown exactly what causes psychosis, but it is known that psychosis is treatable and that the earlier it is identified and treated the more successful remission is.
When Does Schizophrenia Show Up In Women
Both of my parents are mentally ill, my mother suffering from Schizophrenia and my father from Manic Depression. Both of my parents had regular auditory hallucinations and paranoia.
At 21, Ive yet to suffer from any of their symptoms, but have been struggling with PTSD and related anxiety. Since I was aware enough to know my parents were ill, Ive constantly monitored myself to make sure I wasnt sick like they were.
From reading on this site and others, it appears that Schizophrenia shows up in women later than men. Could someone please talk about this more? Since Im a 21 year old woman, Id like to know if its possible for me to still develop Schizophrenia . I also just want to know at what age can I finally relax and know Im past the threshold.
You are correct. Schizophrenia does tend to occur later in women than in males. The average age range for a female to develop schizophrenia is roughly ages 25-29 . The reasons for the age difference between genders are not well understood.
Not every male or female who ultimately develops schizophrenia does so within the above-mentioned age range averages. Males can develop schizophrenia later than late- adolescence and females may get it sooner than their late twenties.
Recommended Reading: What Does The Suffix Phobia Mean
What Causes Schizophrenia
Nobody knows exactly what causes schizophrenia, it is likely to be the result of several factors. For example:
- Stress. Some people can develop the illness as a result of a stressful event, such as the death of a loved one or the loss of a job.
- Genetics. You are more likely to develop schizophrenia if you have a close relation with the illness.
- Brain damage. This is usually damage that has stopped your brain from growing normally when your mother was pregnant. Or during birth.
- Drugs and alcohol. Research has shown that stronger forms of cannabis increase your risk of developing schizophrenia.
- A difficult childhood. If you were deprived, or abused, as a child this can increase your risk of developing a mental illness. Including schizophrenia.
There is research to suggest that may be an association between menopause and schizophrenia. This may be due to the hormonal changes during this stage of life for women.
You can find more information about:
- Does mental illness run in families? by clicking here.
- Drugs, alcohol and mental health by clicking here.
- Cannabis and mental health by clicking here.
How Is It Diagnosed

Your healthcare provider can diagnose schizophrenia or its related disorders based on a combination of questions they ask, the symptoms you describe or by observing your actions. Theyll also ask questions to rule out causes other than schizophrenia. They then compare what they find to the criteria required for a schizophrenia diagnosis.
According to the DSM-5, a schizophrenia diagnosis requires the following:
- At least two of five main symptoms. Those symptoms, explained above, are delusions, hallucinations, disorganized or incoherent speaking, disorganized or unusual movements and negative symptoms.
- Duration of symptoms and effects. The key symptoms you have must last for at least one month. The conditions effects must also last for at least six months.
- Social or occupational dysfunction. This means the condition disrupts either your ability to work or your relationships .
Recommended Reading: What Are The Different Types Of Eating Disorders
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
There arent any diagnostic tests for schizophrenia-spectrum conditions. But healthcare providers will likely run tests to rule out other conditions before diagnosing schizophrenia. The most likely types of tests include:
- Imaging tests. Healthcare providers will often use computerized tomography , magnetic resonance imaging and other imaging tests to rule out problems like stroke, brain injuries, tumors and other changes to your brain structure.
- Blood, urine and cerebrospinal fluid tests. These tests look for chemical changes in bodily fluids that might explain changes in your behavior. They can rule out heavy metal toxicity or other causes of poisoning, infections and more.
- Brain activity testing. An electroencephalogram detects and records the electrical activity in your brain. This test can help rule out conditions like epilepsy.
Psychosocial Factors During Pregnancy And Delivery
Some studies suggest an association between antenatal stress and schizophrenia. The children of mothers whose husband died while they were pregnant have been found to have a significantly increased rate of schizophrenia compared with children who lost their father in infancy in the first year of life. In The Netherlands, rates of schizophrenia have been found to be very slightly higher in individuals exposed in utero to war and flood disaster than in reference subjects.
In the Northern Finland 1966 Birth Cohort the risk of later schizophrenia among unwanted children was elevated 2.4-fold compared with wanted or mistimed children, even after adjustment for confounding by sociodemographic, pregnancy and perinatal variables. Unwantedness might be a marker for features associated with risk in either the mother or the child. In the same cohort, the level of schizophrenia in the offspring of antenatally depressed mothers was elevated by a factor of 1.5-foldly, but the association was not statistically significant. Those mothers of schizophrenia patients with a psychotic first-degree relative had suffered from depressed mood during pregnancy twice as often as other mothers. The familial risk for psychosis, including genetic risk for psychosis, might explain the elevated prevalence of depressed mood during pregnancy among the mothers of the offspring who went on to develop schizophrenia.
Recommended Reading: How Much Money For Ptsd Disability
Childhood Schizophrenia Signs And Symptoms
Some children who develop schizophrenia first go through a period called the prodrome or the prodromal phase. They might withdraw from daily life, with more anxiety and less interest in school or friends. Not all children who show these signs will have a psychotic disorder, so itâs important to talk to your doctor if you notice any issues.
Early childhood schizophrenia symptoms
A baby or toddler may have signs of schizophrenia that are different from those in older children, teens, and adults.
The disorder affects how your child develops. You may notice things like:
- Long periods in which theyâre sluggish or not active
- Floppy arms or legs
- Delays in crawling, walking, or talking
- Odd movements such as rocking or flapping their arms
- A limp or slumped posture
Some of these symptoms show up in children with other problems besides schizophrenia. And some happen in kids without any mental health conditions. Only your child’s doctor can figure out what’s really going on.
Later childhood schizophrenia symptoms
In older kids, you might notice the behavior changes of schizophrenia over time or suddenly, as if out of nowhere. Your child may act withdrawn and clingy, or they may talk about strange and disturbed ideas and fears.
Tell your doctor as soon as you see symptoms of schizophrenia. It’s important to get a diagnosis and start treatment before your youngster shows signs of a break from reality, called psychosis.
Symptoms in older children include:
When Do Symptoms Of Schizophrenia Appear
Early symptoms of schizophrenia vary depending on the person. Symptoms may develop slowly over months or years with several symptoms building sequentially before the diagnosis is made.
A person experiencing schizophrenia symptoms will likely need to see a psychiatrist for an assessment and diagnosis. However, family members and friends sometimes recognize symptoms in the early stages of the disorder. Early signs of schizophrenia usually manifest between the ages of 15 and 30.
You May Like: Is Borderline Personality Disorder The Same As Bipolar
Hope For The Patient And Family
A diagnosis of schizophrenia is life-changing for those affected and everyone who loves them. But, with hard work and dedication, you can help your loved one enjoy a meaningful life.
People with schizophrenia can finish college, work jobs, get married, have families and enjoy a reasonably healthy life, stresses Dr. Bowers.
But it requires a combination of good medication, supportive counseling and being connected to community resources.
The National Alliance on Mental Illness offers support groups for the mentally ill and their families. And organizations like Recovery International and Emotions Anonymous are excellent resources for patients, she says.
When Schizophrenia Symptoms Start
Symptoms usually start to develop in early adulthood, between late adolescence and the early 30s. The disorder typically becomes evident slightly earlier in men than in women. Symptoms often emerge between late adolescence and the early 20s in men and between the early 20s and the early 30s in women.
Recommended Reading: Who Is Schizophrenia Most Common In