What To Do If Youre Not Sure Whats Causing Your Symptoms
If youre not sure whether your asthma symptoms are getting worse or youve got symptoms of anxiety, its very important to talk to your GP or asthma nurse.
- If you mistake your anxiety symptoms for asthma, it could mean that you take more asthma medicine than you need. Some people find that they have palpitations, trembling hands, tingling fingers or lips, or feel a bit nervy and on edge after repeated doses of their reliever inhaler. Symptoms like these could make you feel more anxious.;
- If you mistake your asthma symptoms for anxiety, you may not be treating your asthma symptoms correctly and this could lead to a potentially life-threatening asthma attack.
Next review due June 2022
What Is Asthma & What Causes An Attack
Asthma is a condition that affects more than 22 million Americans, making it one of the most common chronic conditionsespecially in children. Affecting the respiratory system, asthma causes the airways to inflame and swell, making breathing extremely difficult. While asthma is only a minor issue for some, it can be a major health concern for othersinterfering with daily routines and potentially leading to life-threatening asthma exacerbations. An asthma attack can be triggered by a wide range of irritants, including:
- Allergies
- Genetics
- Pollution and other environmental stressors
- Stress
- Exercise
Because these irritants vary so vastly from person to person, understanding your specific triggers can help you control your conditions and avoid exacerbations.;
What Can I Do To Manage My Stress
There are a number of lifestyle changes and active strategies that you can implement as part of a stress management program, such as:
- Eating a well-balanced, healthy diet
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Identifying your stressors and trying to reduce them
- Practicing relaxation techniques
Like many other things in life, if you can measure or identify something you can take action. If you know the situations or stressors that worsen your asthma, you can develop a plan to either avoid the situation or learn some management techniques. If you are not able to do this on your own then you can talk with your doctor about;Exposure and Response Prevention Therapy. You might also consider a shallow breathing technique like the Buteyko breathing exercises. These techniques have been associated with;decreased asthma symptoms, decreased use of rescue inhalers, lowering doses of regular daily asthma medication, and improved quality of life.
Exercise is also a great activity to help prevent or manage anxiety. Exercise helps you improve psychological well-being, maintain a healthy weight, and decreases your risk of heart disease. Talk with your doctor about an exercise regimen that is both good for your asthma and good for your overall health.
Stress does not have to be a big deal for your asthma if you can identify it and make appropriate changes.
Don’t Miss: Fear Of Spoons
How Does Stress Affect Asthma
depicts our working model of stress and asthma. It highlights the importance of both social and physical exposures in the exacerbation of symptoms. The basic premise of the model is that psychological stress operates by altering the magnitude of the airway inflammatory response that irritants, allergens, and infections bring about in persons with asthma. It is important to note that the model suggests that stress on its own is NOT capable of modifying immune functions in a way that leads to asthmatic symptoms. Rather, stress is viewed as a process that accentuates the airway inflammatory response to environmental triggers and, in doing so, increases the frequency, duration, and severity of patients’ symptoms.
Model depicting the interaction of psychological stress with environmental triggers in influencing asthma exacerbations. The basic premise of the model is that stress operates by altering the magnitude of the airway inflammatory response that irritants, allergens, and infections bring about in persons with asthma. The figure provides an overview of the relevant biological pathways to airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction, including the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, the sympathetic-adrenal-medullary axis, and the sympathetic and parasympathetic arms of the autonomic nervous system.
Identify Whether Its Anxiety Or An Asthma Attack

During the moment, it is difficult to determine why you are having difficulty breathing. However, remember that a panic attack does not turn off your lungs. Steady breathing during a panic attack requires focus, but it is physically possible. On the other hand, an asthma attack prevents your lungs from taking in the proper amount of oxygen, so an inhaler may be necessary.
Also Check: What Is A Foot Phobia Called
How Long Do Asthma Attacks Last
There is no set time for how long an asthma attack lasts. As a guideline, you might only have a mild asthma attack for a matter of minutes before you manage to get your symptoms under control and they begin to ease off.
If you have severe asthma, an asthma attack can last longer, from hours to days. Severe asthma is harder to get under control and often doesnt respond in the same way to medications as mild asthma. A severe asthma attack is a medical emergency and you need to call for help for emergency help straight away.
Donât Miss: Does Losing Weight Help Asthma
Is It Anxiety Or Asthma
Did you know that as many as 40 million adults in the U.S. experience anxiety, while 25 million suffer from asthma? Unfortunately, anxiety can trigger asthma symptoms, which makes it difficult to distinguish the two. Consequently, it is important that you understand the relation between the two and how to tell the difference between anxiety and asthma.
Recommended Reading: Does Smoking Weed Make Asthma Worse
You May Like: What Phobia Is Weather Related
Asthma Can Also Cause Anxiety
It’s also important to note that asthma can actually cause anxiety as well – which in turn may further exacerbate the asthma. Asthma and shortness of breath are common triggers of panic attacks, and the general dangers and stress of the asthma experience can play a very strong triggering role in the development of long term anxiety issues.
It’s Easy To Get The Care You Need
See a Premier Physician Network provider near you.
If you suffer from asthma, you know that the feeling of not being able to breathe is very frightening.;
For some people, asthma and anxiety go hand-in-hand. Its often difficult to unravel the connections between the two. Thats because both conditions cause similar symptoms, especially shortness of breath.
You might experience anxiety about when your next asthma attack will occur. The stress of an asthma attack can even lead to a panic attack.
If you know what triggers your asthma or anxiety symptoms, you can take steps to reduce the frequency of attacks and maybe even prevent them.
Don’t Miss: Can Depression Make You Lose Your Appetite
Can Panic Attacks Be Mistaken For Asthma
Yes. Panic attacks can cause many asthma-like symptoms, such as shortness of breath, chest tightness, difficulty breathing, and rapid breathing. Therefore, panic attacks can be mistaken for asthma, asthma symptoms, and asthma attacks.
For more information about the differences, visit our panic attacks article.
Why Does Anxiety Aggravate Asthma Symptoms And Attacks
At this time, the cause of asthma is unknown. Many sources suggest there is a combination of factors that cause asthma, such as environmental and genetic. But the condition of asthma is well understood. Asthma is an inflammatory disease of the airways, says Bradley Chipps, MD, pediatric pulmonologist and allergist in Sacramento, California.
Even though the cause of asthma is unknown, there are many aggravators and triggers of asthma symptoms and attacks, including as mentioned above, stress.
Anxiety is also linked as an asthma aggravator because of how apprehensive behavior affects the body.
Apprehensive behavior, such as worrying, fretting, and being afraid create anxiety. Anxiety activates the stress response, which gives the body an emergency boost when in danger to either fight with or flee from it which is the reason the stress response is often referred to as the fight or flight response.
Because of the many body-wide changes the stress response brings about, stress responses stress the body. Consequently, stress, including anxiety-caused stress can aggravate asthma, asthma symptoms, and asthma attacks.
Furthermore, behaving anxiously too often can cause the body to become stress-response hyperstimulated . Hyperstimulation can chronically stress the body. Chronic stress is a common trigger for asthma symptoms and attacks.
Don’t Miss: Depression And Appetite
Asthma Symptoms Attacks And Anxiety
Common asthma anxiety symptoms descriptions include:
- You notice your asthma symptoms or attacks get worse and more persistent in association with your anxiety.
- You might also notice your overall asthma symptoms have increased, that you are experiencing more asthma attacks, or your asthma condition is more problematic overall than normal when your anxiety is more problematic.
- You have noticed a connection between your anxiety or stress and an increase in asthma symptoms or attacks.
Asthma symptoms include:
- Chest tightness
- Rapid breathing
Many find their asthma symptoms increase more in the early morning or at night. Asthma attacks, however, can occur at any time and can be triggered by a number of factors.
Asthma is caused by a narrowing and swelling of the airways, which can also cause a production of mucus that makes it difficult to breathe.
Some medical sources have linked the swelling of airways to inflammation, which can be triggered by an overly sensitive/reactive immune system. Because stress can suppress the bodys immune system, stress can play a role in the degree and prevalence of asthma.
During periods of stress and anxiety, asthma attacks occur more frequently, and asthma control is more difficult. – Peter Gergen, MP, MPH, a senior medical officer at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
Asthma Attacks Vs Panic Attacks
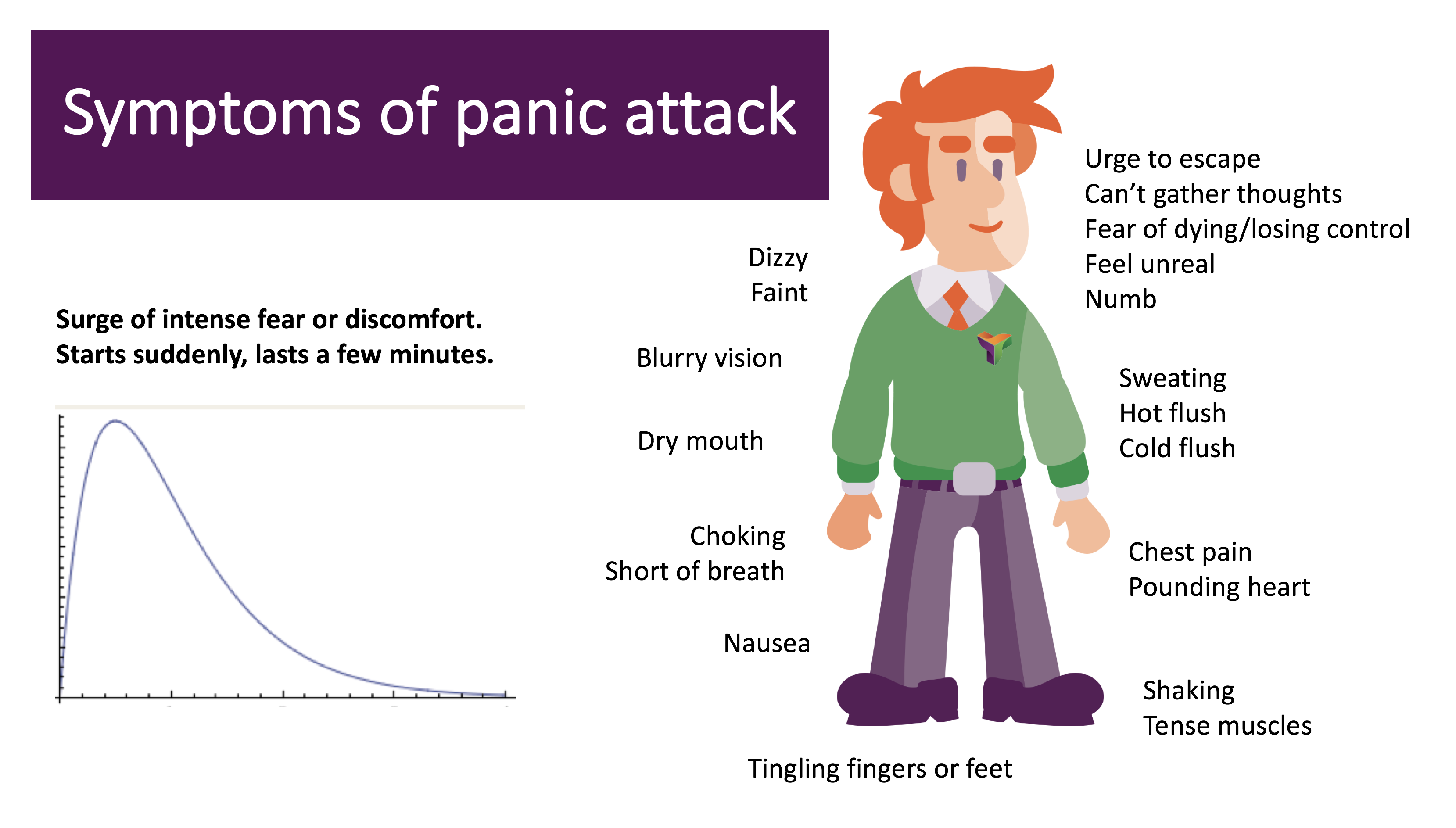
If you have both asthma and an anxiety disorder, it can be hard to tell the difference between an asthma attack and a panic attack. Both cause a feeling of tightness in your chest and difficulty breathing, but wheezing and coughing are typically only associated with asthma attacks. Panic attacks can also cause you to hyperventilate and take in too much oxygen, while asthma attacks significantly decrease your oxygen intake.
Because stress is such a common asthma trigger, living with both an anxiety disorder and asthma can often feel like a vicious cycle. A mental health professional can help you find effective ways to manage stress and reduce the likelihood of a stress-induced asthma attack.
Donât Miss: Does Asthma Cause Swollen Lymph Nodes
Read Also: How To Start An Eating Disorder Essay
Yes Including Other Strong Emotions
Response from Lorene Alba, AE-C:
Anxiety, along with other strong emotions can trigger asthma. Strong emotions can include anxiety, stress, fear, excitement, crying and even laughing too hard, and they often cause asthma symptoms. This does not mean, however, that asthma is all in your head or psychosomatic. Asthma is a real, physical disease. Managing and reducing your stress, just like your other triggers such as dust mites or cigarette smoke, is key to managing your asthma. Try belly or pursed-lip breathing to reduce stress and anxiety.
Treating A Child Who Is Having An Asthma Attack
Take your child to the ER if you notice these symptoms:
- Difficulty breathing. This includes needing to sit up because they cant breathe lying down, gasping or gulping for air, or having trouble taking a complete breath.
- Breathing with the muscles of their stomach, ribs, and neck. The muscles may look like theyre pulling inwards. It means that they are having to work extra hard to breathe.
- Wheezing constantly, even after taking their rescue medications listed on their asthma action plan.
- Lips or fingernails turning blue.
- Seeming more drowsy than normal. For example, they might fall asleep while playing. Or babies doze off feedings.
Recommended Reading: No Appetite Depression Anxiety
What Happens If An Asthma Attack Is Not Treated
Without immediate asthma medication and asthma treatment, an asthma attack may become more severe. Your breathing may become more labored, and wheezing may get louder. If you use a peak flow meter during an asthma attack, your reading will probably be less than your personal best
Without treatment, your lungs will continue to tighten during the asthma attack and you may be unable to use the peak flow meter at all. Gradually, your lungs may tighten so much during the asthma attack that there isnt enough air movement to produce wheezing. This is called silent chest and it is a dangerous sign.
If you do not receive adequate treatment for an asthma attack, you may eventually be unable to speak and can develop a bluish coloring around your lips. This change of color is the result of oxygen deprivation in your blood. Without immediate aggressive treatment in an emergency room or intensive care unit, you may lose consciousness and eventually die.
Read Also: Asthma Without Inhaler
Anxiety Caused By Anxiety
Anxiety is also self-sustaining. Earlier we mentioned panic attacks, and how they can often be caused by periods of stress that become overwhelming. But once youve had your first panic attack, you may get them again and again because of a fear of panic attacks, or because your body becomes more attuned to how it feels, which ultimately triggers them in the future.
We see this in other ways too:
- If you found yourself nervous about a plane ride, you might be fearful on future plane rides.
- If you find yourself worried about a negative thought, you may have that thought more often.
- If you experienced severe anxiety symptoms, you may be anxious about experiencing them again.
Essentially, anxiety and a fear of anxiety symptoms can create more anxiety in the future. They become their own self-sustaining cycle. So even justifiable anxiety can lead to unprompted anxiety.
Recommended Reading: Does Celine Dion Have An Eating Disorder
When Asthma Treatment Triggers More Anxiety
With persistent asthma, you have symptoms more than twice a week. Treating persistent asthma requires long-term maintenance therapy, such as an inhaled steroid, plus rescue therapy when something triggers symptoms. And when your symptoms are out of control , prednisone for asthma might be necessary for a few days. The problem is that prednisone often causes mood swings as a side effect, adding fuel to your anxiety.
Remember, prednisone is a short-term treatment for most people with asthma. After you finish taking the âburstâ of oral steroids, your mood will return to normal. Inhaled steroids donât cause permanent mood changes.
If your long-term asthma medication doesnât work well, and wheezing and chest tightness occur too often, a vicious circle can begin where anxiety worsens asthma, and asthma worsens anxiety. Thatâs when you need to talk to your doctor about your symptoms, triggers, and stress. Also discuss other asthma treatment options that can get asthma under control again, so you can prevent symptoms of asthma.
Poor Control Of Asthma Is Coupled With Increased Anxiety Symptoms
Poor control of asthma has been associated with increased anxiety and depressive symptoms. Alarmingly, poorly controlled asthmatics also appear more likely to smoke, which will further functional impairment and worsen asthma symptoms. Large surveys have found that symptoms of anxiety may occur twice as often in asthmatics compared to patients without asthma. However, these studies did not account for how well asthma can be controlled.
You May Like: What Is The Phobia For Bees
Close Your Eyes And Focus On Relaxing
Learn how to ground yourself by closing your eyes to the world around you and fully relaxing your muscles. While you relax each muscle individually, think about your happiest place, person, or moment. This draws you away from the problem or situation that instigated your panic. You can also ground yourself by focusing on a tangible, nearby object.
Read Also: How To Tell If You Have Asthma
Anxiety Does Not Cause Asthma

Some people worry that anxiety causes asthma. There is currently no evidence that anxiety can create asthma in those that did not originally have the condition. But there is a great deal of evidence that anxiety can worsen existing asthma symptoms.
The most likely reasons for why anxiety exacerbates asthma symptoms include:
- Hyperventilation Anxiety changes breathing habits. Many studies have shown that hyperventilation, whether it’s caused by a disorder or no disorder at all, appears to increase the likelihood of an asthma attack. So those with anxiety that may be more prone to hyperventilating may be unintentionally forcing their own attack symptoms.
- Inflammation Stress can lead to inflammation. Asthma is the inflammation of airways. It’s unlikely that stress causes the inflammation that leads to asthma, but it’s possible that stress makes it harder to control inflammation when your asthma symptoms are acting up.
- General Physiological Changes On a physical level, stress does cause some issues that may contribute to asthma. For example, anxiety can release an excess of histamine that can lead to asthma attacks. Stress may also weaken your immune system in such a way that you become more vulnerable to viruses and external asthma triggers.
- Muscle Constriction Muscle constriction is also very common with anxiety. Muscle constriction can lead to tighter chest and other issues that may trigger asthma.
Also Check: Where Are Bipolar Neurons Found
Stress Test And Cortisol Collection At Age 16 Years
At age 16 years, 715 adolescents performed a stress test, based on the Trier Social Stress Task . The stress test consisted of two parts. In the first part, the adolescents were instructed to prepare a 6-min speech about themselves and their lives and deliver this speech in front of a video camera. The speech was followed by a 3-min interlude in which the adolescents were not allowed to speak. In the second part, adolescents were asked to perform a 6-min mental arithmetic task. The adolescents were instructed to repeatedly subtract the number 17 from a larger sum, starting with 13 287. The mental arithmetic task was followed by a 3-min period of silence, after which the adolescents were debriefed about the experiment. Adolescents with a high risk of mental health problems were over-represented in this population .
Cortisol was assessed from saliva collected prior to the stress test , directly after , and 20 minutes and 40 minutes after the stress test . Non-responders did not differ from responders in terms of sex; non-responders were slightly older .