The Role Of Brain Chemistry And Structure In Schizophrenia
Scientists are looking at possible differences in brain structure and function in people with and people without schizophrenia. In people with schizophrenia, they found that:
- Spaces in the brain, called ventricles, were larger.
- Parts of the brain that deal with memory, known as the medial temporal lobes, were smaller.
- There were fewer connections between brain cells.
People with schizophrenia also tend to have differences in brain chemicals called neurotransmitters. These control communication within the brain.
Studies show that these neurotransmitters are either too active or not active enough in people with schizophrenia.
Doctors also believe the brain loses tissue over time. And imaging tools, like PET scans and MRIs, show that people who have schizophrenia have less âgray matterâ — the part of the brain that contains nerve cells — over time.
Studies of brain tissue in people with schizophrenia after death even show that their brain structure is often different than it was at birth.
Amphetamines And Other Stimulants
As amphetamines trigger the release of dopamine and excessive dopamine function is believed to be responsible for many symptoms of schizophrenia , amphetamines may worsen schizophrenia symptoms. Methamphetamine, a potent neurotoxic amphetamine derivative, induces psychosis in a substantial minority of regular users which resembles paranoid schizophrenia. For most people, this psychosis fades away within a month of abstinence but for a minority the psychosis can become chronic. Individuals who develop a long lasting psychosis, despite abstinence from methamphetamine, more commonly have a family history of schizophrenia.
Drugs such as ketamine, PCP , and LSD , have been used to mimic schizophrenia for research purposes. Using LSD and other psychedelics as a research model has fallen out of favor, as the differences between the drug-induced states and the typical presentation of schizophrenia have become clear. The dissociatives ketamine and PCP, however, are still considered to produce states that are remarkably similar, and are considered to be even better models than stimulants since they produce both positive and negative symptoms.
Neuropsychological Function Among Adult Relatives
In an initial study, Faraone et al assessed neuropsychological functioning in 35 nonpsychotic adult relatives of schizophrenic patients and 72 normal controls. We used linear combinations of neuropsychological tests to create scales assessing 10 neuropsychological functions: abstraction/executive function, verbal ability, spatial ability, verbal memory, visual memory, learning, perceptual-motor speed, mental control/encoding, motor function, and auditory attention. Based on previous neuropsychological studies of patients with schizophrenia and our review of family studies, we predicted that relatives of patients with schizophrenia would exhibit deficits in abstraction/executive function, learning and memory, and components of attention .
Within the relative group, we found significant intercorrelations among skills of abstraction, verbal memory, and auditory attention, both within and between these functions. In addition, the significant, correlations among relatives between attention and verbal memory and between attention and abstraction differed significantly from these correlations in the control group. Thus, the greater level of cooccurrence between these putative neuropsychological risk indicators within the high-risk group provides further support for their status as risk indicators of the same underlying vulnerability to schizophrenia.
You May Like: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
Family Environment And Schizophrenia
Family environment seems to play a role in triggering schizophrenia development. A stressful or unhealthy family environment can worsen the risk, while a more calm one can act as a strong protective factor in people with a genetic predisposition for the condition.
According to a Finnish adoption study, researchers saw how genes and environment might interact to determine a persons risk of schizophrenia.
In the study, adopted children whose biological mothers had schizophrenia-spectrum disorder were compared with adopted children of mothers without the diagnosis.
The adoptive families were later evaluated by psychiatrists as either healthy family environments or unhealthy family environments. Researchers defined an unhealthy family environment as one that was stressful, highly critical, conflict-ridden, and had problems with boundaries.
According to the studys findings, of the adoptees with a high genetic risk of schizophrenia placed in an unhealthy family environment, 36% of them developed a psychotic disorder.
In contrast, only 6% of those with a high genetic risk placed in an environment deemed healthy by the study developed psychosis.
For the adoptees with low genetic risk, the family environment they were placed into did not contribute either way to onset of psychosis.
If Your Siblings Have It
- If your full sibling has schizophrenia: a risk of 9 in 100
- If your identical twin has schizophrenia: a risk of 40 to 50 in 100
- If your non-identical twin has schizophrenia: a risk of 17 in 100
These figures arent fixed. They vary across the world, and science peeps have called for more studies looking at schizophrenia risk in people of African and Latinx ancestry.
What else stirs the pot of schizophrenia?
You May Like: Phobia Suffix Meaning
Regulator Of G Protein Signaling
Attention focused on RGS-4 following a microarray study finding that the brains of schizophrenics showed decreased RGS-4 expression , and because of the location of the gene in a linkage region on chromosome 1q21q22 of RGS-4 . The function of RGS proteins is to decrease the effect of G protein coupled receptor agonists. This could link with current theories on the etiology of schizophrenia relating to activity of dopamine, serotonin or metabo-tropic glutamate receptors.
Stability Of Neuropsychological Deficits
The neuropsychological studies discussed thus far used data from a baseline assessment. These were extended recently, in two ways. First, by completing a. follow-up study, we tested the hypothesis that neuropsychological deficits among adult relatives of schizophrenic patients would be stable over time. Second, with the addition of new tests of executive functioning, we tested the hypothesis that, neuropsychological differences between controls and relatives of schizophrenic patients would be evident on delayed-response tasks. These tasks are sensitive to working memory, ic, the neuropsychological function that, briefly holds information on line for use in other cognitive tasks such as reasoning. Differences between the groups included measures of immediate verbal memory, delayed verbal memory , and complex attention . Immediate and delayed verbal and visual memories showed interactions with gender, but. none of the test scores showed group-by-time interactions, showing that, the discriminating power of the tests remained stable over time. As we found at. baseline, the relatives showed significantly poorer performance than the controls at follow-up.
These results are consistent with the idea that neuropsychological dysfunction among relatives of schizophrenic patients is a. stable trait that assesses the predisposition to schizophrenia.
You May Like: Does Dehydration Cause Anxiety
Traumatic Experiences Early In Life
A have suggested a correlation between traumatic experiences in childhood and adolescence and the development of schizophrenia in people with a genetic risk.
For people with a genetic predisposition to schizophrenia, the risk of onset for this condition is
- vitamin A
- vitamin D
One thing to keep in mind is that insufficient vitamin D during pregnancy isnt always associated with access to nutritious foods. Instead, it can be related to less sunlight and time outdoors.
Because of this, the review noted that children born in the winter and spring carry a slightly higher genetic risk of schizophrenia.
Other Family Environmental Factors
In the British 1946 Birth Cohort, schizophrenia in offspring has been linked with problems in mothers general understanding and management of their children . Goldstein concluded that communication deviance in the family increased the risk for schizophrenia. Having a positive relationship with both the mother and father might be protective against schizophrenia among high-risk children. These findings may be explained by geneenvironment interaction.
In Finnish studies some possible stress factors have not generally been linked to schizophrenia. Very early temporal separation from parents and transfer to adequate nursing homes immediately after birth because of tuberculosis in the family did not predict schizophrenia, and neither did living in a single-parent family in childhood, low socio-economic status, or the size of the family of origin and multiparity. The connection between childhood socio-economic status and schizophrenia is not yet entirely resolved. Low or high socio-economic status in the family of origin has been found to be at least a modest risk factor for schizophrenia in some studies, while other studies report no increased risk.
Don’t Miss: Is Tequila A Stimulant Or Depressant
Pedigree Studies: Lod Score Methods
In pedigrees with multiple ill individuals, the LOD score method can be used to determine whether the distribution of DNA markers alleles within each pedigree predicts presence of disease. The LOD score is based on a mathematical model of the mode of inheritance . Our uncertainty of the precise mode of inheritance in complex genetic disorder such as schizophrenia introduce the possibility of mis-specifying the model, resulting in inappropriate linkage data.
Risk Factors Of Schizophrenia
Risk factors of schizophrenia include multiple genetic and environmental risk factors. The prevailing model of schizophrenia is that of a neurodevelopmental disorder with no precise boundary, or single cause, and is thought to develop from complex geneenvironment interactions with involved vulnerability factors. The interactions of these risk factors are complicated, as numerous and diverse insults from conception to adulthood can be involved. The combination of genetic and environmental factors leads to deficits in the neural circuits that affect sensory input and cognitive functions.
A genetic predisposition on its own, without interacting environmental factors, will not give rise to the development of schizophrenia. Environmental risk factors are many, and include pregnancy complications, prenatal stress and nutrition, and adverse childhood experiences. An environmental risk factor may act alone or in combination with others.
Schizophrenia typically develops between the ages of 1630 about 75 percent of people living with the illness developed it in these age-ranges. Childhood schizophrenia that develops before the age of 13 is quite rare. There is on average a somewhat earlier onset for men than women, with the possible influence of the female sex hormone estrogen being one hypothesis and socio-cultural influences another. Estrogen is seen to have a dampening effect on dopamine receptors.
You May Like: Hippopotomonstrosesquipedaliophobes.
Learn More About Schizophrenia:
- Footnote 2
-
Government of Canada. The human face of mental health and mental illness in Canada. 2006. www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/publicat/human-humain06/pdf/human_face_e.pdf
- Footnote 3
-
Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System , August 2019. Schizophrenia and use of health services for schizophrenia . CCDSS data are based on people with diagnosed schizophrenia who had contact with the health system during the data collection period, which may underestimate the total number of people diagnosed with schizophrenia during a lifetime. Saskatchewan data from year 2016-2017 were not available. Nunavut data were excluded before 2005â2006. Yukon data were excluded before 2010â2011. Crude rates were based on randomly rounded counts to an adjacent multiple of 10.
- Footnote 4
Can You Prevent Schizophrenia If Your Parents Have It

You cant prevent schizophrenia if your parents have it. Because schizophrenia has a whole bunch of possible causes, there isnt one definite way to prevent it.
You can reduce your risk of developing schizophrenia by reducing other risk factors. People with schizophrenia can also reduce the symptoms. They can manage their mental health using meds, therapy, and even texting.
Read Also: Mental Health Symptoms Diagnosis
Other Candidate Genes And Regions
Schizophrenia has not been convincingly associated with polymorphism in genes related to dopaminergic function, although meta-analyses have suggested a small but significant association for homozygosity at a polymorphism in DRD3 . A modest but significant association between schizophrenia and a polymorphism in the serotonin-2A receptor gene was reported in a meta-analysis . There is a number of evidence that suggested the role for glutamatergic dysfunction in the pathogenesis or pharmacology of schizophrenia . Cholecystokinin , which modulates dopaminergic neurotransmission has also been hypothesized to play a role in schizophrenia . In extensive review of the recent literature on molecular genetics of schizophrenia, Levinson found that new genome scan project, seen in the light of previous scans, provide support for schizophrenia candidate regions on chromosomes 1q, 2q, 5q, 6p, 6q, 8p,10p,13q,15q, and 22q.
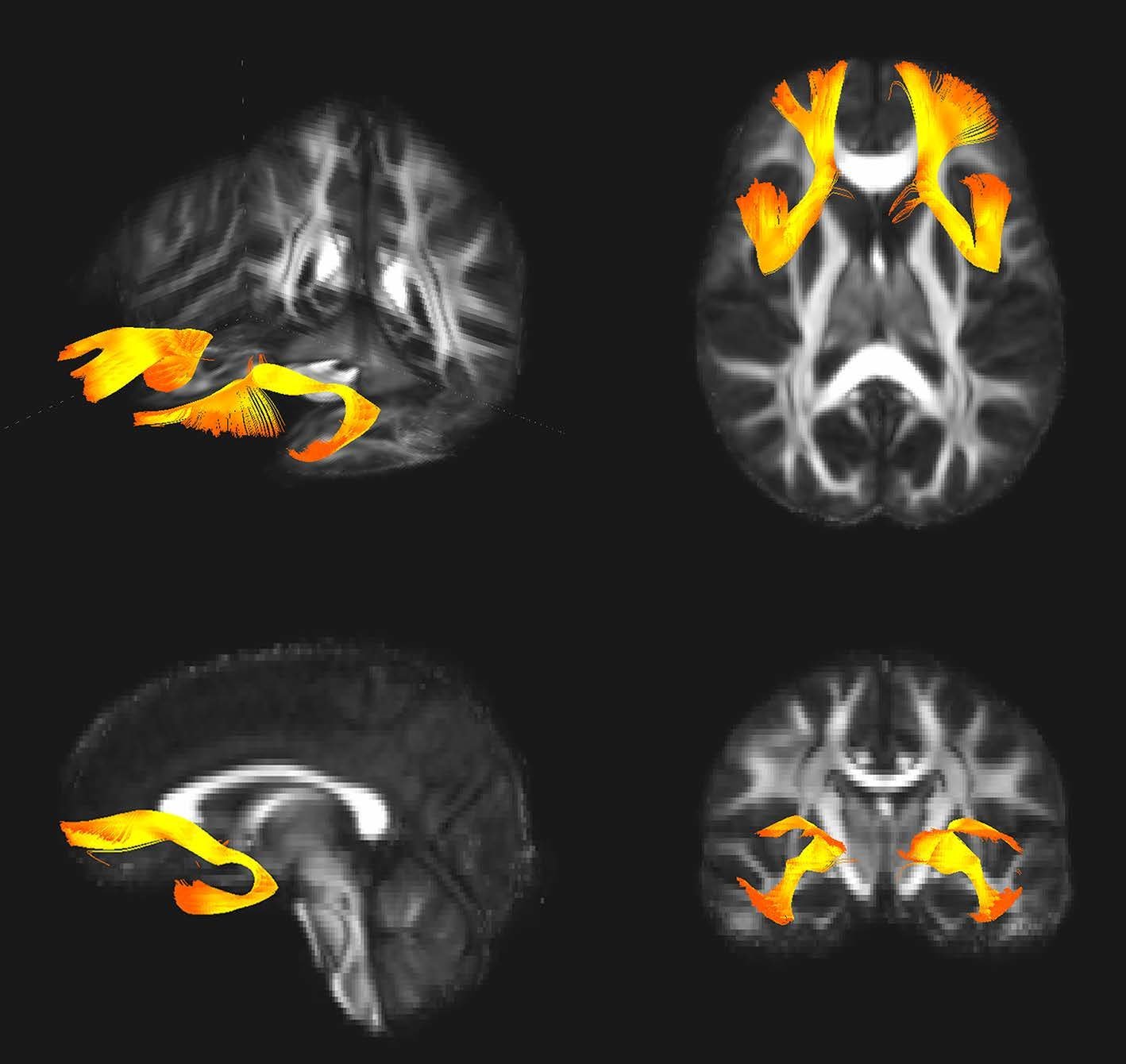
Remote Collaborative Research Drives New Insights On A Rare Genetic Disorder Linked To Schizophrenia
The key to a better understanding of schizophrenia may exist in a genetic disorder so rare that researchers havent been able to conduct an adequate study until now.
The genetic disorder 22q11.2 deletion syndrome , caused by a small segment of missing DNA on chromosome 22, is the strongest known genetic risk factor for developing schizophrenia. About a quarter of people with the disorder develop schizophrenia or experience psychotic symptoms, so studying it provides a unique window into how such psychiatric problems develop over time.
But theres one problem: Only about one in 4,000 people have it. Even a large city like Los Angeles may hold just a few hundred people with the condition.
Fortunately, the Enhancing Neuro Imaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis consortium, led by Paul M. Thompson, PhD, associate director of the Mark and Mary Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute at the Keck School of Medicine of USC, has spent the past 10 years uniting researchers around the world to pool data and insights on rare diseases. Now, ENIGMA has launched a new working group to study 22q11DS using data collected by researchers across the U.S., Canada, Europe, Australia and South America.
Weve pieced together many of the major research centers studying 22q11DS around the world to create the largest-ever neuroimaging study of the disorder, said Christopher Ching, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at the INI and lead author of the working groups latest study.
Read Also: Does Celine Dion Have An Eating Disorder
Is Schizophrenia A Genetic Disorder
The organic studies of schizophrenia outnumber, by far, the psychological ones.
The quantity of these works and the variety of directions that they have taken reveal that no breakthrough has been made. Even in fields like genetics and biochemistry where some evidence of the organic nature of schizophrenia has been collected, the results are unclear and controversial. Some approaches popular in the 1920s and 1930s have been totally abandoned and would seem absurd today, such as the studies that investigated the supposed tubercular origin of schizophrenia or an etiologic connection with rheumatic fever. The constitutional, cardiovascular, endocrinological, and neuropathological researches have lost ground. On the other hand, the genetic, biochemical, and neurophysiological approaches have gained support.
Have a question about
Heredity has been studied in reference to schizophrenia since the early period of classic psychiatry. There are two major types of genetic research. The first one includes collecting statistical data from family studies and surveys of total populations to determine whether the morbidity risk is higher than expected in certain families or other groups. A second set of studies involves investigating schizophrenics’ special physical characteristics that are connected with genetic characteristics.
Have Rates Of Schizophrenia Changed Over Time
Between 2002-2016:
- The number of Canadians living with diagnosed schizophrenia increased by an average of 3% per year.Footnote 3
- The number of new cases declined during this period.Footnote 3Footnote 4
The Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System is supported by a pan-Canadian partnership between the Public Health Agency of Canada and all provinces and territories. Schizophrenia data in CCDSS are updated biennially.
Read Also: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
What Should I Consider If I Want To Start A Family
If you have a mental illness, and youre thinking of starting a family, you could talk to a professional genetics counsellor.
Genetic counsellors work directly with patients and families. They can give specialist advice and information to people who have relatives with certain health conditions.
If you want to speak to a genetic counsellor, you will need to be referred by a doctor. So, you should speak to your GP or psychiatrist.
Schizophrenia Study Suggests Advanced Genetic Scorecard Cannot Predict A Patient’s Fate
With the help of cutting-edge computer programs, researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai went through the genetic and medical records of more than 8,000 schizophrenia patients. They found that a tool commonly used in research for evaluating a person’s genetic risk for a disease, called a polygenic risk score, was no better at predicting the outcome of a patient’s disease over time than written reports. The results raise important questions about the use of polygenic risk scores in real-world, clinical situations, and also suggest that a doctor’s written report may be an untapped source of predictive information.
“Treating schizophrenia patients is a heart-wrenching experience. One of the hardest parts about taking care of patients is trying to determine whether each patient’s condition will worsen or improve. If we could do that, then we might help relieve the suffering that the patients and their loved ones experience,” said Alexander W. Charney, MD, Ph.D., Assistant Professor in the Departments of Psychiatry and Genetics and Genomic Sciences at Icahn Mount Sinai and the senior author of the study published in Nature Medicine. “Our results show that for the mental illnesses most deeply characterized at the genetic level, the current state of genetics research cannot solve this problem just yet.”
Explore further
Recommended Reading: Is Tequila A Stimulant Or Depressant
Overlap With Other Disorders
Several studies have suggested a genetic overlap and possible genetic correlation between schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders including autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. One genome-wide association study analyzed single-nucleotide polymorphism data for the five disorders four gene areas overlapped with the five disorders, two of which regulate calcium balance in the brain.