Can Someone With Schizophrenia Live A Normal Life
While schizophrenia cannot be cured, with the right treatment plan many people with schizophrenia can live relatively normal lives outside of a healthcare setting. The treatment must be ongoing for the person with schizophrenia to continue to live a productive, fulfilling life, including maintaining a job or socializing with friends and family.
Schizophrenia: Old Wine In New Bottles And New Wine In Old Bottles
As commonly acknowledged, schizophrenia is characterized by an immense variability in individuals clinical expression and experiences. Further, it is clear that causal factors are complex and numerous. To address the problem of heterogeneity across patients, we further propose that generic sex and gender differences influence the clinical expression, risk, treatment, and outcome of schizophrenia . There are no sex differences unique to schizophrenia or explicitly pointing to other disorders. Men and women have the same core experience, namely disruption of the self, but express such experiences differently as they might be influenced by sex and gender roles that are transdiagnostic in their importance. The term transdiagnostic in this manuscript refers to research and theory that crosses traditional psychiatric diagnoses as represented in DSM-5 and focuses on common between diagnoses functions such as affect and cognition . To be clear, sex and gender are complex concepts encompassing a broad range of biopsychosocial processes, perhaps best characterized by the description of gender is the social meaning of sex embedded in social practices .
Emanuel Schwarz, … Sabine Bahn, in, 2011
What Is Schizoaffective Disorder
People with schizoaffective disorder typically show symptoms of a mood disorder, such as mania or depression, alongside schizophrenia symptoms.
In the past, the process of diagnosing schizoaffective disorder may have been imprecise. Today, there is a distinction between having schizophrenia and mood episodes and having schizoaffective disorder.
Because the symptoms can overlap, it is not always clear whether a person has bipolar disorder or depression with psychotic features, post-traumatic stress disorder , or a schizophrenia-like illness, such as schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder.
What Are The Early Signs Of Schizophrenia
The most common early signs of schizophrenia may include social withdrawal, depression, hostility, oversleeping or insomnia, inability to cry or express joy, and deterioration of personal hygiene. The early stage of the schizophrenia is called the prodromal phase. It is difficult to diagnose schizophrenia during this early stage, as these symptoms could result from a number of other problems.
Schizophrenia Research And Statistics

The exact prevalence of schizophrenia is hard to measures, but the NIMH estimates that schizophrenia affects between 0.25 and 0.64 percent of U.S. adults, while the NAMI has put it closer to 1 percent.
Men typically start to show symptoms of schizophrenia in their late teens or early twenties. Women tend to show symptoms a bit later, usually in their late twenties or early thirties.
Men are about 1.4 times more likely to be diagnosed with schizophrenia than women.
Schizophrenia can occur at any age, but it’s less commonly diagnosed for the first time in a person older than 40 or younger than 12.
What Kind Of Symptoms Might People With Schizophrenia Have
People with schizophrenia may have a number of psychotic symptoms. These symptoms can come and go in phases, or they can happen only once or twice in a lifetime. When the illness begins, psychotic symptoms are usually sudden and severe.
During psychotic phases, the person may still understand parts of reality. He or she may lead a somewhat normal life, doing basic activities such as eating, working and getting around. In other cases, the person may be unable to function. Symptoms during psychotic phases include:
- Seeing, hearing, feeling or smelling things that are not real .
- Having strange beliefs that are not based on facts . For example, the person may believe that people can hear his or her thoughts, that he or she is God or the devil, or that people are putting thoughts into his or her head.
- Thinking in a confused way, being unable to make order out of the world, shifting quickly from one thought to the next.
- Having emotions, thoughts and moods that do not fit with events.
People with schizophrenia also may:
- Have a lot of energy or be overly active, or become “catatonic,” a state in which the body becomes rigid and cannot be moved.
- Talk in sentences that do not make sense.
- Not wash or groom.
- Cut themselves off from family, friends and the outside world.
- Be unable to function in school, work, or other activities.
- Lose interest in life.
- Be very sad or have mood swings.
- Have dulled emotions.
Whats The Outlook For An Individual With Schizophrenia
The challenges facing people with schizophrenia are plentiful and often severe. But with proper treatment, some of the more severe symptoms, such as hallucinations and delusions, may be made more manageable.
Lifelong treatment is necessary and medication needs may change through the years. Dosages may have to be adjusted and certain medications may need to be changed, added, or subtracted, depending on how the individual responds.
A study in the journal Revista Colombiana de Psiquiatria suggests that about one in seven people with schizophrenia can achieve functional recovery. With no cure in sight, that means the majority of people with schizophrenia will have to deal with symptoms for the rest of their lives.
Schizophrenia should be considered a treatable disease, though the effectiveness of treatment can vary dramatically from one person to the next. Access to proper healthcare is essential, as is commitment to a treatment regimen.
Individuals who are reluctant or unable to take their medications regularly and follow through on other components of their treatment may need a family member or health aide to assist them. The severity of schizophrenia also varies, so expectations of symptom management and quality of life need to be tempered based on the nature of the individuals condition.
When To See A Doctor
As schizophrenia usually develops gradually, it can be difficult to pinpoint when changes in behavior start or know whether they are something to worry about. Identifying that you are experiencing a pattern of concerning behaviors can be a sign you should consult with a professional.
Symptoms may intensify in the run-up to an acute episode of psychosis in schizophrenia. The warning signs include:
- A worrying drop in grades or job performance
- New difficulty thinking clearly or concentrating
- Suspiciousness of or uneasiness with others
- Withdrawing socially, spending a lot more time alone than usual
- Unusual, overly intense new ideas, strange feelings, or having no feelings at all
- Decline in self-care or personal hygiene
- Difficulty telling reality from fantasy
- Confused speech or trouble communicating
While these changes might not be concerning by themselves, if you or a loved one are experiencing a number of these symptoms, you should contact a mental health professional. It can be difficult for those with schizophrenia to want to get help, especially if they are experiencing symptoms such as paranoia.
If you or your loved one is thinking of or talking about harming themselves, contact someone who can help right away. You can call the toll-free, 24-hour National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 800-237-8255.
If you require immediate emergency care, call 911 for emergency services or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
What Are The Treatments For Schizophrenia
Ninety-nine percent of patients with schizophrenia need lifelong treatment with antipsychotic drugs, counseling and social rehabilitation, says Dr. Bowers.
This will reduce their symptoms and help them get to a place of stability in their lives, she says.
Antipsychotics are given orally or by injection. Depending on the type of schizophrenia, other medications may be needed as well:
- People with paranoid schizophrenia usually respond well to antipsychotics, which decrease paranoid thinking and help them readjust to their environment.
- People with catatonic schizophrenia require benzodiazepines to relax their muscles, allowing them to become more active and to react to the environment.
- People with undifferentiated schizophrenia are slower to respond to antipsychotics because thinking is disturbed across the board. The medication makes them more alert and able to care for themselves, but it doesnt always clear their thinking, she says.
- People with schizoaffective disorder require a combination of antipsychotics and antidepressants or mood stabilizers.
Despite significant side effects, its important to keep taking these medications.
When people go on and off their meds, their symptoms return, and they often end up back in the hospital, says Dr. Bowers. Also, the more episodes you have, the further you get from your healthy baseline.
Can Schizophrenia Be Cured
Schizophrenia affects an estimated 0.25 to 0.64 percent of the U.S. population, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. But despite years of research, scientists have yet to come up with a cure for schizophrenia or a way to prevent it.
Great advances have been made, however, in the treatment and understanding of this serious mental illness.
Can Schizophrenia Be Treated
Yes. The main types of treatment are counseling and medicines to lessen or stop psychotic symptoms. Medicines will control psychotic symptoms in most people. In milder cases of schizophrenia, medications may not be needed. Medicines can:
- Lessen or stop hallucinations
- Help the person tell the difference between hallucinations and the real world
- Lessen or stop false beliefs
- Lessen feelings of confusion
- Help the person think more clearly
Lessening of these symptoms can help the person resume his or her normal lifestyle and activities. Medicines for schizophrenia need to be taken regularly, even after symptoms are gone. Some people with schizophrenia will stop taking their medicine because they believe the medicine is no longer needed, or they dislike the medication’s side effects. Psychotic symptoms often return when medication is stopped. Do not stop taking medicine without the advice of your healthcare provider.
Discuss any concerns you have about side effects with your healthcare provider.
Other Considerations In Diagnosing Schizophrenia
The DSM-5 includes other things that can help determine schizophrenia. Theyre not necessary diagnostic criteria, but their presence points to this serious mental illness.
- Inability to understand someones intentions
- Thinking insignificant things are highly, personally meaningful
- Manic behavior
In addition to these, people with schizophrenia often experience what is known as neurological soft sign, subtle abnormalities that arent severe enough to fit into any disorder but are problematic and indicative of a bigger problem, like schizophrenia. They can include:
- Coordination problems
- Left-right confusion
- Difficulty with complex movement
To diagnose schizophrenia, professionals examine all of the symptoms and features that are present . They also must look at what is not present.
Who Is Schizophrenia This Quiz For

Below is a list of 10 questions designed for people who are concerned about schizophrenia. Read each question carefully, and indicate how often you have experienced the same or similar challenges.
If you have any been struggling for a month or more and those struggles have caused difficulties in functioning for the past six months, let your doctor know. This interactive quiz has been structured in a manner to allow for a short and simple self-assessment. The questions relate to life experiences common among people who have been diagnosed with schizophrenia and are based on criteria in the DSM-5.
To learn more about the causes, symptoms, and treatment of schizophrenia, read Psycoms comprehensive overview article.
Hope For The Patient And Family
A diagnosis of schizophrenia is life-changing for those affected and everyone who loves them. But, with hard work and dedication, you can help your loved one enjoy a meaningful life.
People with schizophrenia can finish college, work jobs, get married, have families and enjoy a reasonably healthy life, stresses Dr. Bowers.
But it requires a combination of good medication, supportive counseling and being connected to community resources.
The National Alliance on Mental Illness offers support groups for the mentally ill and their families. And organizations like Recovery International and Emotions Anonymous are excellent resources for patients, she says.
Iischizophrenia And Neurocognitive Impairment: A Challenge For Drug Development
The diagnosis of schizophrenia requires the presence of positive symptoms , negative symptoms , and social/occupational dysfunction over a period of time, as defined by the DSM . Dozens of studies have also identified neurocognitive impairment as a core component of the disorder, characterized by deficits in global cognition, problem solving, and learning and memory. Despite decades of clinical trials leading to the development of dozens of antipsychotics that can be effective in treating positive and negative symptoms, there is little evidence that these agents can modulate neurocognitive impairment in an enduring, meaningful way. This limitation presents a significant obstacle for treatment as neurocognitive impairment in schizophrenia is linked to functional disability and poor outcomes. Fortunately, many groups have identified and validated neurophysiological biomarkers, discussed in the succeeding text, which show great promise in aiding development of procognitive agents aimed at targeting neurocognitive impairment in schizophrenia.
Jeffrey M. Lyness, in, 2012
Why Does Schizophrenia Happen
The exact cause of schizophrenia is unknown. However, most experts believe the condition is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
It is thought certain things make you more vulnerable to developing schizophrenia, and certain situations can trigger the condition.
Read more about the causes of schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia Diagnosis: Rule Out Other Conditions
A diagnosis involves what someone is experiencing as well as what he is not. Some disorders have some features or symptoms that are shared with schizophrenia; therefore, doctors check to see if something else fits better than schizophrenia. Some of the conditions that, according to criteria in the DSM-5, have some similarities with schizophrenia are
- Mood disorders with psychotic features
- Schizophreniform
The Most Common Early Warning Signs Include:
While these warning signs can result from a number of problemsnot just schizophreniathey are cause for concern. When out-of-the-ordinary behavior is causing problems in your life or the life of a loved one, seek medical advice. If schizophrenia or another mental problem is the cause, getting treatment early will help.
Schizophrenia: The 7 Keys To Self
Seek social support. Friends and family vital to helping you get the right treatment and keeping your symptoms under control. Regularly connecting with others face-to-face is also the most effective way to calm your nervous system and relieve stress. Stay involved with others by continuing your work or education. If thats not possible, consider volunteering, joining a schizophrenia support group, or taking a class or joining a club to spend time with people who have common interests. As well as keeping you socially connected, it can help you feel good about yourself.
Manage stress. High levels of stress are believed to trigger schizophrenic episodes by increasing the bodys production of the hormone cortisol. As well as staying socially connected, there are plenty of steps you can take to reduce your stress levels. Try adopting a regular relaxation practice such as yoga, deep breathing, or meditation.
Get regular exercise. As well as all the emotional and physical benefits, exercise may help reduce symptoms of schizophrenia, improve your focus and energy, and help you feel calmer. Aim for 30 minutes of activity on most days, or if its easier, three 10-minute sessions. Try rhythmic exercise that engages both your arms and legs, such as walking, running, swimming, or dancing.
Helping A Suicidal Friend Or Relative
If you see any of these warning signs:
- get professional help for the person, such as from a crisis resolution team or the duty psychiatrist at your local A&E department
- let them know they are not alone and you care about them
- offer your support in finding other solutions to their problems
If you feel there is an immediate danger of the person committing suicide, stay with them or have someone else stay with them. Remove all available means of suicide, such as sharp objects and medication.
Want to know more?
Articles On Schizophrenia Overview
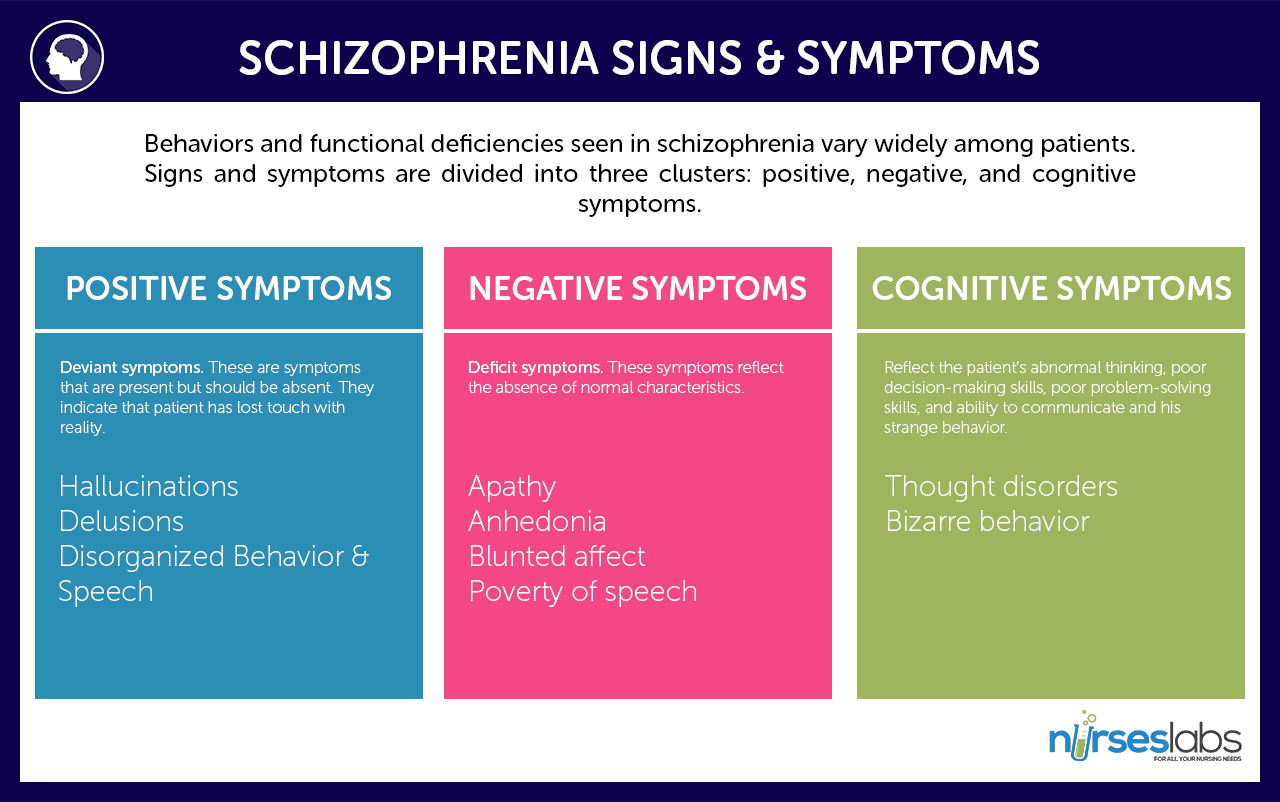
To get an official diagnosis of schizophrenia, a person has to show at least two of the following symptoms most of the time for a month, and some mental disturbance over 6 months:
- Delusions
- Hallucinations
- Disorganized speech and behavior
- Catatonic or coma-like daze
- Bizarre or hyperactive behavior
Making A Final Diagnosis
Doctors follow set guidelines to determine if someone has . The latest recommendations from mental health experts on how to diagnose this disease say that someone with schizophrenia:
- Must have at least two of the major symptoms
- Must have had symptoms for at least six months
- Must have had active symptoms for at least one full month
- Has had other possible causes for ruled out
Right now, observing symptoms is the only way to diagnose schizophrenia. Research is being done to find other ways. These may include brain scans or blood tests.
What About Remission Or Functional Recovery From Schizophrenia
Like some other types of mental illness, schizophrenia symptoms can sometimes wax and wane throughout a persons life. An individual may have an intense schizophrenic episode and go for months or years with little or no issue related to the disease. In most cases, however, even people receiving effective and consistent treatment must contend with at least some consequences of the disease.
But with a combination of medications, psychosocial therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, functional recovery and functional well-being are realistic goals for people with schizophrenia. Though an exact picture of what functional recovery looks like is still somewhat debated among clinicians, a survey of mental health experts reported in BMC Psychiatry suggests that functional recovery involves concepts such as:
- quality of life
- symptom management or remission
- maintaining social relationships
The goal of functional recovery is not just that serious symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions are held in check, but that an individual can live, work, and have positive family relationships and friendships, as well as live independently or with minimal assistance.
Recognizing The Symptoms Of Schizophrenia Early
Finding schizophrenia in its early stages can be a difficult task, but with proper help, catching it early can better the chances of getting well and staying well. The symptoms are similar between teenagers and adults, but it can be hard to acknowledge the signs in a teen because some of the early onset symptoms are similar to typical development during teen years. This includes; lack of motivation, irritability, depression, withdrawal from friends and family, and a drop in performance at school. Another reason that it is hard to diagnose schizophrenia in teens is that they do not experience delusions or hallucinations as frequently as adults.
Tests Used To Diagnose Schizophrenia
The doctor may also want to do a urine or blood test to make sure that alcohol or drug abuse isnât causing the symptoms.
Tests that scan and make pictures of the body and brain, like magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography , might also help rule out other problems, like a brain tumor.
Theyâll also do tests to measure how much the person understands , personality tests, and open-ended tests like the inkblot test .
Getting the diagnosis as early as possible will improve your loved oneâs chances of managing the illness. If they get the proper care, which will probably include medication and psychotherapy, a kind of talk therapy, they are likely to do better.
American Psychiatric Association, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fourth edition, text revision , American Psychiatric Association, 2000.
Keith, S. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 1991.
Andreasen, N. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 1991.
National Alliance on Mental Illness: âSchizophrenia.â
Mayo Clinic: âSchizophrenia, tests and diagnosis.â
Lack Of Emotional Expressions
A characteristic symptom of schizophrenia is a lack of emotional expression. People with this condition may show little or no reactions to good or bad news.
They also begin to show fewer facial expressions and gestures when they talk. Their voice may become flat when they speak.
Interestingly, suggests that while they appear to have a wooden expression, what they express outward may not be the same as what they feel inside.
Sometimes, they can have unexplained and seemingly inappropriate reactions to things, like overwhelming anger or inappropriate laughter.
Rehabilitation Programs And Community Support Activities
Rehabilitation and support programs, such as on-the-job coaching, are directed at teaching people the skills they need to live in the community, rather than in an institution. These skills enable people with schizophrenia to work, shop, care for themselves, manage a household, and get along with others.
Community support services provide services that enable people with schizophrenia to live as independently as possible. These services include a supervised apartment or group home where a staff member is present to ensure that a person with schizophrenia takes drugs as prescribed or to help the person with finances. Or a staff member may visit the person’s home periodically.
Hospitalization may be needed during severe relapses, and involuntary hospitalization may be needed if people pose a danger to themselves or others. However, the general goal is to have people live in the community.
A few people with schizophrenia are unable to live independently, either because they have severe, persistent symptoms or because drug therapy has not been effective. They usually require full-time care in a safe and supportive setting.
Support and advocacy groups, such as the National Alliance on Mental Illness, are often helpful to families.
First Episode Of Psychosis
The first episode of psychosis refers to when you first show signs of being unable to distinguish whats real from what isnt. It typically involves hallucinations and delusions, which can seem very real to the person experiencing them.
Experts say the average age at which people first experience psychosis is 24 years old. The oldest age of onset was 63 years and the youngest age was 3 years.
Acting quickly to connect yourself or your loved one with the right treatment during early psychosis can help dramatically. If you are a family member or friend, consider reaching out to a healthcare professional on behalf of the person you care about.
Frequently Asked Questions About Schizophrenia
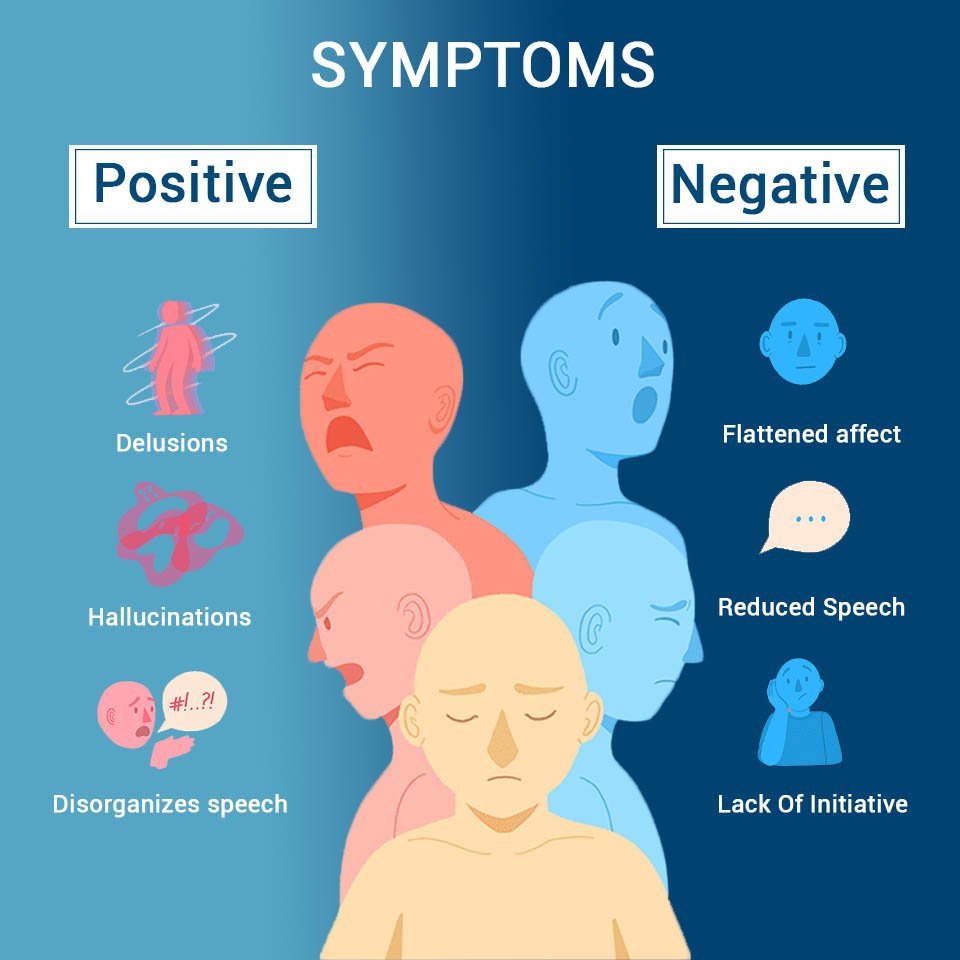
Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. People with schizophrenia may seem like they have lost touch with reality. Although schizophrenia is not as common as other mental disorders, the symptoms can be very disabling.
Schizophrenia is a severe and debilitating brain and behavior disorder affecting how one thinks, feels and acts. People with schizophrenia can have trouble distinguishing reality from fantasy, expressing and managing normal emotions and making decisions. Thought processes may also be disorganized and the motivation to engage in lifes activities may be blunted. Those with the condition may hear imaginary voices and believe others are reading their minds, controlling their thoughts or plotting to harm them.
While schizophrenia is a chronic disorder, it can be treated with medication, psychological and social treatments, substantially improving the lives of people with the condition.
A moving presentation by Dr. Kafui Dzirasa on Schizophrenia
View Webinar on Identifying Risk Factors and Protective Pathways for Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia affects men and women equally. It occurs at similar rates in all ethnic groups around the world. Symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions usually start between ages 16 and 30.
Learn more about childhood-onset schizophrenia from this expert researcher:
Find answers to more questions about Schizophrenia in our Ask the Expert section.
Functioning In Social And Professional Situations
When social and work functioning is impaired it may be helpful to consult with a doctor. Because the symptoms tend to develop over time you may not realize how long you have been experiencing trouble in these areas of your life. Noticing that a pattern has developed can be a signal to consult with a professional.
Section 1: Diagnosis And Classification Of Schizophrenia
Classification is the process of organising symptoms into categories based on which symptoms cluster together in sufferers. Psychologists use the DSM and ICD to diagnose a patient with schizophrenia.
Diagnosis refers to the assigning of a label of a disorder to a patient. The ICD-10 is used worldwide and the DSM-5 is used in America.
In order to diagnose Schizophrenia the Mental Health Profession developed the DSM still used today as a method of classifying mental disorders .
It is also used as a basis for the ICD used by the World Health Organisation in classifying all disorders .
Note: you may come across the terms DSM-IV and ICD-10. These refer to the latest editions of the two classification systems.