How Well Is Social Anxiety Disorder Recognised
Recognition of social anxiety disorder in adults, children and young people by general practitioners is often poor. The problem of under-recognition for anxiety disorders in general has recently been highlighted by evidence that the prevalence of PTSD is significantly under-recognised in primary care . In part this may stem from GPs not identifying the disorder, a general lack of understanding about its severity and complexity, and a lack of clearly defined care pathways. But it may also stem from service users’ lack of knowledge of its existence, their avoidance of talking about the problem and stigma.
The early age of onset and effects on educational achievement mean that recognition of social anxiety disorders in educational settings is also an issue. As well as underachieving, children with social anxiety disorder may be particularly likely to be the targets of bullying and teasing. Teachers and other educational professionals may have limited knowledge of how to recognise and oversee the management of the condition.
In primary care many service users report being misdiagnosed as having pure major depression. Missing the diagnosis may also occur in secondary care if an adequate history has not been taken. This is a serious omission because having a comorbidity has treatment and outcome implications.
Stats That Prove Social Anxiety Needs To Be Taken Seriously
Social anxiety disorder is more than a fleeting feeling of shyness. Its a mental illness that can disrupt the regular flow of life, making everyday tasks and responsibilities seem impossible.
When someone has social anxiety, they can experience it so severely that it inhibits their pursuit of life goals, prevents them from forming relationships, pursuing career or school, being assertive, or being in public places, explains Larry Cohen, chair of the National Social Anxiety Center.
People with social anxiety often suffer in silence, their behavioral and emotional symptoms not apparent to friends and family. As the number of young adults with social anxiety continues to increase, mental health experts are trying to help dispel the notion that social anxiety is as simple to overcome as shyness.
Here are some numbers to help you understand the full scope of social anxiety disorder the number of American adults diagnosed, the number of symptoms and more.
Getting Plenty Of Sleep
Getting at least eight hours of sleep per night is recommended. Lack of sleep can increase anxiety and worsen symptoms of social phobia.
Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications that treat anxiety and depression if your condition doesnt improve with therapy and lifestyle changes. These medications do not cure social anxiety disorder. However, they can improve your symptoms and help you function in your daily life. It can take up to three months for medication to improve your symptoms.
Medications approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat social anxiety disorder include Paxil, Zoloft, and Effexor XR. Your healthcare provider may start you with a low dose of medication and gradually increase your prescription to avoid side effects.
Common side effects of these medications include:
- insomnia
- upset stomach
- lack of sexual desire
Talk to your health care provider about the benefits and risks to decide which treatment is right for you.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Genetic Causes Of Social Anxiety Disorder
People with a parent or parents whove suffered from social anxiety disorder have a 30-40 percent greater likelihood of developing the condition themselves. However, it is impossible to know how much of the parent-child social anxiety association is based on genetics and how much is based on parenting style, which is naturally affected by the presence of the disorder.
Recent research into specific genetic markers for social anxiety have focused on changes in a gene called SLCGA4, which is involved in the transport of the neurotransmitter serotonin, a chemical that can help soothe nerves and stabilize moods. Both shortages and excesses of serotonin have been linked to social anxiety symptoms, and people with social anxiety disorder struggle to produce serotonin consistently and without fluctuation.
Aberrations in the performance of the gene SLCGA4 appear to be linked to this problem, and these faulty genes can be passed from parents to children.
Negative Cognitions And Perceived Social Danger
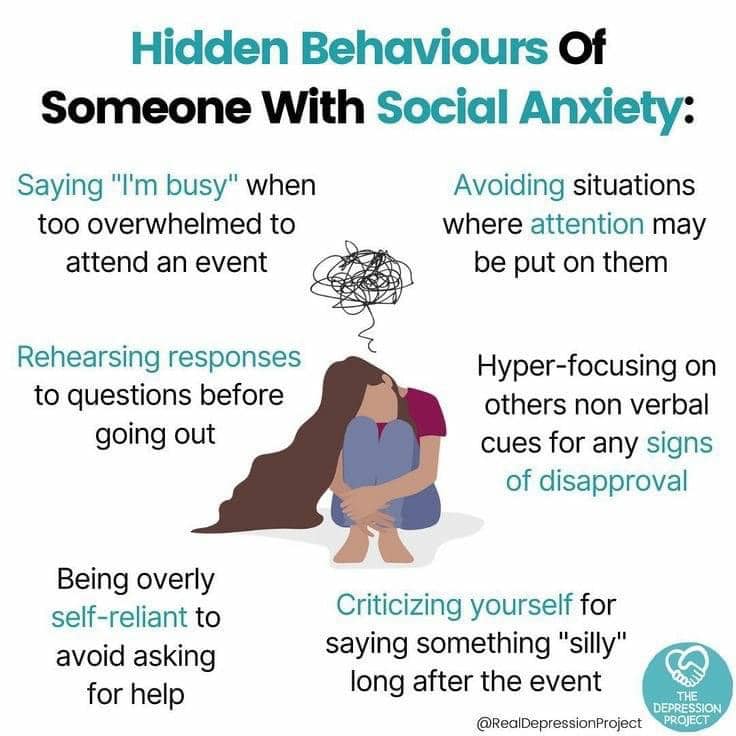
Negative Social Attitudes and Cognitions
Using a semi-structured interview methodology, Ranta et al. asked adolescents to identify a time when they had felt very socially anxious and to then recall the thoughts that they had during the experience. Those scoring higher on the Social Phobia Inventory recalled more negative thoughts than those scoring lower . Although the numbers of young people with clinical levels of SAD were small, the findings were similar when the authors compared those assigned a diagnosis of clinical or subclinical social anxiety disorder compared to those with no diagnosis of SAD . Negative thoughts recalled by all participants were most commonly self-focused rather than focused on other people or the interaction. In another study comparing a sample of adolescents with social anxiety disorder with a group of healthy controls, Alfano et al. asked participants to engage in a role-play task. The authors found that not only did socially anxious youth make more negative predictions about their performance than controls , but they also went on to believe they performed less well than they had expected, whereas control participants did not draw negative conclusions about their performance . Negative self-talk was significantly more frequent in socially anxious adolescents compared to controls and compared to socially anxious children .
Negative Interpretation Bias
You May Like: Mdd Vs Bpd
Prevalence Of Social Anxiety Disorder Among Adults
- Based on diagnostic interview data from National Comorbidity Survey Replication , Figure 1 shows past year prevalence of social anxiety disorder among U.S. adults aged 18 or older.1
- An estimated 7.1% of U.S. adults had social anxiety disorder in the past year.
- Past year prevalence of social anxiety disorder among adults was higher for females than for males .
Figure 1
| Demographic |
|---|
| 3.1 |
Million Americans Suffer From Social Anxiety Disorder
The disorder leaves many isolated, ashamed and often misdiagnosed. Thirty-six percent of those with social anxiety disorder have symptoms for 10 years or more before seeking help, the Anxiety Disorders Association of America reports.
“Social anxiety disorder is when somebody has an intense, persistent and irrational fear of social or performance situations,” Jerilyn Ross, the association’s president and CEO, said during a teleconference Wednesday.
“The condition causes people to avoid common, everyday situations and even other people for fear of being judged or criticized or humiliated or embarrassing themselves,” Ross said.
Social anxiety disorder can interfere with daily routines and job performance, Ross noted. “It also makes it very difficult for people to develop friends and romantic partnerships,” she said.
People with this disorder recognize their fear is excessive and irrational, Ross noted. “But they feel powerless to do anything about it,” she said.
Social anxiety disorder can start in the early teens, Dr. Mark H. Pollack, director of the Center for Anxiety and Traumatic Stress Disorders and a professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, said during the teleconference.
“This is a disorder that starts affecting people early on,” Pollack said. “The typical age of onset is early adolescence, age 12 or 13, and many individuals report a history of anxiety dating back to earlier childhood.”
Among other key survey findings were:
More information
Don’t Miss: Can Dehydration Cause Panic Attacks
What Are The Symptoms Of Social Anxiety
You may have social anxiety if you have a combination of some of the following:
- worry about your performance and being judged by others when you are in social situations
- dread or avoid everyday activities, such as meeting strangers, starting conversations, speaking on the phone, catching public transport, or talking to shop assistants
- avoid or worry a lot about social activities, such as group conversations, eating with company, and going to parties
- worry about doing something in public that you think is embarrassing, such as blushing, sweating, or making some social error
- find it difficult to do things when others might be watching like eating, drinking, or writing
- often have symptoms such as feeling queasy, hot, sweating, trembling or a pounding heartbeat when anticipating or entering social situations
- have panic attacks panic attacks, where there is an overwhelming sense of fear and anxiety .
Some people with social anxiety may also have other mental health issues, such as depression, generalised anxiety disorder or body dysmorphic disorder.
Alternative And Complementary Therapies
Various herbal supplements have been studied as treatments for anxiety, with mixed results, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Supplements such as kava and valerian increase the risk of serious liver damage. Others, such as passionflower or theanine, may have a calming effect, but they’re often combined with other products, so their effectiveness on their own remains unclear. Talk to your doctor before taking any herbal remedies or supplements to make sure they’re safe for you and won’t interact with any medications you take.
Healthy lifestyle changes may help reduce the frequency of social anxiety attacks, including exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, and having regularly scheduled meals. Reducing or avoiding the use of caffeine, some over-the-counter cold medicines, and other stimulants may also be beneficial. Joining a support group may also reduce the stress of having social anxiety.
The following tips may also help you avoid triggering your social anxiety symptoms:
- Learn stress reduction skills
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet
- Socialize with people you feel comfortable being around
You May Like: Prodromal Stage Of Schizophrenia
When To Get Help For Social Anxiety
It’s a good idea to see a GP if you think you have social anxiety, especially if it’s having a big impact on your life.
It’s a common problem and there are treatments that can help.
Asking for help can be difficult, but a GP will be aware that many people struggle with social anxiety and will try to put you at ease.
They’ll ask you about your feelings, behaviours and symptoms to find out about your anxiety in social situations.
If they think you could have social anxiety, you’ll be referred to a mental health specialist to have a full assessment and talk about treatments.
You can also refer yourself directly to an NHS psychological therapies service without a referral from a GP.
What Fears Are Involved
With social phobia, a person’s fears and concerns are focused on their social performance whether it’s a major class presentation or small talk at the lockers.
People with social phobia tend to feel self-conscious and uncomfortable about being noticed or judged by others. They’re more sensitive to fears that they’ll be embarrassed, look foolish, make a mistake, or be criticized or laughed at. No one wants to go through these things. But most people don’t really spend much time worrying about it. The fear and anxiety are out of proportion to the situation.
You May Like: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
Researchers Reveal The Link Between Social Anxiety And Depression
Many people suffer from depression around the world as well. Scientists have recently discovered a link between social anxiety disorder and depression. Perhaps this can give those suffering a greater understanding of these disorders so they can learn to overcome them, or at least manage them, a bit better.
To give you an idea of the prevalence of these disorders, here are some statistics about both:
Social Anxiety Disorder
- According to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America, almost 50% of those diagnosed with depression are also diagnosed with an anxiety disorder.
- SAD affects 15 million adults, or 6.8% of the U.S. population.
- SAD occurs equally among men and women and onset is usually around age 13.
- According to a 2007 ADAA survey, 36% of people with social anxiety disorder have symptoms for 10 or more years before seeking help.
- SAD is the second most commonly diagnosed anxiety disorder following specific phobia.
- People with SAD have a higher risk of developing alcohol use disorders as well as major depressive disorder.
Depression
- Approximately 322 million people worldwide suffer from depression.
- Its the leading cause of disability in the U.S. for people aged 15 to 44.
- MDD is more common in women than men, and typical onset is around age 32.5.
- MDD affects more than 6.7% of the U.S. population, or 16.1 million American adults.
- While there are many different types of depression, MDD is the most common.
Statistical Methods And Measurement Caveats
National Comorbidity Survey Replication
Diagnostic Assessment and Population:
- The NCS-R is a nationally representative, face-to-face, household survey conducted between February 2001 and April 2003 with a response rate of 70.9%. DSM-IV mental disorders were assessed using a modified version of the fully structured World Health Organization Composite International Diagnostic Interview , a fully structured lay-administered diagnostic interview that generates both International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, and DSM-IV diagnoses. The DSM-IV criteria were used here. The Sheehan Disability Scale assessed disability in work role performance, household maintenance, social life, and intimate relationships on a 0â10 scale. Participants for the main interview totaled 9,282 English-speaking, non-institutionalized, civilian respondents. The NCS-R was led by Harvard University.
Survey Non-response:
- In 2001-2002, non-response was 29.1% of primary respondents and 19.6% of secondary respondents.
- Reasons for non-response to interviewing include: refusal to participate respondent was reluctant- too busy but did not refuse circumstantial, such as intellectual developmental disability or overseas work assignment and household units that were never contacted .
- For more information, see NIMH NCS-R study page.
National Comorbidity Survey Adolescent Supplement
Diagnostic Assessment and Population:
Survey Non-response:
Also Check: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
Statistics On Anxiety Treatment
While anxiety disorders are fairly common across the globe, not everyone who needs treatment receives it. Statistics on thetreatment of anxietyshow that around one-third of people with an anxiety disorder get treatment, according to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America.
Fortunately, treatment for anxiety disorders is available and effective. These treatments may involve medication, counseling or a combination of the two. People with anxiety disorders can also benefit from cognitive behavioral therapy to help them replace irrational thoughts and fears with more productive, realistic thoughts.
If you or a loved one is suffering from a co-occurring anxiety disorder and substance abuse, The Recovery Village can provide comprehensive services to meet your needs. Reach out to an admissions representative today atto begin the treatment process.
- Sources
World Health Organization. Depression and other common mental disorders: Global health estimates. 2017. Accessed April 3, 2019.
Anxiety and Depression Association of America. Understand the facts.. Accessed April 3, 2019.
Complications Of Social Anxiety Disorder
People with social phobia are at high risk for alcohol or other drug use, because they may wind up relying on substances to relax in social situations.
Social anxiety disorder can also lead to loneliness and social isolation.
Without treatment, social anxiety disorder can interfere with work, school, relationships, and enjoyment of life, per the Mayo Clinic.
It can also cause:
- Low academic and employment achievement
- Suicide or suicide attempts
Also Check: Pristiq What Is It Used For
Tip : Learn To Control Your Breathing
Many changes happen in your body when you become anxious. One of the first changes is that you begin to breathe quickly. Overbreathing throws off the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your bodyleading to more physical symptoms of anxiety, such as dizziness, a feeling of suffocation, increased heart rate, and muscle tension.
Learning to slow your breathing down can help bring your physical symptoms of anxiety back under control. Practicing the following breathing exercise will help you stay calm:
- Sit comfortably with your back straight and your shoulders relaxed. Put one hand on your chest and the other on your stomach.
- Inhale slowly and deeply through your nose for 4 seconds. The hand on your stomach should rise, while the hand on your chest should move very little.
- Hold the breath for 2 seconds.
- Exhale slowly through your mouth for 6 seconds, pushing out at much air as you can. The hand on your stomach should move in as you exhale, but your other hand should move very little.
- Continue to breathe in through your nose and out through your mouth. Focus on keeping a slow and steady breathing pattern of 4-in, 2-hold, and 6-out.
How Common Is Social Phobia
- About 3.7% of the U.S. population ages 18 to 54 – approximately 5.3 million Americans – has social phobia in any given year.
- Social phobia occurs in women twice as often as in men, although a higher proportion of men seeks help for this disorder.
- The disorder typically begins in childhood or early adolescence and rarely develops after age 25.
Read Also: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
Defining Social Anxiety And Social Anxiety Disorder
Social anxiety can profoundly affect someones ability to socialize and communicate with other people. For those suffering from full-blown social anxiety disorder, which in any given year includes up to seven percent of the adult population, the symptoms of social anxiety can be overwhelming, debilitating, and beyond their ability to control.
* Intense fear of social interactions in a wide variety of contexts
* Anticipatory anxiety that leads social anxiety sufferers to avoid opportunities for conversation or public speaking
* Extreme symptoms of anxiety experienced during unwanted or stressful social interactions
* Poor verbal communication skills, complicated by a persons inability to think clearly while experiencing anxiety
* Overly critical self-evaluations of performance after conversations or spoken presentations are finished
* Low self-esteem and a lack of self-confidence, which are reinforced by constant self-criticism
When not interacting with close friends or family, people with severe social anxiety have a deep-seated fear of being judged, rejected, embarrassed or humiliated during social interactions. As irrational as those fears may be, they are difficult to escape.