What To Read Watch And Listen To About Coronavirus
New Scientist Weekly features updates and analysis on the latest developments in the covid-19 pandemic. Our podcast sees expert journalists from the magazine discuss the biggest science stories to hit the headlines each week from technology and space, to health and the environment.
The Jump is a BBC Radio 4 series exploring how viruses can cross from animals into humans to cause pandemics. The first episode examines the origins of the covid-19 pandemic.
Why Is Covid Killing People of Colour? is a BBC documentary, which investigates what the high covid-19 death rates in ethnic minority patients reveal about health inequality in the UK.
Panorama: The Race for a Vaccine is a BBC documentary about the inside story of the development of the Oxford/AstraZeneca vaccine against covid-19.
Race Against the Virus: Hunt for a Vaccine is a Channel 4 documentary which tells the story of the coronavirus pandemic through the eyes of the scientists on the frontline.
The New York Times is assessing the progress in development of potential drug treatments for covid-19, and ranking them for effectiveness and safety.
Humans of COVID-19 is a project highlighting the experiences of key workers on the frontline in the fight against coronavirus in the UK, through social media.
Coronavirus, Explained on Netflix is a short documentary series examining the coronavirus pandemic, the efforts to fight it and ways to manage its mental health toll.
Symptom Profile In Teenagers
Schizophrenia symptoms in teenagers are similar to those in adults, but the condition may be more difficult to recognize.
This may be in part because some of the early symptoms of schizophrenia in teenagers are common for typical development during teen years and can easily be overlooked by parents.
Residual schizophrenia had higher chances to be prevalent in teenagers because of these reasons, such as:
- Withdrawal from friends and family in their daily lives as their thoughts may be disturbed
- A drop in performance at school
- Irritability or depressed mood
- lack of motivation
Compared with schizophrenia symptoms in adults, teens may be less likely to have delusions and More likely to have visual hallucinations.
Child And Adolescent Brain Development
The increased spatial resolution available with magnetic resonance imaging allows a reliable, automated quantitative measurement of several brain regions, which combined with periodic rescanning in pediatric and adult populations, allows us to examine trajectories of brain change longitudinally. Over the past 20 years, longitudinal anatomic brain imaging of children and adolescents has established the trajectories of brain gray matter and white matter volumes, cortical thickness, along with finer maps of GM and WM development across time.
Recommended Reading: Feritriphobia
What Are The Three Phases Of Schizophrenia
Research has identified schizophrenia to have three phases, these are as follows:
- Prodromal
- Acute / active
- Residual
It may sometimes seem as though schizophrenia suddenly develops out of nowhere, this, however, is not the case. There is no such thing as waking up one morning and have bouts of full-blown psychosis. The disease instead consists of psychotic symptoms that slowly start to appear, and the sufferer begins to show a way of thinking that is distorted and has difficulty relating to others.
The phases can be explained accordingly:
Are There Any Diagnostic Tests For Paranoid Delusions
Harvard Health Publishing says that if the person allows it, the following can be useful in the diagnostic process of paranoid delusions related to delusional disorder: 4 Diagnostic tests such as an electroencephalogram, magnetic resonance imaging, or computed tomography scans when a neurological cause is suspected.
Recommended Reading: What Does Phobic Mean
The Age Of Onset Distribution Of Treated Psychosis
Psychotic disorders rarely occur before age 14, but show a marked increase in prevalence between at ages 1517 . Schizophrenia spectrum diagnoses account for approximately twothirds of all psychotic disorders. Schizophrenia usually bens in the age range 1535. Disorderspecific estimates of AOO distributions for nonaffective and affective psychotic disorders have not been separately reported in any of the WMH surveys due to the underrepresentation of these cases in surveys.
As noted above, studies that either establish the treated incidence of psychosis in a well defined catchment area or that observe onsets in longterm prospective general population cohorts are preferred. An integrated communitybased treatment system is needed to obtain accurate data on treated incidence. A good example of such a system can be found at the Early Psychosis Prevention and Intervention Centre in Melbourne, Australia. This is a communitybased specialized service mandated to treat all people between 15 and 29 years who present with a first psychotic episode to public mental health services in a geographically defined catchment area. Between 1997 and 2000, 1019 individuals were registered at EPPIC with a first episode of psychosis. The median age of initial presentation in this cohort was 22 with an IQR of 1925. The same median and IQR existed for patients with SSD and those with nonSSD .
What Risks And Complications Can Schizophrenia Cause
Physical health
Research suggests that people with serious mental illness , such as schizophrenia, have a shorter life expectancy. People with mental illness may die 15 to 20 years earlier than the general population. This may because people who live with SMI are at higher risk of having a range of health issues. Such as being overweight, having heart disease, smoking and diabetes.
Because of these issues, NICE recommends that when you start taking antipsychotic medication, your doctor should do a full range of physical health checks. This should include weight, blood pressure and other blood tests. These checks should be repeated regularly.
Mental health professionals are responsible for doing these checks for the first year of treatment. Responsibility may then pass to your GP. Your doctor or mental health team should offer you a programme which combines healthy eating and physical health checks. You should be supported by a healthcare professional to help stop smoking.
Suicide
The risk of suicide is increased for people with schizophrenia. Research indicates that around 513% of people who live with with schizophrenia die by suicide.
Research has found that the increased risk is not usually because of positive symptoms. The risk of suicide is associated more to affective symptoms, such as low mood.
Key risk factors for suicide include:
- previous suicide attempts,
Don’t Miss: Celine Dion Anorexic
Age Of Onset Distributions Of Commonly Occurring Disorders
Disorderspecific estimates of AOO distributions have either been published for WMH surveys in Italy , Metropolitan China , Mexico , New Zealand , Nigeria , Spain , Ukraine , and the USA . In addition, a comparative analysis of these distributions across 16 WMH countries has been completed . Systematic comparison of these results documents a number of clear crossnational consistencies both within and between disorders.
The impulsecontrol disorders have the earliest AOO distributions, with median AOO across countries of 79 years for attentiondeficit/hyperactivity disorder , 715 for oppositionaldefiant disorder , 914 for conduct disorder , and 1321 for intermittent explosive disorder . Impulsecontrol disorders also have an extremely narrow age range of onset risk. For example, 80% of all lifetime ADHD begins in the age range 411, while the vast majority of ODD and CD begins between ages 5 and 15. Fully half of all lifetime IED begins in childhood or adolescence.
Some anxiety disorders the phobias and separation anxiety disorder also have very early AOO distributions, with median AOO in the range 714 and interquartile range of 420. The other anxiety disorders , in comparison, have considerably later AOO distributions, although the crossnational variation in both median AOO and in IQR AOO is considerably wider than for the impulsecontrol disorders or the phobias or SAD.
Efforts Are Underway To Treat Schizophrenia Early
When properly diagnosed, early treatment is considered essential, Duckworth says. Earlier treatment is already becoming a reality across the country. The NIMH has launched a program called Recovery After an Initial Schizophrenia Episode Early Treatment Program , which emphasizes state-of-the-art medication and psychosocial treatments, delivered by trained multidisciplinary teams, to improve the outcomes and quality of life for patients after the first episode of psychosis, according to research published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Initial treatment typically includes inpatient hospitalization with medication therapy. After discharge, treatment usually consists of prescribed medication, cognitive behavioral therapy, family support and education, and other services to keep the individual on track in school or work and developmentally.
All but one state in the country now have early-psychosis programs, Duckworth says.
Also Check: Dehydration Panic Attacks
Talking To A Professional
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of paranoid schizophrenia, it is important to seek professional help. A mental health professional can provide a diagnosis and develop a treatment plan that is right for you or your loved one. You donât have to go through this alone. There are many different types of support available, so please reach out for help.
Early Warning Signs Of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia can be hard to diagnose for a few reasons. One is that people with the disorder often don’t realize they’re ill, so they’re unlikely to go to a doctor for help.Another issue is that many of the changes leading up to schizophrenia, called the prodrome, can mirror other normal life changes. For example, a teen who’s developing the illness might drop their group of friends and take up with new ones. They may also have trouble sleeping or suddenly start coming home with poor grades.
Some research suggests that if a doctor strongly thinks someone is getting the disorder while still in this early phase, low doses of antipsychotic medication might delay it. More studies need to be done to know whether these drugs work for young people at risk for the disease. Cognitive behavioral therapy, family therapy, and social skills training appear to have clearer benefits for them, at least in the short term, when used early on. Learn more about the prodrome phase of schizophrenia.
Recommended Reading: Can You Faint From A Panic Attack
The Most Common Early Warning Signs Include:
While these warning signs can result from a number of problemsnot just schizophreniathey are cause for concern. When out-of-the-ordinary behavior is causing problems in your life or the life of a loved one, seek medical advice. If schizophrenia or another mental problem is the cause, getting treatment early will help.
Mental Disorders And Evolution: What Would Darwin Say About Schizophrenia
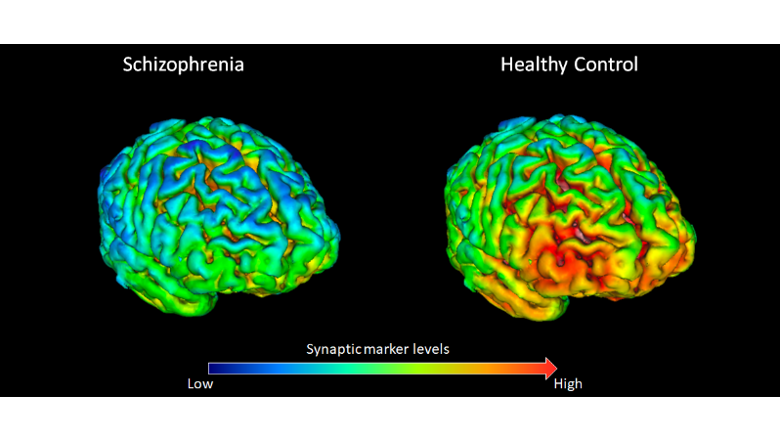
“This is an experiment far before its time,” says Allen Frances.
McFarlane believes the benefits of these programs are borne out in the work done at his clinic and others based on his model. In July, he the results of a two-year study of two groups of young people at risk for, or in the early stage of, schizophrenia, which showed better functional outcomes for those who went through treatment.
Read Also: What Is A Depression On A Map
Is It Possible To Recover From Schizophrenia
Many people who live with schizophrenia have recovery journeys that lead them to live meaningful lives.
Recovery can be thought of in terms of:
- clinical recovery, and
- personal recovery.
What is clinical recovery?
Your doctor might have talked to you about recovery. Some doctors and health professionals think of recovery as:
- no longer having mental illness symptoms, or
- where your symptoms are controlled by treatment to such a degree that they are not significantly a problem.
Sometimes this is called clinical recovery.
Everyones experience of clinical recovery is different.
- Some people completely recover from schizophrenia and go on to be symptom free.
- Some who live with schizophrenia can improve a great deal with ongoing treatment.
- Some improve with treatment but need ongoing support from mental health and social services.
What is personal recovery?
Dealing with symptoms is important to a lot of people. But some people think that recovery is wider than this. We call this personal recovery.
Personal recovery means that you can live a meaningful life.
What you think of as being a meaningful life might be different to how other people see it. You can think about what you would like to do to live a meaningful life and work towards that goal.
Below are some ways you can think of recovery.
What can help me recover?
You may want to think about the following questions.
The following things can be important in recovery.
Practical Difficulties In Studying Age Of Onset
The dearth of information on AOO of mental disorders is presumably due to reluctance on the part of epidemiologists to rely on the retrospective reports obtained in general population surveys that, as a practical matter, must be used to generate the survival distributions needed to study AOO. Two theoretical alternatives exist to relying on these retrospective reports, although neither of the two is broadly feasible. The first applies largely to psychosis: to use information obtained about totalpopulation incidence of treated disorder from studies of psychotic disorders in catchment areas that monitor all points of contact with the treatment system . The implicit assumption in this approach, that the vast majority of psychotics eventually come to clinical attention, is likely to be true, making this approach useful for studying AOO of nonaffective psychosis. The same approach would not be nearly as useful, though, for less severely impairing disorders, as many people with such disorders never come to clinical attention. Even for nonaffective psychosis, epidemiological surveys show that the time between onset of the first episode and first contact with the treatment system is sometimes quite long , although analysis of incident treated cases is still the best available approach due to the substantial underrepresentation of psychosis in community epidemiological surveys .
Don’t Miss: Blurred Vision Panic Attack
How Can I Help A Friend Or Relative With Schizophrenia
It can be difficult to know how to help someone who is experiencing psychosis. Here are some things you can do:
- Help them get treatment and encourage them to stay in treatment.
- Remember that their beliefs or hallucinations seem very real to them.
- Be respectful, supportive, and kind without tolerating dangerous or inappropriate behavior.
- Look for support groups and family education programs, such as those offered by the National Alliance on Mental Illness.
If your loved one is thinking about attempting suicide or otherwise harming themselves or others, seek help right away:
- Call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 1-800-273-TALK .
- Text the Crisis Text Line .
Health Solutions From Our Sponsors
Molecular PsychiatryDiagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth EditionDiagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, Text RevisionIndian Journal of PsychiatryPsychiatric ServicesClinical Child Psychology and PsychiatryPsychiatric TimesFrontiers in PsychiatryPsychiatry ResearchJournal of the American Medical AssociationBritish Journal of PsychiatryAmerican Academy of Social Work and Social WelfareScience DailyClinical NeuropsychiatryCurrent Antipsychotics, Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, Vol. 212Molecular PsychiatryPsychiatria DanubinaSchizophrenia BulletinBritish Journal of PsychiatryScienceSocial Studies of ScienceThe British Journal of PsychiatryAmerican Journal of PsychiatryPatient CareAm J PsychiatryMen and MasculinitiesHistory of PsychiatrySchizophrenia Research TreatmentGerman Journal of PsychiatryLancetPsychiatric ServicesCurrent Opinion in PsychiatryEpidemiologic ReviewsPsychiatric ServicesNeuropsychopharmacology: The Fifth Generation of Progress, Fifth EdClinical Schizophrenia and Related PsychosesPsychological BulletinSchizophrenia ResearchClinical TherapeuticsHarvard Mental Health LettAmerican Journal of PsychiatryAmerican Journal of PsychiatrySchizophrenia BulletinJournal of PsychopharmacologySchizophrenia BulletinAmerican Journal of PsychiatryPsychiatric TimesSchizophrenia BulletinAutismAmerican Journal of Psychiatry
Read Also: Fear Of Spoons Phobia Name
What Is The History Of Schizophrenia
The word schizophrenia has only been in use since about 1908, attributed to psychiatrist Eugen Bleuler. It was deemed a separate mental illness in 1887 by Emil Kraepelin. The positive, disorganized symptoms of psychosis were called hebephrenia. Despite that relatively recent history, it has been described throughout written history. Ancient Egyptian, Hindu, Chinese, Greek, and Roman writings described symptoms similar to the positive symptoms of schizophrenia. During medieval times, schizophrenia, like other illnesses, was often viewed as evidence of the sufferer being possessed by spirits or having evil powers.
A number of accomplished individuals suffer from schizophrenia. The film A Beautiful Mind describes the life of John Nash, a noted scientist, and his struggles with what was previously called paranoid schizophrenia. The film The Soloist explores the challenges faced by Juilliard-trained musician Nathaniel Ayers as a result of schizophrenia. Despite those prominent portrayals of people with schizophrenia, this condition, like most mental illnesses, usually remains shrouded in secrecy and shame.
Read Also: Phobia Means
What Is The Outlook For The Future
The outlook for people with schizophrenia continues to improve. Although there is no cure, treatments that work well are available. Many people with schizophrenia improve enough to lead independent, satisfying lives.
Continued research and understanding in genetics, neuroscience, and behavioral science will help scientists and health professionals understand the causes of the disorder and how it may be predicted and prevented. This work will help experts develop better treatments to help people with schizophrenia achieve their full potential. Families and individuals who are living with schizophrenia are encouraged to participate in clinical research.
Read Also: What Is Pristiq For
Don’t Miss: Does Dehydration Cause Panic Attacks
Positive Symptoms Of Schizophrenia: Things That Might Start Happening
Positive symptoms are highly exaggerated ideas, perceptions, or actions that show the person canât tell whatâs real from what isnât. Here the word “positive” means the presence of symptoms. They can include:
- Hallucinations. People with schizophrenia might hear, see, smell, or feel things no one else does. The types of hallucinations in schizophrenia include:
- Auditory. The person most often hears voices in their head. They might be angry or urgent and demand that they do things. It can sound like one voice or many. They might whisper, murmur, or be angry and demanding.
- Visual. Someone might see lights, objects, people, or patterns. Often itâs loved ones or friends who are no longer alive. They may also have trouble with depth perception and distance.
- Olfactory and gustatory. This can include good and bad smells and tastes. Someone might believe theyâre being poisoned and refuse to eat.
- Tactile. This creates a feeling of things moving on your body, like hands or insects.