Criteria Used To Diagnose Ptsd
Clinical psychologists, psychologists, and Licensed Clinical Social Workers can diagnose PTSD. If you are experiencing symptoms of PTSD and/or relate to any of the criteria below, we highly encourage you to seek out a mental health professional.
Criterion A: Exposure
Being exposed to death, threatened death, actual or threatened serious injury, actual or threatened sexual violence through direct exposure, witnessing the trauma, learning that a relative or close friend was exposed to a trauma, or indirect exposure to aversive details of the trauma, usually in the course of professional duties
Criterion B: Intrusive Symptoms
The traumatic event is persistently re-experienced in the following way: unwanted upsetting memories, nightmares, flashbacks, emotional distress after exposure to traumatic reminders, physical reactivity after exposure to traumatic reminders
Criterion C: Avoidance
Avoidance of trauma-related stimuli after the trauma, in the following way: trauma-related thoughts or feelings, trauma-related external reminders
Criterion D: Negative alterations in cognitions and mood
Negative thoughts or feelings that began or worsened after the trauma, in the following way: Inability to recall key features of the trauma, overly negative thoughts and assumptions about oneself or the world, exaggerated blame of self or others for causing the trauma. negative affect, decreased interest in activities, feeling isolated, difficulty experiencing positive affect
Changes In Physical And Emotional Reactions
Sometimes referred to as arousal symptoms, these symptoms emerge in reaction to the trauma and include things like:
- Easily startled
- Feelings of detachment from friends and family
- No interest in things that once brought you joy
- Inability to experience positive emotions
- Emotional numbness
- Memory problemseven difficulty remembering key details of your trauma
PTSD symptoms may come and go over time. Seeking treatment can help you recognize certain triggers so that you can manage the emotions they bring about if you cant avoid these triggers.
Who Is At Risk For Post
You can develop PTSD at any age. Many risk factors play a part in whether you will develop PTSD. They include:
- Your sex women are more likely to develop PTSD
- Having had trauma in childhood
- Feeling horror, helplessness, or extreme fear
- Going through a traumatic event that lasts a long time
- Having little or no social support after the event
- Dealing with extra stress after the event, such as loss of a loved one, pain and injury, or loss of a job or home
- Having a history of mental illness or substance use
You May Like: A Phobia Definition
Getting Professional Help For Ptsd
If you suspect that you or a loved one has post-traumatic stress disorder, its important to seek help right away. The sooner PTSD is treated, the easier it is to overcome. If youre reluctant to seek help, keep in mind that PTSD is not a sign of weakness, and the only way to overcome it is to confront what happened to you and learn to accept it as a part of your past. This process is much easier with the guidance and support of an experienced therapist or doctor.
Its only natural to want to avoid painful memories and feelings. But if you try to numb yourself and push your memories away, PTSD will only get worse. You cant escape your emotions completelythey emerge under stress or whenever you let down your guardand trying to do so is exhausting. The avoidance will ultimately harm your relationships, your ability to function, and the quality of your life.
Why you should seek help for PTSD
Early treatment is better. Symptoms of PTSD may get worse. Dealing with them now might help stop them from getting worse in the future. Finding out more about what treatments work, where to look for help, and what kind of questions to ask can make it easier to get help and lead to better outcomes.
PTSD symptoms can change family life. PTSD symptoms can get in the way of your family life. You may find that you pull away from loved ones, are not able to get along with people, or that you are angry or even violent. Getting help for your PTSD can help improve your family life.
Arousal And Reactivity Symptoms Include:

- Being easily startled
- Feeling tense or on edge
- Having difficulty sleeping
- Having angry outbursts
Arousal symptoms are usually constant, instead of being triggered by things that remind one of the traumatic events. These symptoms can make the person feel stressed and angry. They may make it hard to do daily tasks, such as sleeping, eating, or concentrating.
Don’t Miss: Can Anxiety Raise Blood Sugar In Non Diabetics
Why Do Some People Develop Ptsd And Other People Do Not
Not everyone who lives through a dangerous event develops PTSDmany factors play a part. Some of these factors are present before the trauma others become important during and after a traumatic event.
Risk factors that may increase the likelihood of developing of PTSD include:
- Exposure to dangerous events or traumas
- Getting hurt or seeing people hurt or killed
- Childhood trauma
- Feeling horror, helplessness, or extreme fear
- Having little or no social support after the event
- Dealing with extra stress after the event, such as loss of a loved one, pain and injury, or loss of a job or home
- Having a personal history or family history of mental illness or substance use
Resilience factors that may reduce the likelihood of developing PTSD include:
- Seeking out support from friends, family, or support groups
- Learning to feel okay with ones actions in response to a traumatic event
- Having a coping strategy for getting through and learning from a traumatic event
- Being prepared and able to respond to upsetting events as they occur, despite feeling fear
Next Steps For Ptsd Research
In the last decade, progress in research on the mental and biological foundations of PTSD has lead scientists to focus on better understanding the underlying causes of why people experience a range of reactions to trauma.
- NIMH-funded researchers are exploring trauma patients in acute care settings to better understand the changes that occur in individuals whose symptoms improve naturally.
- Other research is looking at how fear memories are affected by learning, changes in the body, or even sleep.
- Research on preventing the development of PTSD soon after trauma exposure is also under way.
- Other research is attempting to identify what factors determine whether someone with PTSD will respond well to one type of intervention or another, aiming to develop more personalized, effective, and efficient treatments.
- As gene research and brain imaging technologies continue to improve, scientists are more likely to be able to pinpoint when and where in the brain PTSD begins. This understanding may then lead to better targeted treatments to suit each persons own needs or even prevent the disorder before it causes harm.
Read Also: Prodromal Psychotic Disorder
When To Seek Medical Advice
It’s normal to experience upsetting and confusing thoughts after a traumatic event, but in most people these improve naturally over a few weeks.
You should visit your GP if you or your child are still having problems about 4 weeks after the traumatic experience, or the symptoms are particularly troublesome.
Your GP will want to discuss your symptoms with you in as much detail as possible.
They’ll ask whether you have experienced a traumatic event in the recent or distant past and whether you have re-experienced the event through flashbacks or nightmares.
Your GP can refer you to mental health specialists if they feel you’d benefit from treatment.
Biological And Neurological Factors
Two risk factors that have been shown to possibly influence the development of PTSD after trauma are IQ and neuroticism. Those who tend to score lower on IQ tests have been shown to be more susceptible to developing PTSD.
In addition, people who have greater neuroticism have shown to be more likely to have PTSD.
Neuroticism is a personality trait of people who are more likely than average to experience anxiety, feelings of guilt, worry, fear, anger, frustration, and sadness.
As mentioned previously, there is an increasing number of research studies dedicated to exploring the role of genetics in the development of PTSD. Being that PTSD does not occur in everyone who experiences a traumatic event, these continued findings help to better determine who may be at greatest risk so that interventions and treatments can be of the most help.
Post-traumatic stress disorder, along with other conditions such as major depression, is associated with decreased brain volume, particularly in the prefrontal areas. Research has shown that this decreased volume was associated with greater self-reports of anxiety in participants.
Understanding that the emotional impact of trauma can have a cumulative effectit can be easier to understand how past traumatic experiences can be a risk factor for someone developing PTSD after a marked traumatic event.
Recommended Reading: Can You Blackout During A Panic Attack
Diagnostic And Statistical Manual
PTSD was classified as an anxiety disorder in the DSM-IV, but has since been reclassified as a “trauma- and stressor-related disorder” in the DSM-5. The DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for PTSD include four symptom clusters: re-experiencing, avoidance, negative alterations in cognition/mood, and alterations in arousal and reactivity.
Treatment For Children And Teenagers With Ptsd
For children and teenagers who are struggling to recover after a traumatic event, the recommended treatment is trauma-focussed cognitive behavioural therapy . This treatment involves:
- learning about the type of traumatic event experienced and common reactions to trauma
- teaching how to relax and manage anxiety
- helping to create a coherent story of the traumatic event, and correct any unhelpful beliefs about the event such as self-blame
- gradual exposure to trauma-related objects or situations that are feared or avoided
- helping to get back into everyday activities.
Don’t Miss: Was Audrey Hepburn Anorexia
Do Children React Differently Than Adults
Children and teens can have extreme reactions to trauma, but some of their symptoms may not be the same as adults. Symptoms sometimes seen in very young children , these symptoms can include:
- Wetting the bed after having learned to use the toilet
- Forgetting how to or being unable to talk
- Acting out the scary event during playtime
- Being unusually clingy with a parent or other adult
Older children and teens are more likely to show symptoms similar to those seen in adults. They may also develop disruptive, disrespectful, or destructive behaviors. Older children and teens may feel guilty for not preventing injury or deaths. They may also have thoughts of revenge.
How Is Ptsd Diagnosed
A psychiatrist will diagnose PTSD through a mental health assessment. Your GP should carry out an initial assessment to decide what care you need. Your assessment should include information about:
- your physical needs,
- your social needs, and
- risk.
As part of the assessment they will decide if you need to be referred to the community mental health team . You should be referred to the CMHT if you have had symptoms for more than 4 weeks. Or your symptoms are very bad. A CMHT is part of the NHS. They are a team of mental health professionals.
Doctors use the following manuals to help to diagnose you:
- International Classification of Diseases produced by the World Health Organisation , and
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual produced by the American Psychiatric Association.
The manuals are guides which explain different mental health conditions.
Read Also: Define Aphobia
Beyond Treatment: How Can I Help Myself
It may be very hard to take that first step to help yourself. It is important to realize that although it may take some time, with treatment, you can get better. If you are unsure where to go for help, ask your family doctor. You can also check NIMH’s Help for Mental Illnesses page or search online for mental health providers, social services, hotlines, or physicians for phone numbers and addresses. An emergency room doctor can also provide temporary help and can tell you where and how to get further help.
To help yourself while in treatment:
- Talk with your doctor about treatment options
- Engage in mild physical activity or exercise to help reduce stress
- Set realistic goals for yourself
- Break up large tasks into small ones, set some priorities, and do what you can as you can
- Try to spend time with other people, and confide in a trusted friend or relative. Tell others about things that may trigger symptoms.
- Expect your symptoms to improve gradually, not immediately
- Identify and seek out comforting situations, places, and people
Caring for yourself and others is especially important when large numbers of people are exposed to traumatic events .
What Events Can Lead To The Development Of Ptsd
You dont have to experience a specific trauma to develop PTSD. Many people associate this disorder with military veterans. While PTSD is common in military populations, simply witnessing an event, like a car accident, can trigger PTSD symptoms.
In these cases, painful, traumatic memories can appear out of nowhere, creating intense physical and emotional reactions. During World War I, this was referred to as shell shock. When the horrors of war were too much for the brain to manage, the brain, or at least part of the brain, simply shut off.
Children and teens often experience PTSD as a result of traumas that impact them, such as school shootings, domestic violence, auto accidents, neglect, or abuse. 15-43% of adolescents will experience a traumatic event, with about a quarter of those individuals experiencing symptoms of PTSD.
You May Like: Define Aerophobia
Key Points About Posttraumatic Stress Disorder In Children
-
PTSD is a mental health problem. A child with PTSD has constant, scary thoughts and memories of a past event.
-
A traumatic event, such as a car crash, natural disaster, or physical abuse, can cause PTSD.
-
Children with PTSD may relive the trauma over and over again. They may have nightmares or flashbacks.
-
PTSD is diagnosed only if symptoms keep occurring for more than 1 month and are negatively affecting the childs life.
-
A child with PTSD may need therapy and medicine. They are at higher risk for other mental health problems such as depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts
International Classification Of Diseases
The International Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10 classifies PTSD under “Reaction to severe stress, and adjustment disorders.” The ICD-10 criteria for PTSD include re-experiencing, avoidance, and either increased reactivity or inability to recall certain details related to the event.
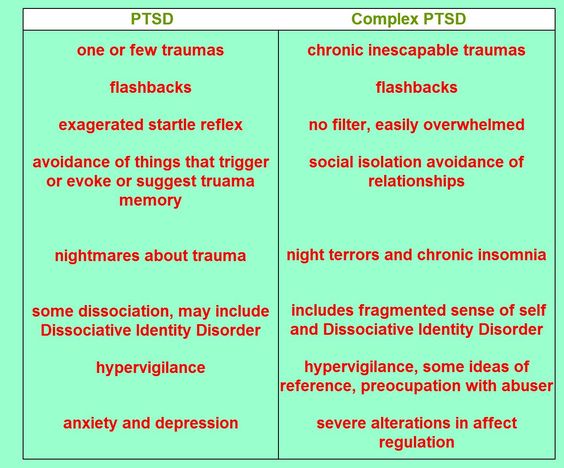
The ICD-11 diagnostic description for PTSD contains three components or symptom groups re-experiencing, avoidance, and heightened sense of threat. ICD-11 no longer includes verbal thoughts about the traumatic event as a symptom. There is a predicted lower rate of diagnosed PTSD using ICD-11 compared to ICD10 or DSM-5. ICD-11 also proposes identifying a distinct group with complex post-traumatic stress disorder , who have more often experienced several or sustained traumas and have greater functional impairment than those with PTSD.
You May Like: Which Organization Sets The Standards For Diagnosing Eating Disorders
Cognition And Mood Symptoms
- Trouble remembering key features of the traumatic event
- Negative thoughts about oneself or the world
- Distorted thoughts about the event that cause feelings of blame
- Ongoing negative emotions, such as fear, anger, guilt, or shame
- Loss of interest in previous activities
- Feelings of social isolation
- Difficulty feeling positive emotions, such as happiness or satisfaction
Cognition and mood symptoms can begin or worsen after the traumatic event and can lead a person to feel detached from friends or family members.
Who Develops Ptsd
Anyone can develop PTSD at any age. This includes combat veterans as well as people who have experienced or witnessed a physical or sexual assault, abuse, an accident, a disaster, a terror attack, or other serious events. People who have PTSD may feel stressed or frightened, even when they are no longer in danger.
Not everyone with PTSD has been through a dangerous event. In some cases, learning that a relative or close friend experienced trauma can cause PTSD.
According to the National Center for PTSD, a program of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, about seven or eight of every 100 people will experience PTSD in their lifetime. Women are more likely than men to develop PTSD. Certain aspects of the traumatic event and some biological factors may make some people more likely to develop PTSD.
You May Like: Does Dehydration Cause Anxiety
Where To Get Help
- Your doctor
- Mental health specialist, such as a psychiatrist, psychologist or social worker, with experience in treatment of PTSD
- Community health centre
- Phoenix Australia – Centre for Posttraumatic Mental Health Tel. 9035 5599
- Australian Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Stress Disorder and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder, 2013, Australian Centre for Posttraumatic Mental Health. More information here.
Ptsd In Children And Teenagers

Older children and teenagers experience similar problems to adults when they develop PTSD. Younger children can express distress in a different way. For example, they may re-live the traumatic event through repetitive play rather than having unwanted memories of the event during the day. Many children have frightening dreams without recognisable content rather than nightmares that replay the traumatic event. Children may also lose interest in play, become socially withdrawn, or have extreme temper tantrums.
About one third of children who experience a traumatic event will develop PTSD.
Other problems that can develop alongside PTSD include anxiety or depression, defiant behaviour, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and in teenagers and young adults, suicidal thoughts and alcohol or drug use.
Read Also: What Is The Name Of The Phobia Of Long Words
How Is Ptsd Treated In A Child
Treatment will depend on your childs symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is.
PTSD can be treated. Early diagnosis and treatment is very important. It can ease symptoms and enhance your childs normal development. It can also improve your childs quality of life.
Treatment may include:
-
Cognitive behavioral therapy. A child learns skills to handle his or her anxiety and to master the situation that led to the PTSD.
-
Medicines for depression or anxiety. These may help some children feel calmer.
Recovery from PTSD varies. Some children recover within 6 months. Others have symptoms that last much longer. Recovery depends on the childs inner strengths, coping skills, and ability to bounce back. It is also affected by the level of family support. Parents play a vital role in treatment.