How Can I Help My Child Live With Ocd
OCD can be treated, often with a combination of one-on-one therapy and medicines. You play a key supportive role in your childs treatment. Here are things you can do to help your child:
-
Keep all appointments with your childs healthcare provider.
-
Talk with your childs healthcare provider about other providers who will be included in your childs care. Your child may get care from a team that may include counselors, therapists, social workers, psychologists, and psychiatrists. Your childs care team will depend on your childs needs and how serious the OCD is.
-
Keep strong and open lines of communication with your child. Children with OCD can feel embarrassed about their disorder.
-
Tell others about your childs disorder. Work with your childs healthcare provider and school to create a treatment plan.
-
Reach out for support from local community services. Being in touch with other parents who have a child with OCD may be helpful.
Types Of Anxiety Disorders
Many of the feelings or experiences listed above are symptoms of Generalized Anxiety Disorder , but some can be signs of related disorders, as well. For example, Panic Disorder is when a person suffers from recurrent panic attacks, while a phobia is a fear of a specific thing, like heights, performance situations, enclosed spaces or being outside the home alone.
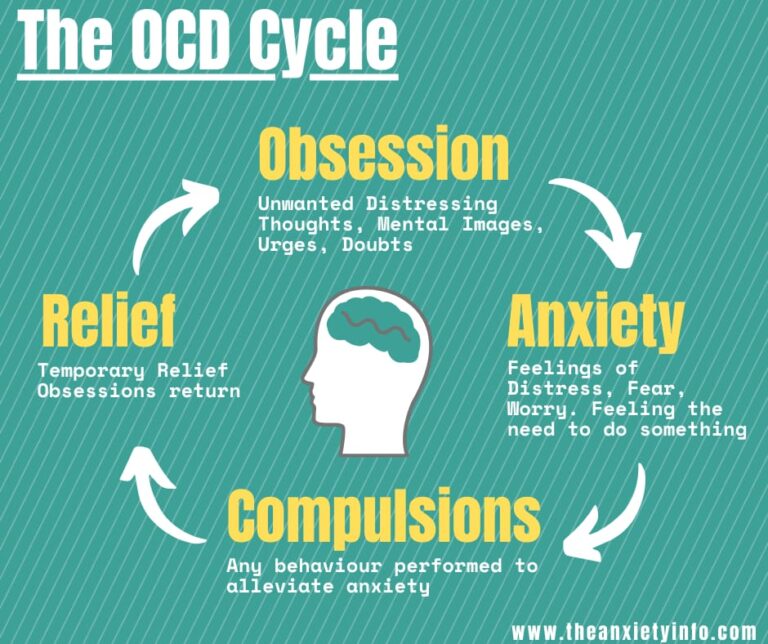
Another common diagnosis is Obsessive Compulsive Disorder , an anxiety disorder characterized by constant unwanted thoughts and fears, and repetitive behaviors that momentarily ease those fears before bringing them back even stronger.
While many common compulsions of OCD sufferers are well-known , many people who suffer from OCD will experience compulsions related only to their own worries and fears. For example, someone who has obsessive thoughts about a loved ones death may find themselves repeatedly checking that the loved one is still alive. Meanwhile, a person who has obsessive fears of losing something they need may hoard unnecessary items and even junk.
Luckily, all of these anxiety disorders are treatable. You dont have to let your worries, fears, phobias or compulsions be in charge anymore.
Can Someone With Ocd Fall In Love
If you have obsessive-compulsive disorder , you know that your symptoms can often get in the way of establishing and maintaining romantic relationships. Indeed, many individuals with OCD are single, and those who are in a relationship or married often report a significant amount of relationship stress.
You May Like: How To Get Motivated To Exercise When Depressed
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- What is causing my OCD?
- What is the best treatment for me?
- Should I go into therapy?
- Should I see a psychiatrist or psychologist?
- Am I more likely to have depression or other mental health issues?
- How can I best deal with my compulsions?
- Will a medicine help?
- Will I have to take medicine and be in therapy the rest of my life?
- Is there anything I can do to help myself at home?
What’s It Like To Live With Ocd
Although many people experience minor obsessions and compulsions , these don’t significantly interfere with daily life, or are short-lived.
If you experience OCD, it’s likely that your obsessions and compulsions will have a big impact on how you live your life:
- Disruption to your day-to-day life. Repeating compulsions can take up a lot of time, and you might avoid certain situations that trigger your OCD. This can mean that you’re not able to go to work, see family and friends, eat out or even go outside. Obsessive thoughts can make it hard to concentrate and leave you feeling exhausted.
- Impact on your relationships. You may feel that you have to hide your OCD from people close to you or your doubts and anxieties about a relationship may make it too difficult to continue.
- Feeling ashamed or lonely. You may feel ashamed of your obsessive thoughts, or worry that they can’t be treated. You might want to hide this part of you from other people, and find it hard to be around people or to go outside. This can make you feel isolated and lonely.
- Feeling anxious. You may find that your obsessions and compulsions are making you feel anxious and stressed. For example, some people feel that they have to carry out their compulsions so frequently that they have little control over them. You can read more about anxiety here.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Motivated To Exercise When You’re Depressed
Common Symptoms Of Illness Anxiety Disorder
People with Illness Anxiety Disorder may have the following symptoms:
- Excessive worry about having a severe physical disease.
- Preoccupation with bodily functions, sensations, or performance.
- Obsessive rumination with intrusive thoughts about condition.
- Ideas and fears of having an illness that cannot be easily stopped.
- Extreme suggestibility, for example a person may become alarmed at the slightest hint of illness, or even from reading about a disease, knowing someone who becomes sick, etc.
- Obsessions with medical information. For example, the person may read medical books or journals, watch television programs about health or medicine, be preoccupied in news about health, etc.
- Unrealistic fears of being infected or contaminated by something touched, something eaten, or contact with another person.
- Excessive health-preserving behavior, for example eating only certain health food , intensive exercise, or overdoing things to keep fit.
- Over-focus on the possible cause of symptoms. For example the patient needs an explanation for the symptoms and is more concerned about the meaning of the symptoms than the distress they cause.
- Fear of taking prescribed medication.
Whats Normal And Whats Not
Everybody worries at times. Its normal to worry about things like school, how you look, what you said or did in a certain situation, how your parents will react to something you did, or what the future will bring. But OCD takes worries and doubts to the extreme.
For example, most people have thoughts about others spreading germs or doubts about whether they locked their front door. Usually these thoughts crop up and then disappear. But if they keep returning and cause you a lot of anxiety if you dont wash your hands or repeatedly check the front door, it could be OCD.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Is A Type Of Anxiety Disorder Characterized By Intrusive And Frequent Obsessions And Repetitive And Ritualistic Behaviors
Individuals with obsessive compulsive disorder can describe feeling driven to do things with an irresistible urge in order to relieve stress and feel better. For those with this condition, ignoring these urges is not easy, and if they can manage, the urge will come back again later. For those with a fear of being infected by germs, it can be common to adopt a handwashing ritual that results in chapped or sore skin, and the condition is often accompanied by shame or other feelings of embarrassment related to the symptoms of the condition.
How Is Ocd Diagnosed In A Child
A child psychiatrist or other mental health expert can diagnose OCD. He or she will do a mental health evaluation of your child. To be diagnosed with OCD, your child must have obsessions and compulsions that are continuous, severe, and disruptive. They must harm your childs day-to-day living.
In most cases, the activities of OCD such as handwashing or checking the locks on doors use up more than 1 hour each day. They also cause mental health distress and affect how your child thinks. In most cases, adults realize that their actions are not normal to some degree. But often children can’t see that their behavior is irrational and abnormal.
Don’t Miss: Phobia Suffix
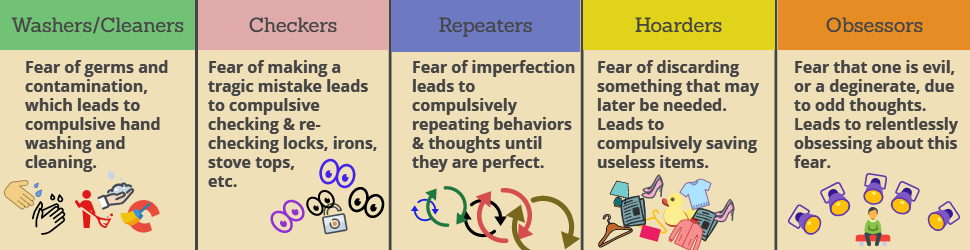
The Many Different Types Of Ocd
Even in a modern society thats far more advanced and progressive when it comes to categorizing mental and anxiety disorders, there still remains a lot of work to be done on examining the different types of obsessive compulsive disorder.
And while there surely are many more types of this disorder that have yet to be categorized, specialists generally lump cases of OCD types into six separate categories:
- Checking
- Ruminations
- Intrusive Thoughts
Although these categories of OCD can be helpful in designating symptoms, risks, and treatment plans, it is not uncommon for sufferers to present symptoms from multiple types of OCD.
Whats more, research into mental illnesses is and will likely always be a work in progress. Its worth mentioning, then, that this list is in no way the be-all and end-all authority on the types of obsessive compulsive disorder.
As such, more types of OCD may still be out there and may remain undiscovered and uncategorized for years. The science on mental health is always changing.
While there may not be a definitive types of OCD test, the Anxiety and Depression Association of America does offer an OCD test that helps you recognize and mark off a variety of types of obsessive-compulsive behaviors to help you and your physician diagnose the problem.
A number of the most beneficial types of OCD tests available are listed below.
As such, be sure to speak with a licensed physician before self-diagnosing and jumping to any drastic conclusions.
The Failure To Recognize Distinct Symptoms Points To Just How Poorly Ocd Is Understood
It says something about the public mood that part of the opposition to the change in the DSM-5 came from OCD groups. They were concerned that removing OCD from the anxiety disorder section would add to the stigma. But fighting stigma comes from better understanding, not from disguising one illness as another and that is still an uphill battle. At the moment, its shocking how little is known about OCD.
Part of the problem is that while OCD is one of the more common mental illnesses, its still occurs less frequently than anxiety disorders. While this says nothing about the seriousness of either, one of the effects is that OCD lags behind in the conversation about mental illness. This has consequences because as an illness gets ignored, so do patients. The tragedy is that we have an excellent idea of how to reduce OCD symptoms, but only if we understand what the illness is and how to treat it. Like your poor co-worker, its not too late to ask her name.
Related:
Read Also: What Is A Depression On A Map
Tip : Make Lifestyle Changes To Ease Ocd
A healthy, balanced lifestyle plays a big role in easing anxiety and keeping OCD compulsions, fears, and worry at bay.
Exercise regularly.Exercise is a natural and effective anti-anxiety treatment that helps to control OCD symptoms by refocusing your mind when obsessive thoughts and compulsions arise. For maximum benefit, try to get 30 minutes or more of aerobic activity on most days. Ten minutes several times a day can be as effective as one longer period especially if you pay mindful attention to the movement process.
Get enough sleep. Not only can anxiety and worry cause insomnia, but a lack of sleep can also exacerbate anxious thoughts and feelings. When youre well rested, its much easier to keep your emotional balance, a key factor in coping with anxiety disorders such as OCD.
Avoid alcohol and nicotine. Alcohol temporarily reduces anxiety and worry, but it actually causes anxiety symptoms as it wears off. Similarly, while it may seem that cigarettes are calming, nicotine is actually a powerful stimulant. Smoking leads to higher, not lower, levels of anxiety and OCD symptoms.
So Why Has This Major Shift Been Almost Completely Ignored
Its true that the DSM, and some of the changes between different editions, can be a lightning rod for controversy. But, while categories in the DSM may not be permanently fixed, that doesnt make them meaningless. They reflect our changing understanding of the brain and mental illness, as well as developmental and neurological conditions. Changes are significant, particularly in relation to conditions like OCD which have historically been under-researched.
You Might Also Like: What I Wish Other People Knew About OCD
Another reason for the ongoing confusion is that anxiety plays an integral role in OCD. For many people with the illness, anxiety is intricately bound up with compulsions. But the presence of anxiety doesnt mean that a mental illness is, in fact, a variety of anxiety disorder. Most mental illnesses, from OCD to schizophrenia, will produce anxiety.
Don’t Miss: Feretrophobia
Anxiety Management Techniques For Ocd
Anxiety management techniques can help a person to manage their own symptoms. Such techniques can include relaxation training, slow breathing techniques, mindfulness meditation and hyperventilation control. These techniques require regular practice and are most effective if used together with a cognitive behaviour therapy treatment program.
What Are Some Common Compulsions
The following are some common compulsions:
- Cleaning and grooming, such as washing hands, showering, or brushing teeth over and over again.
- Checking drawers, door locks, and appliances to be sure they are shut, locked, or turned off.
- Repeating actions, such as going in and out of a door, sitting down and getting up from a chair, or touching certain objects several times.
- Ordering and rearranging items in certain ways.
- Counting to a certain number, over and over.
- Saving newspapers, mail, or containers when they are no longer needed.
- Seeking constant reassurance and approval.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Whats The Outlook For People With Ocd
Without treatment, OCD symptoms may worsen over time and affect your personal relationships and quality of life.
According to the DSM-5, people with poor insight those who have more belief in OCD obsessions and compulsions may have worse treatment outcomes. Having poor insight about OCD may make treatment especially important.
With treatment, OCD symptoms often improve. Getting treatment can help improve day-to-day function and quality of life.
Treatment isnt always easy at times. Therapy in particular can often bring up feelings of anxiety and distress. But stick with your treatment plan, even if you have a hard time with it at first.
If therapy really doesnt seem to work or your medication causes unpleasant side effects, talk to your therapist. You may need to try a few different approaches before you find the one that leads to the most improvement.
Working with a compassionate therapist who understands your symptoms and needs is key to improvement.
How Gad Can Affect A Persons Life
Anxiety is normal. It helps us get out of harms way and prepare for important events. It warns us when we need to take action. However, if you have persistent, irrational, and overwhelming anxiety that interferes with daily activities, you may have an anxiety disorder.
People with GAD experience persistent, excessive, and unrealistic worries that go on every day, possibly all day. They feel its beyond their control. People with GAD also often expect the worst, even when there is no reason for any concern. Their worrying occurs on more days than not for at least six months and often concerns health, family, money, or work. The exaggerated, unrelenting worrying interferes with everyday living. Physical symptoms often accompany it and include restlessness, irritability, muscle tension, fatigue, and difficulty sleeping or concentrating. However, despite the anxiety, those who suffer from GAD do not engage in obsessive and compulsive behavior.
GAD can affect all areas of life, including social, work, school, and family. According to a national survey conducted by the Anxiety Disorders Association of America, seven out of ten people with GAD agreed their chronic anxiety impacted their relations with spouses or significant others. Two-thirds also reported that GAD harmed their friendships.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
Panic Attacks & Panic Disorder
Panic disorder is a debilitating anxiety disorder that is very different from GAD. Panic disorder is not about “panicking.” It’s not about getting very worried because you might lose your job or a lion is about to attack you in the jungle. That type of panic is normal.
Panic disorder is when you experience severe feelings of doom that cause both mental and physical symptoms that can be so intense that some people call an ambulance, worried that something is dangerously wrong with their health.
Panic disorder is characterized by two things:
- Panic attacks.
- Fear of getting panic attacks.
Panic attacks are intense physical and mental sensations that can be triggered by stress, anxiety, or by nothing at all. They often involve mental distress, but are most well-known for their physical symptoms, including:
- Rapid heartbeat .
- Excessive sweating or hot/cold flashes.
- Tingling sensations, numbness, or weakness in the body.
- Depersonalization .
- Trouble breathing or feeling as though you’ve had a deep breath.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness.
- Chest pain or stomach pain.
- Digestive problems and/or discomfort.
Panic attacks may have some or all of the above physical symptoms, and may also involve unusual symptoms as well, like headaches, ear pressure, and more. All of these symptoms feel very real, which is why those that experience panic attacks often seek medical attention for their health.
Three Main Elements Of Ocd
Explained in detail are the 2 main elements obsessions and compulsive behaviour:
Obsessions
Obsessions refer to recurring, uncontrollable, and unwanted thoughts, sensations, ideas, or feelings. Practically, everyone has unwanted thoughts at some point and it could be things like have I forgotten to turn off the stove or the iron? or an unwanted violent image. But the difference is if the thought is persistent and dominates your thoughts to the extent that it interrupts other normal thoughts and take up a lot of your time. It is important to identify if it is an obsession or just a normal thought.
Compulsive behaviour
Compulsions are behaviors that an individual feels the urge to keep repeating over and over again. Compulsions typically start as a technique of trying to prevent or lessen anxiety caused by the obsessive thought. Common forms of compulsive behavior in individuals with OCD include:
- Checking such as checking if the doors are locked or that the iron is off
- Counting
- Asking for reassurance
- Avoiding circumstances or places which might trigger those obsessive thoughts
It is possible to only have obsessive thoughts or only compulsions, but most individuals with OCD experience both.
You May Like: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words