What Parents Should Know About Schizophrenia And Teens
Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder that people can develop at any age. Some studies show that not only can teenagers start showing signs of the disorder, but males who develop schizophrenia most often do so in the teen years and early 20s. Females tend to develop it in their 20s and 30s, but its possible for them to have signs earlier.
Despite the prevalence in teens, fewer than 20 percent of people who have psychosis say that their parents noticed the symptoms and did something to help. All parents can do their part to reverse this sad trend by learning about the disorder, the symptoms of schizophrenia in teens, and what to do if someone they know shows these signs.
Informed Consent And Decisional Capacity
Patients with schizophrenia are routinely asked to provide informed consent for their antipsychotic medication treatment. However, because of the cognitive deficits, as well as insight, deficits, which are sometimes present among those with schizophrenia,, some schizophrenia patients may lack the capacity to provide independent consent for treatment. On the other hand, empirical data document considerable heterogeneity among older as well as younger schizophrenia patients in terms of the level of decisional capacity,- and age is not itself a strong predictor of the level of decisional capacity among such patients.- Nonetheless, due to the increased likelihood of medical comorbidity and polypharmacy present, in the older population,, together with the increased physical frailty of some elderly persons, and the still relatively limited empirical database on the safety and efficacy of antipsychotic medications for use with realworld elderly patients, the very nature of treatment decisions and consent may be particularly complex in the context of treating older patients with schizophrenia, and thus consent, issues are particularly salient.
How Does It Feel To A Child
In the video below, Prof. Rochelle Caplan, an expert on childhood schizophrenia, talks about how the symptoms appear and the effect that they can have. The Child Mind Institute, a nonprofit organization, produced the video.
Prof. Caplan describes how symptoms appear gradually in most cases. She explains how the experience can be very scary for the child at first. To parents or caregivers, this may present similarly to anxiety.
The child may feel afraid, for example, because the hallucinations or delusions can feel threatening.
The child might also have trouble paying attention, and they may become irritable or have difficulty sleeping. Prof. Caplan notes that some of these changes can resemble rebellious behavior.
Understanding what the child is experiencing can help parents and caregivers react in a constructive way that can help the child.
According to the authors of one case study, early onset schizophrenia is when a child aged 1318 years experiences symptoms of schizophrenia.
Very early onset schizophrenia is when symptoms appear before the age of 13 years.
The researchers describe a child who experienced unusual perceptions from the age of 3 months.
There are no separate criteria to distinguish between childhood and adult schizophrenia.
The Complications Of Schizophrenia
When left untreated, Schizophrenia symptoms can quickly degenerate into more complex issues that can affect every area of life. Suicide, suicide attempts, or thoughts of committing suicide are some of the complications of untreated Schizophrenia.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder and some other anxiety-related disorders may also be complications from Schizophrenia. Similarly, abuse of alcohol, nicotine, and other drugs may also arise from the condition.
Inability to concentrate at work or school may be a complication. In some cases, Schizophrenia may lead to a financial crisis, which may lead to homelessness. Social isolation from friends and family may occur, and so are other secondary medical conditions.
Though aggressive behavior may be a complication of Schizophrenia, it is pretty uncommon. In many cases, a schizophrenia patient becomes victimized.
How Is Childhood Schizophrenia Diagnosed
Schizophrenia in children is difficult to diagnose. Many healthy, nonpsychotic children have hallucinations or delusions. For example, a young child may talk to an imaginary friend.
Also, other psychiatric illnesses can cause symptoms that may be mistaken for schizophrenia. These conditions include attention deficit hyperactivity disorder , major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder and schizoaffective disorder.
No one test can tell whether a child has schizophrenia. To make a diagnosis, a doctor must rule out other diseases or conditions, and consider other psychiatric illnesses, developmental disorders or drug toxicity.
Doctors diagnose childhood schizophrenia with a combination of mental and physical tests. To check for physical causes, your doctor may use:
- Magnetic resonance imaging : This test uses radio waves and strong magnetic fields to help doctors see whether there are any abnormalities in the brain.
- Positron emission tomography and single photon emission computed tomography : A radioactive chemical called a tracer is injected into the bloodstream to allow the doctor to see blood flow in the brain.
What Are The Early Signs Of Schizophrenia
The most common early signs of schizophrenia may include social withdrawal, depression, hostility, oversleeping or insomnia, inability to cry or express joy, and deterioration of personal hygiene. The early stage of the schizophrenia is called the prodromal phase. It is difficult to diagnose schizophrenia during this early stage, as these symptoms could result from a number of other problems.
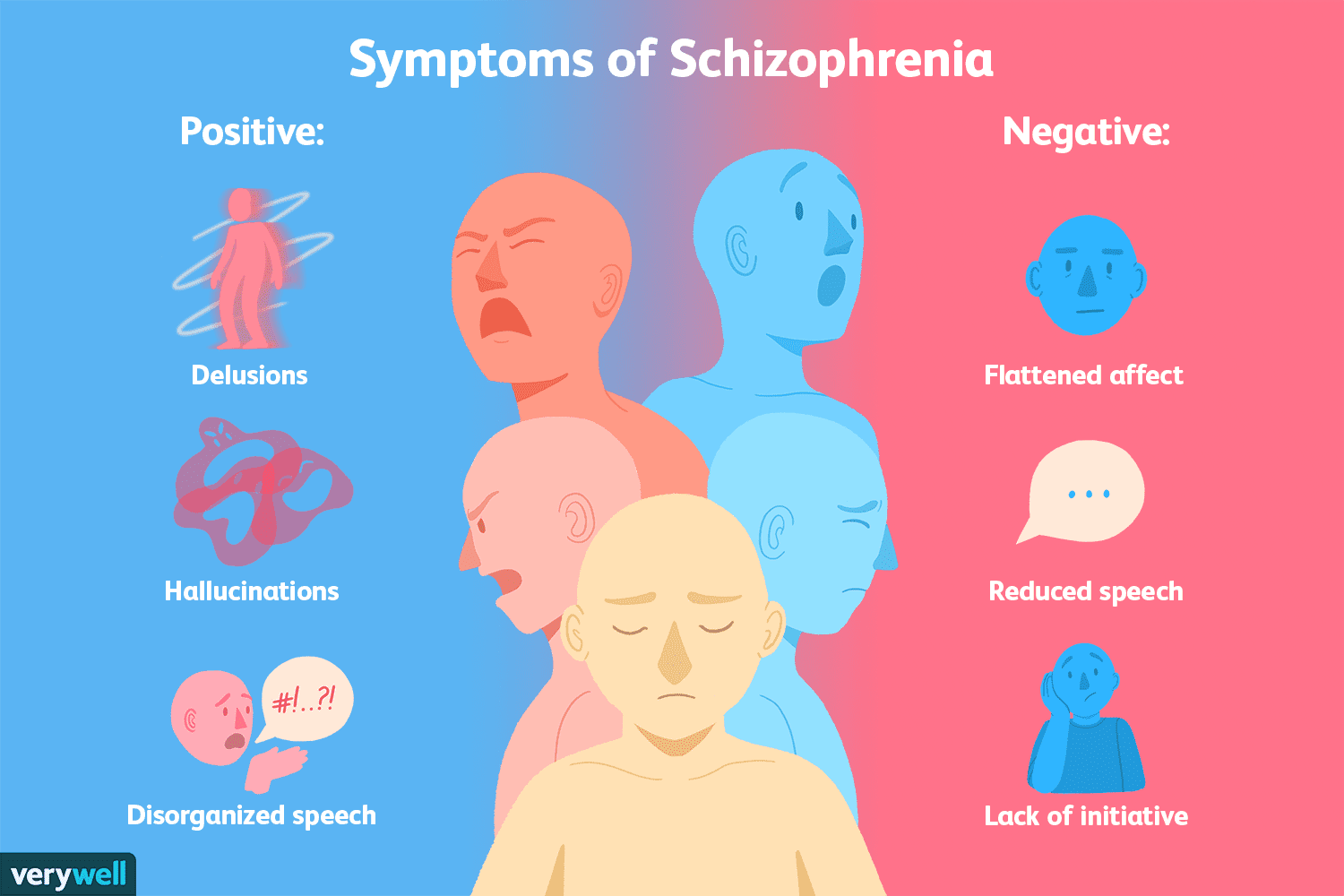
Positive And Negative Symptoms
What psychiatrists call the positive symptoms of schizophrenia are more obvious:
- Abnormal thinking and inappropriate emotions.
- Hallucinations, delusions and odd communication.
What they call the negative symptoms are more subtle and can last longer:
- Not talking much.
- Blunted feelings/little facial expression.
- Staying in bed to avoid people.
Whether their symptoms are positive or negative, people with schizophrenia dont seem to interact with the world in a healthy way, says Dr. Bowers.
What Is Childhood Schizophrenia
Childhood schizophrenia is a severe mental health disorder in children younger than 13 that affects the way they deal with reality. They might have unusual thoughts, feelings, or behaviors. Itâs also called childhood-onset or very early onset schizophrenia.
The disorder is rare and may be hard to spot. Thereâs no cure, but treatment can help.
The Public Health Challenge
A recent, report by Bartcls and colleagues examined the annual health care costs for adults with schizophrenia, depression, dementia, or physical illnesses in one small US state . In general, except, for dementia, costs of care increased with the age of patients, with those over 85 incurring the greatest per-capita expense. Among people aged 65 or over, annual per-person care for those with schizophrenia, $40 000 or more, was the most, costly: . The patients with schizophrenia incurred higher annual costs in all age-groups compared with depression or medical conditions. The cost-by-age data were different for patients with dementia, where younger patients incurred higher costs. However, among patients over age 65, the cost of care was higher for the patients with schizophrenia compared with those with dementia.
Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia: Things That Might Stop Happening
Negative symptoms refer to an absence or lack of normal mental function involving thinking, behavior, and perception. You might notice:
- Lack of pleasure. The person may not seem to enjoy anything anymore. A doctor will call this anhedonia.
- Trouble with speech. They might not talk much or show any feelings. Doctors call this alogia.
- Flattening: The person with schizophrenia might seem like they have a terrible case of the blahs. When they talk, their voice can sound flat, like they have no emotions. They may not smile normally or show usual facial emotions in response to conversations or things happening around them. A doctor might call this affective flattening.
- Withdrawal. This might include no longer making plans with friends or becoming a hermit. Talking to the person can feel like pulling teeth: If you want an answer, you have to really work to pry it out of them. Doctors call this apathy.
- Struggling with the basics of daily life. They may stop bathing or taking care of themselves.
- No follow-through. People with schizophrenia have trouble staying on schedule or finishing what they start. Sometimes they can’t get started at all. A doctor might call this avolition.
Depression has some of the same symptoms, too. They can be hard to spot, especially in teens, because even healthy teens can have big emotional swings between highs and lows.
What Type Of Schizophrenia Has The Most Favorable Diagnosis
The prognosis of schizophrenia is more dependent on the factors relating to the individual themselves, rather than the sub-type of schizophrenia they are diagnosed with. Research suggests multiple factors are associated with a more favorable prognosis: being female, rapid onset of symptoms, older age of first episode, and the presence of predominantly positive symptoms are all examples of such factors.
Development Of The Working Memory
Your prefrontal cortex the part of your brain responsible for storing memories and decision-making finishes developing by . When this happens, your brain has completed the process of determining how you should respond to what happens around you.
Some believe that a variety of outside factors can cause the prefrontal cortex to finish developing differently than it would have, causing a person to develop schizophrenia.
Hope For The Patient And Family
A diagnosis of schizophrenia is life-changing for those affected and everyone who loves them. But, with hard work and dedication, you can help your loved one enjoy a meaningful life.
People with schizophrenia can finish college, work jobs, get married, have families and enjoy a reasonably healthy life, stresses Dr. Bowers.
But it requires a combination of good medication, supportive counseling and being connected to community resources.
The National Alliance on Mental Illness offers support groups for the mentally ill and their families. And organizations like Recovery International and Emotions Anonymous are excellent resources for patients, she says.
What Can Happen If Schizophrenia Goes Untreated
Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder that affects about 3.5 million Americans. This illness can cause severe symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, strange behaviors, and suicidal thoughts. It is a lifelong illness and one of the top reasons people are on disability.
Despite the serious and life-threatening symptoms, about half of the people who receive this diagnosis do not get treatment. Furthermore, there may be many more who go undiagnosed and untreated. This lack of treatment is dangerous and can cause several additional problems. Thats why its important to break the stigma about schizophrenia and encourage those who live with the disorder to get help.
What Are The Symptoms Of Childhood Schizophrenia
Childhood schizophrenia causes symptoms similar to schizophrenia in adults. In many cases, children who have schizophrenia first show social and developmental delays that occur with other conditions, including:
- Disorganized behaviors, including inappropriate outbursts
- Motor skill delays, including a delay in learning to walk
- Poor attention span
- Speech delays or other problems, such as echolalia
Can Schizophrenia Be Treated
Yes. The main types of treatment are counseling and medicines to lessen or stop psychotic symptoms. Medicines will control psychotic symptoms in most people. In milder cases of schizophrenia, medications may not be needed. Medicines can:
- Lessen or stop hallucinations
- Help the person tell the difference between hallucinations and the real world
- Lessen or stop false beliefs
- Lessen feelings of confusion
- Help the person think more clearly
Lessening of these symptoms can help the person resume his or her normal lifestyle and activities. Medicines for schizophrenia need to be taken regularly, even after symptoms are gone. Some people with schizophrenia will stop taking their medicine because they believe the medicine is no longer needed, or they dislike the medication’s side effects. Psychotic symptoms often return when medication is stopped. Do not stop taking medicine without the advice of your healthcare provider.
Discuss any concerns you have about side effects with your healthcare provider.
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
If symptoms are present, your doctor will perform a complete medical history and physical examination. Although there are no laboratory tests to specifically diagnose schizophrenia, the doctor might use various diagnostic tests â such as or scans or blood tests â to rule out physical illness as the cause of your symptoms.
If the doctor finds no physical reason for the symptoms, he or she might refer the person to a psychiatrist or psychologist, healthcare professionals who are specially trained to diagnose and treat mental illnesses. Psychiatrists and psychologists use specially designed interview and assessment tools to evaluate a person for schizophrenia. The doctor or therapist bases his or her diagnosis on the personâs report of symptoms, and his or her observation of the personâs attitude and behavior.
The doctor or therapist then determines if the personâs symptoms point to a specific disorder as outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , which is published by the American Psychiatric Association and is the standard reference book for recognized mental illnesses. According to the DSM-5, a diagnosis of schizophrenia is made if a person has two or more core symptoms, one of which must be hallucinations, delusions, or disorganized speech for at least one month. The other core symptoms are gross disorganization and diminished emotional expression. Other DSM-5 criteria for a diagnosis of schizophrenia include:
Treating Women With Schizophrenia
Though treatment for mental illness is not typically separated by gender, clinicians serve women best by considering their unique experience of schizophrenia as well as the unique challenges they face. Because women have later onset of the illness and are less likely to experience affective symptoms, clinicians must be careful to rule out other mental illnesses, such as schizoaffective disorder or bipolar disorder, when giving a diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Treatment for women with schizophrenia should include psychoeducation and support for the needs of mothers with children. Antipsychotic medication can affect the ability to breast feed and the amount of energy a mother has to parent her children.7 Treatment plans tailored for women should include education about physical health as well. Women with schizophrenia are less likely to care for their physical health. This leaves them at risk for untreated breast cancer, osteoporosis, and thyroid conditions. Mental health professionals should also consider creating safety plans for women with schizophrenia who are at increased risk for committing suicide.
Women Tend To Develop Symptoms Of Schizophrenia Later Than Men And Often Exhibit Different Symptoms
There is no disparity in the occurrence and prevalence of schizophrenia between men and women, though schizophrenia is more closely associated with younger men. This may be due to the fact that women are more likely to experience the onset of schizophrenia later than men. Women tend to develop symptoms in their late 20s whereas the onset in men is typically in their early 20s.1 Also, because women with schizophrenia tend to be more socially active, their schizophrenia may be less detectable.
Treatment Of Schizophrenia In The Elderly
With proper treatment individuals with schizophrenia can live a normal life and, even though there is no cure, symptoms can be well-managed. Medications are often diagnosed to relieve hallucinations and delusions. Antipsychotics, in particular, can help with any chemical imbalances in the brain. Unfortunately, as with any medication there is the risk of side effects especially in the elderly.
Common side effects experienced by the elderly due to the use of antipsychotic drugs are:
- Uncontrolled movements
- Rehabilitation
- Integrated substance abuse treatment
Emily Lunardo studied medical sociology at York University with a strong focus on the social determinants of health and mental illness. She is a registered Zumba instructor, as well as a Canfit Pro trainer, who teaches fitness classes on a weekly basis. Emily practices healthy habits in her own life as well as helps others with their own personal health goals. Emily joined Bel Marra Health as a health writer in 2013.
What Are The Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia often involves a wide range of issues with cognition, emotions, and behavior. The signs and symptoms of this condition may vary from one individual to the other. In general terms, symptoms of Schizophrenia may include delusions, hallucinations, and impaired ability to handle daily functions.
Can Someone With Schizophrenia Live A Normal Life
While schizophrenia cannot be cured, with the right treatment plan many people with schizophrenia can live relatively normal lives outside of a healthcare setting. The treatment must be ongoing for the person with schizophrenia to continue to live a productive, fulfilling life, including maintaining a job or socializing with friends and family.
Disorganized Thinking And Speech
Disorganized thinking is very evident in the speeches made by someone who has Schizophrenia. Effective communication in patients can become impaired, and the answers they give to questions may be entirely or partially unrelated. Schizophrenia patients are known to put together words that are hard to understand.
Moving Into Adulthood: A Turning Point
Schizophrenia is typically diagnosed after age 18, most often in a persons 20s or early 30s.
It may be fairly well-controlled early in life, but moving from home to college and encountering new rules, or no rules exposes vulnerable young people to things theyre not prepared to deal with, says Dr. Bowers.
Living with a college roommate can prove difficult. It may seem easier to avoid talking or eating with others. You tend to isolate yourself and seem preoccupied with your own world, she says.
Increased exposure to alcohol or drug use is also a trigger.
Among 50 college students who smoke pot, a few may get a drug-induced psychosis that clears in weeks, says Dr. Bowers. But one may go on to develop a serious mental health disorder.
Exposure to disturbing news events or potentially false information on the internet and social media can provoke extreme reactions in the vulnerable.
They misperceive whats happening in the environment and develop delusions, she says. They may not make sense or become too aggressive.
Its easy to become so distracted by thoughts that schoolwork and jobs get neglected.
If someone constantly plays video games or focuses only on personal interests, and offers an irrational explanation for avoiding studies or work, thats a warning sign, says Dr. Bowers.
Can Schizophrenia Appear Even Later In Life
While the majority of cases are diagnosed between a persons late teens to early 30s, schizophrenia can still occur later. This is called late-onset schizophrenia.
While research is still limited, more and more people are being diagnosed with schizophrenia later in life. In fact, its believed that a quarter of people with schizophrenia develop it after age 40.
Many researchers currently believe these later diagnoses happen because the person had untreated cognitive obstacles and a small or poor network of support and camaraderie.
What Is The Major Difference Between A Diagnosis Of Schizophrenia And Schizoaffective Disorder
The main difference between schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder is the presence of a mood disorder. For people with schizoaffective disorder, the mood disorder is a prominent and persistent part of their condition. People with schizophrenia may experience mood episodes, but the total duration of the mood symptoms is brief and psychotic symptoms are more frequently present.
Early Warning Signs Of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia can be hard to diagnose for a few reasons. One is that people with the disorder often don’t realize they’re ill, so they’re unlikely to go to a doctor for help.Another issue is that many of the changes leading up to schizophrenia, called the prodrome, can mirror other normal life changes. For example, a teen who’s developing the illness might drop their group of friends and take up with new ones. They may also have trouble sleeping or suddenly start coming home with poor grades.
Some research suggests that if a doctor strongly thinks someone is getting the disorder while still in this early phase, low doses of antipsychotic medication might delay it. More studies need to be done to know whether these drugs work for young people at risk for the disease. Cognitive behavioral therapy, family therapy, and social skills training appear to have clearer benefits for them, at least in the short term, when used early on. Learn more about the prodrome phase of schizophrenia.
Statistical Methods And Measurement Caveats
The prevalence rate of schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders is difficult to estimate using typical household survey methods alone. Accurate assessment of schizophrenia is best achieved using clinicians trained in the diagnosis of mental illnesses. The U.S. prevalence studies cited here were selected based on their use of U.S. population samples and use of methods that involved clinical diagnosis, either via clinical reappraisal studies or clinical record studies.3,4,5
Individuals with schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders may be under-counted in prevalence estimation studies. These individuals may be under-represented in household surveys because they may reside in prisons, other institutions, or may lack a permanent address. Similarly, some people with schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders may not be fully reflected in medical records data because they may not have a documented diagnosis, and/or may receive little or no health care.
Information on statistical methods and measurement caveats can be found in the papers cited on this page and listed in the reference section. Below we provide additional background information for large datasets used in two studies cited on this page.3,5
National Comorbidity Survey Replication
- For more information, see NIMH NCS-R study page.
Treatment Of Late Onset Schizophrenia
Antipsychotic medications have proven to be very effective in treating the late-onset of schizophrenia. This type of the disorder also has the best prognosis and symptoms are almost exclusively due to neurostructural causes rather than neurotransmitter function. Therefore, antipsychotic medications can properly treat positive symptoms.
A downside of late onset schizophrenia is that cognitive treatment is much less successful and often, if cognitive damage is severe, patients are not likely to recuperate completely or re-learn certain cognitive functions.
The late onset of schizophrenia can also be challenging to treat given the fact that as a disease of age-related reasons , it is likely to be the cause of multiple reasons completely unrelated to schizophrenia under normal conditions. Patients of elderly age may have psychotic symptoms, but these can be related to general cognitive dysfunction brought about by aging.
Also, since late onset schizophrenia is devoid of any negative symptoms it is unlikely that the disorder will be misdiagnosed and thus mistreated with antidepressants.
At What Age Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
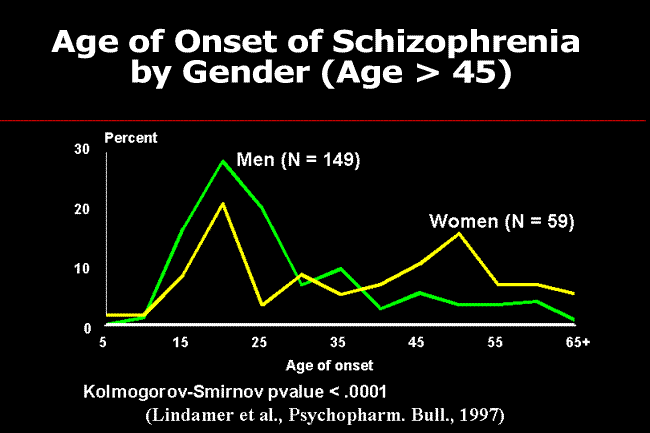
Schizophrenia usually develops after puberty, with most people being diagnosed with schizophrenia in their late teens to early 30s. The typical age of onset and diagnosis also varies between males and females. Males are more likely to be diagnosed in their late teens to early 20s, while females are more likely to be diagnosed in their late 20s to early 30s.
When Schizophrenia Symptoms Start
Symptoms usually start to develop in early adulthood, between late adolescence and the early 30s. The disorder typically becomes evident slightly earlier in men than in women. Symptoms often emerge between late adolescence and the early 20s in men and between the early 20s and the early 30s in women.
Medical Expenditure Panel Survey
- The MEPS collect data from community-dwelling people in the U.S. It does not include patients living in group homes, supported living arrangements, prisons, and institutions. In addition, homeless people and undocumented immigrants are excluded. These groups may have a higher prevalence of schizophrenia. MEPS survey responses were obtained from a single respondent for all the members of the family, therefore some recall bias may be associated with the responses.
- Patients for the schizophrenia study were selected based on ICD-9 codes only. Due to the stigma associated with the condition, physicians are known to give patients an interim non-schizophrenia diagnosis when uncertain about schizophrenia until it can be confirmed. To capture patients who may be given an interim non-schizophrenia diagnosis, researchers used the ICD-9 code for non-organic psychoses in addition to that for schizophrenic disorder in their study.5 MEPS collects information about conditions through patient interviews and some miscoding may occur as the household participants describe their conditions during the interviews and the coders record the ICD-9 codes for the diagnosis.
Its Easy To Live In Denial
Even though your loved one isnt functioning well, isnt meeting their own expectations in life, and is using alcohol or drugs to cope, they may not see theres a problem.
Because of the natural urge to protect those you love, families can stay in denial, as well.
Its often the college that sends a young adult to the hospital for the first time because of erratic behavior or an overdose. The parents get involved only because the college requests their child be evaluated by a psychiatrist.
Families often dont seek help on their own, says Dr. Bowers.
They may continue to struggle try to understand their loved ones symptoms. Or ignore those symptoms until they escalate, sometimes into violent behavior.
But early, continuous treatment is critical, she stresses. Without help, a young adults problems will continue especially if they use drugs or alcohol.
If you find them up all hours of the night, or painting their room black, or too irritable without their meds, or scaring their little sister, call the doctor, she says. And encourage them to keep their appointments.