What Are The Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia usually happens in stages, with different symptoms and behaviors depending on the stage.
- Onset . This is an early phase that happens before a person develops more severe symptoms. It can include social withdrawal, anxiety, lack of motivation and neglect of personal hygiene.
- Active. This is when psychotic symptoms take full effect. Another term for this is psychotic break, where a person shows a disconnection from reality. That includes showing at least two of the five main symptoms listed immediately below.
- Residual. People in this stage still have some schizophrenia signs and symptoms, but theyre not as severe. Odd beliefs, lack of motivation, decreased feelings of enjoyment or pleasure, limited speaking and reduced emotional expression tend to be the most noticeable effects. Many people often improve to the point where they seem mostly or fully recovered. However, this is usually temporary, and symptoms of schizophrenia will return as a person goes back into the active stage of the condition.
What are the early signs of schizophrenia?
The early symptoms of schizophrenia, which happen in the onset stage, usually arent severe enough for a schizophrenia diagnosis but are still a cause for concern. This stage sometimes happens quickly, only taking weeks before moving to the next stage.
The most common symptoms or changes in this stage include:
What are the active stage symptoms?
Are there other possible symptoms?
Lack of insight
Why The Subtypes Were Removed
With the release of the DSM-5, these subtypes were removed for
- They werent very reliable descriptions.
- People living with schizophrenia didnt always experience the same symptoms or subtype.
- There was no difference in brain functioning between the subtypes.
- The subtypes didnt help predict how the condition would play out over time.
- Some people couldnt be assigned a subtype based on their symptoms.
- They didnt help with treatment decisions.
- Scientists had stopped using the subtypes in their reports.
Instead, the APA believed it was more accurate to describe the symptoms of schizophrenia as a spectrum.
This means that people with schizophrenia may experience different symptoms at different times. It also means that not everyone with a schizophrenia diagnosis experiences the same symptoms.
This is why the condition is now called Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Disorders in the DSM-5, compared with just Schizophrenia and Other Disorders in the DSM-4.
How Is It Diagnosed
A healthcare provider, usually a mental health specialist like a psychiatrist, diagnoses schizophrenia using a combination of tools and techniques. Some of the techniques involve analyzing your medical and personal history, asking you questions about your experiences and symptoms, and observing your behavior and actions.
Combining those methods is necessary because diagnosing schizophrenia requires the following:
- At least two of the five main symptoms.
- Main symptoms that have lasted at least one month, and overall effects that have lasted at least six months.
- Disruption in your social or work life.
Read Also: What Is It Like To Be Bipolar
What Are Schizophrenia Disorders
Schizophrenia disorders are mental health disorders that interfere with a persons perception of reality. They are often characterized by delusions and hallucinations. These disorders are usually severe and require mental health care in order for the person to manage their symptoms and lead a more normal life.
Schizophrenia Dsm 5 Criteria What Is The Dsm 5 Code For Schizophrenia

Schizophrenia Dsm 5 Diagnostic Criteria. Here are a number of highest rated Schizophrenia Dsm 5 Diagnostic Criteria pictures on internet. We identified it from honorable source. Its submitted by doling out in the best field. We give a positive response this kind of Schizophrenia Dsm 5 Diagnostic Criteria graphic could possibly be the most trending subject later than we part it in google plus or facebook.
Diagnostic Categories Covered In K Sads Pl Dsm 5 Download Table, What Is Schizophrenia Dsm 5 Schizophrenia Definition Symptoms, Pin By Angela Tomecko On Psychology Dsm Iv Delusional Psychology, Clinical Characteristics Of Schizophrenia Essay College Paper Directory,
Crumbtrail.org is an open platform for users to share their favorite wallpapers, By downloading this wallpaper, you agree to our Terms Of Use and Privacy Policy. This image is for personal desktop wallpaper use only, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, DMCA report please Contact Us
Recommended Reading: What Does Schizophrenia Literally Mean
Recommended Reading: What Does It Mean To Have An Eating Disorder
What Are The Symptoms Of Paranoid Schizophrenia
Over time, the DSMs classifications of schizophrenia subtypes have changed. The DSM-1 identified nine separate types of schizophrenia. The DSM-5-TR does not break schizophrenia down into different subtypes. The reason for this may be the lack of clinical value in defining separate types.
However, mental health professionals may recognize several clinical subtypes of schizophrenia. These include disorganized, catatonic, undiferentiated, and paranoid. Doctors often regard paranoid schizophrenia as the most common subtype. One study of 731 patients diagnosed with schizophrenia found that 82 percent had paranoid schizophrenia. Undifferentiated is the next-most common type with about 9 percent of those with schizophrenia having symptoms of this type.
A person with paranoid schizophrenia will typically have paranoid delusions. This means that a person may think friends and family are out to get them. They may believe there are conspiracies of government or religion that are targeting the person, such as that the FBI is following the person.
Because a person with paranoid delusions cannot recognize the thoughts they have arent real, the paranoia can overtake their life. They may avoid going outdoors due to fears of someone following them. They may alienate friends and family due to their suspicions their family are conspiring against them.
Dsm 5 Schizophrenia Treatment
The person who has this type of mental illness must understand that schizophrenia is a disorder that has no cure.
The treatment is intended to reduce symptoms so that the person can have a better quality of life.
The person who is diagnosed with DSM 5 Schizophrenia must understand the importance of following the treatment indicated by the area professional.
This disease does not heal itself over time, however, if the person is not treated for this disease the symptoms can get worse causing problems to obtain a better quality of life.
Also Check: Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of Bipolar Disorder
Medication Or Drug Management
Drug intake can help reduce symptoms like hallucinations, delusions, paranoia, and disorganized thinking.
Doctors may recommend the best medication depending on the severity of the symptoms, especially because not everyone responds to medication the same way.
The most usually prescribed drugs are atypical antipsychotics or second-generation antipsychotics that are less likely to cause some of the side effects normally seen in typical medication.
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
Although the diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia changed, the actual process of being diagnosed with the condition remains the same.
Theres currently no single test that can confirm or diagnose schizophrenia. Instead, a healthcare or mental health professional will evaluate your symptoms and medical history.
They may also work to rule out other factors and medical conditions that can cause psychosis, such as:
- neurological conditions, such as encephalitis
- other psychiatric conditions, such as bipolar disorder
Once other causes have been ruled out, a diagnosis of schizophrenia may be made.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell Someone You Have Depression
How Schizophrenia Is Diagnosed
Schizophrenia is diagnosed on the basis of a consultation with the affected person. Specific diagnostic tools, in the form of a series of structured questions, will be used during the consultation to facilitate an accurate diagnosis.
Other relevant information about the patient may be also be taken into account, often from relatives or people who are very close to the patient.1
Specifiers Of Course Of Illness In Dsm
There is significant variability in the course of schizophrenia and a wide range of factors need to be considered in order to characterize it. Gaebel reviewed general principles of course characteristics in mental disorders with an emphasis on affective disorders and schizophrenia, distinguishing temporal macro-aspects from micro-aspects (days
You May Like: How To Help Someone In A Ptsd Episode
Diagnosing Schizophrenia From Dsm
DSM-II was published in 1968. DSM-5 will be published in 2013. How much progress have we made? I propose that we approach this question with a quiz.
DSM-II was published in 1968. DSM-5 will be published in 2013. How much progress have we made? I propose that we approach this question with a quiz.
My criterion of progress will be your ability to distinguish definitions and criteria from one DSM to the next. If the subsequent edition of the manual represents progress over its predecessor, that should be evident in the DSM text. If, on the other hand, you cant distinguish an earlier from a later edition, we can question what has been accomplished with all the work of revision.
Lets try this for the king of disorders, schizophrenia. Well start with definitions in DSM-II, -III, and -IV, as we dont have definitions posted on the Web site for DSM-5.
Item #1. Your first challenge is the definition of schizophrenia, disorganized type . Here are the three definitions from DSM-II, -III, and -IV. Match the definition to the manual.
Schizophrenia, disorganized type
The essential features of this type are incoherence, marked loosening of associations, or grossly disorganized behavior, and, in addition, flat or grossly inappropriate affect. There are no systematized delusions, although fragmentary delusions or hallucinations, in which the content is not organized into a coherent theme, are common.
Schizophrenia, paranoid type
Schizophrenia Criteria A
Greater Harmonization With Icd
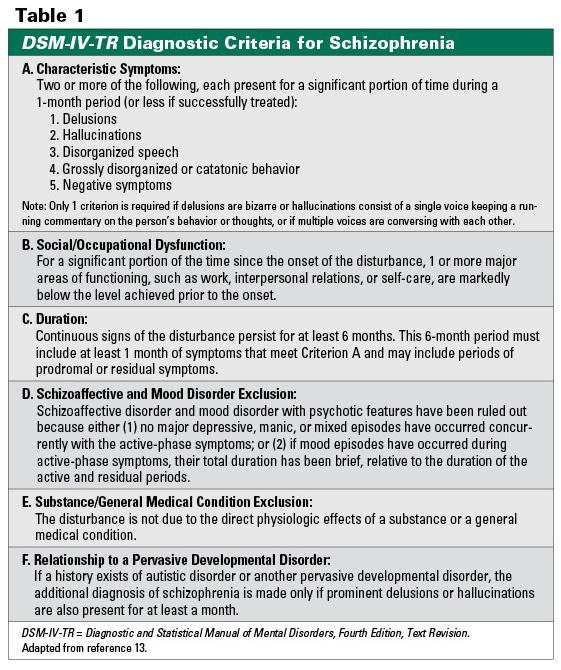
Although the gap between the DSM and ICD definitions of schizophrenia narrowed from ICD-8/DSM II to the current ICD-10/DSM-IV, some significant differences remained. Whereas DSM-IV mandated a total duration of a minimum of 6 months, ICD-10 required a minimum duration of 1 month. In contrast to the DSM-IV requirement for social/occupational dysfunction, ICD-10 had no such requisite. Although both DSM-IV and ICD-10 provided special treatment to Schneiderian first-rank symptoms, ICD-10 placed a
Also Check: Why Did God Make Me Depressed
How Is Schizophrenia Treated
Schizophrenia is a condition that is dependent upon treatment. Traditional schizophrenia treatment plans include a combination of psychotherapy and medication.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy is the preferred psychotherapy treatment. It challenges negative thought patterns, creates tactics for managing emotional responses, and can help facilitate healthy relationships.
Antipsychotic medications help manage symptoms. It is important to remember that medication in conjunction with psychotherapy is critical for optimal treatment. By dropping the schizophrenia subtypes, doctors were able to clarify symptoms, leading to more efficient medication management.
What Are The Dsm
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual-V is the manual most mental health professionals use to diagnose disorders such as schizophrenia. The DSM-5-TR specifies six diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia :
- Catatonic behavior or grossly disorganized behavior
- Negative symptoms, which include avolition, or a lack of motivation
- Significant behavioral disturbance such that a person does not work or interact with others well over the course of six months
A person must have at least two of the first five symptoms over the course of one month for a mental health professional to diagnose a person with schizophrenia.
Read Also: What Causes Social Phobia Disorder
Other Considerations In Diagnosing Schizophrenia
The DSM-5 includes other things that can help determine schizophrenia. Theyre not necessary diagnostic criteria, but their presence points to this serious mental illness.
- Inability to understand someones intentions
- Thinking insignificant things are highly, personally meaningful
In addition to these, people with schizophrenia often experience what is known as neurological soft sign, subtle abnormalities that arent severe enough to fit into any disorder but are problematic and indicative of a bigger problem, like schizophrenia. They can include:
- Coordination problems
- Left-right confusion
- Difficulty with complex movement
To diagnose schizophrenia, professionals examine all of the symptoms and features that are present . They also must look at what is not present.
What Can I Do If A Loved One Shows Signs Of Schizophrenia Or A Similar Condition
Because people with schizophrenia often can’t recognize their symptoms or condition, they often don’t believe they need medical care or treatment. That can be frustrating or frightening for both the person with the symptoms and those who care about them.
If you notice a loved one showing signs of schizophrenia or a related condition, you can try to help them by doing the following:
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Paranoid schizophrenia is an outdated term for the condition schizophrenia, but paranoia is still a common part of the symptoms that people experience. Schizophrenia is a disorienting and often frightening condition for people who have it, causing them to lose touch with reality and their ability to tell whats real and what isnt.
When people experience paranoia, they may struggle to trust people who want to help. That can make diagnosing and treating this condition very difficult. However, with medical care, especially medications, people with schizophrenia can avoid severe complications and can live fulfilling lives.
Don’t Miss: Is Schizophrenia A Mental Disability
Criteria For Schizophrenia Diagnosis In Dsm
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition is the authority on mental illness. Created and published by the American Psychiatric Association, this comprehensive manual describes all known mental disorders, among them schizophrenia.
Mental health professionals use the DSM-5 when determining what someone is experiencing. Doctors use the information and analyze:
- diagnostic features and symptoms
- duration of symptoms
- other conditions that share symptoms
They also look at age. While its not part of the diagnostic criteria, they do consider someones age. The typical age of schizophrenia diagnosis is between late adolescence and the mid-30s. This varies, though, with peak ages ranging from the early- to mid-20s for males and late-20s for females . Further, while its rare, schizophrenia can be diagnosed as early as childhood and as late as the 40s .
Age provides a general idea of the likelihood that someone has schizophrenia. Schizophrenia wont be the first consideration for a man in his 40s, for example. Beyond this, age isnt a diagnostic criterion. Just what are the diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia?
Also Check: Can Untreated Anxiety Lead To Schizophrenia
Conditions Related To Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is the most well-known condition of its type, but a range of conditions involve psychosis and other schizophrenia-like symptoms.
The DSM-5-TR lists schizophrenia alongside several other conditions that it groups under schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders. These conditions include:
- Schizotypal personality disorder: This involves discomfort in close relationships, disturbances in cognition or perceptions, and eccentric behavior.
- Delusional disorder: This involves the person having delusions for 1 month but no other psychotic symptoms.
- Brief psychotic disorder: This occurs when symptoms of psychosis last for longer than a day but less than a month.
- Schizophreniform disorder: This occurs when symptoms of schizophrenia last for less than 6 months.
- Schizoaffective disorder: This mainly involves symptoms of schizophrenia, but a person may also have significant mood symptoms, such as mania or depression.
- Substance- or medication-induced psychotic disorder: Psychotic symptoms can arise from the use of alcohol, cannabis, hallucinogen, or sedatives. They may also appear after taking certain medications, such as anesthetics, anticonvulsants, heart medications, chemotherapy drugs, or antidepressants.
- Psychotic disorder due to another medical condition: There are various possible causes of psychosis, including untreated endocrine, metabolic, or autoimmune conditions and temporal lobe epilepsy.
more likely to die early than the general population.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Help With Binge Eating Disorder
Can You Recover From Paranoid Schizophrenia
Currently, there is no cure for paranoid schizophrenia or any other schizophrenia subtype. Doctors do, however, have several treatments that can help a person better cope with their symptoms. Examples of these include anti-psychotic medications as well as individual and family counseling. Counseling may focus on helping a person recognize their delusions, learn how to process their thoughts, or enhance a persons ability to communicate with others. This can be very difficult to accomplish because the delusions and paranoia feel very real to the person experiencing them.
Ideally, the goals for paranoid schizophrenia treatment are to keep a person out of a state of psychosis, where they lose touch with reality. However, many patients with paranoid schizophrenia may require a hospital stay if they experience an acute episode of paranoid psychosis. Through consistent treatment, a person can ideally manage their paranoid schizophrenia symptoms.
Paranoid schizophrenia can significantly affect a client, their friends, and family. For more in-depth learning on paranoid schizophrenia, view Symptom Medias CE Courses and video case studies.
How Can I Support A Person Suffering From Schizophrenia

If you know someone or have a friend with schizophrenia, it is important to show your support.
Encourage that person to seek professional help and tell them that this is something it will be able to overcome.
Find information about the disorder so you can know more about the symptoms and help at the time of its manifestation.
Keep a positive attitude all the time and let that person know that he can count on you.
Recommended Reading: What Does A Minor Panic Attack Feel Like
What Is The Difference Between Schizophrenia And Psychosis
Schizophrenia and psychosis are two strongly connected terms, but they also have significant differences.
- Psychosis: This is a grouping of symptoms that involve a disconnection from reality and the world around you . Psychosis can happen with other medical conditions and mental health disorders, such as bipolar disorder.
- Schizophrenia: This is a spectrum of conditions that involve psychotic symptoms.
What Is Dsm 5 Schizophrenia
DSM 5 schizophrenia belongs to a category in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
Schizophrenia includes symptoms such as delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech and behavior, and other symptoms that cause social or occupational dysfunction.
The DSM 5 schizophrenia criteria changed with the latest version of the DSM.
In contrast with the previous version the threshold now is set to include at least two of the related symptoms and must have been present for six months, including at least one month of active symptoms .
The new criteria eliminated the subtypes.
Many clinicians thought they were not helpful when diagnosing because the patients symptoms often changed from one subtype to the other .
Read Also: When Is Ptsd Awareness Month