Does Inflammation Affect Specific Circuits And Neuromodulatory Systems
Although there is no doubt that the immune system plays a critical role in shaping brain development and contributes to disease states when dysregulated, there is a need to understand which specific circuits and neuromodulatory systems in particular are most impacted by abnormal immune signaling. It is clear that complement proteins facilitate the removal of synapses and that the upregulation of complement proteins contributes to circuit miswiring . However, SCZ is also characterized by alterations in inhibitory circuits , neuromodulatory systems such as dopamine and glutamate , and changes in the connectivity between brain regions such as the hippocampus and PFC . Do inflammatory responses alter specific neurotransmitter systems and networks differentially?
Figure 4. Neuroinflammation-induced dysfunctions that alter glutamatergic transmission in SCZ. Changes in glutamatergic transmission are known to occur in SCZ. Neuroinflammation impacts excitatory circuitry in SCZ through complement-mediated engulfment of excitatory synapses, the production of autoantibodies against NMDARs, changes in glutamate homeostasis potentially mediated by alterations in astrocytes and changes in the gut-brain axis, a known regulator of glutamate synthesis that is able to impact CNS functions such as stress responses. These changes in excitatory transmission can alter brain circuitry, for example, by altering synaptic plasticity and long-range excitation.
What Myths Are There About Schizophrenia
There are some myths or mistaken beliefs about schizophrenia which come from the media. For example,
- Schizophrenia means someone has a split personality
This is not the case. The mistake may come from the fact that the name schizophrenia comes from two Greek words meaning split and mind.
- Schizophrenia causes people to be violent
Research shows that only a small number of people with the illness may become violent. The same way as a small minority of the general public may become violent.
People with schizophrenia are far more likely to be harmed by other people than other people are to be harmed by them. But as these incidents can be shocking, the media often report them in a way which emphasises the mental health diagnosis. This can create fear and stigma in the general public.
Inside Schizophrenia: Psychosis In Schizophrenia
What exactly is psychosis? What happens in the brain of a person with schizophrenia who is hallucinating?
Schizophrenic Rachel Star Withers shares her personal hallucinations and delusions and Dr. Joseph Goldberg, who specializes in researching what goes on in the brain when someone is experiencing psychosis, joins to break down how the brain functions during psychotic episodes.
Host Rachel Star Withers, a diagnosed schizophrenic, and co-host Gabe Howard delve into these intense subjects in this episode of Inside Schizophrenia.
Rachel, do you hallucinate?
What is psychosis?
Signs to spot that someone might be starting to lose grip with reality
The types of psychosis
Rachel and her wings in Walmart
Audio Hallucinations
Guest Interview with Dr. Joseph F Goldberg
What happens in the brain when you hallucinate
The mouse study
Also Check: What Does Having Schizophrenia Feel Like
Hope From Scans Of Schizophrenia In The Brain
Imaging scans of schizophrenia in the brain have helped researchers locate a small area of the brain that may help them predict whether people will develop schizophrenia with 71 percent accuracy for high-risk patients. The study results, which appear in the September 2009 issue of Archives of General Psychiatry, pinpoint the exact area of a part of the brain that shows hyperactivity in schizophrenics.
The researchers used high-resolution MRI equipment to show what areas of the brain are affected by schizophrenia. The scientists discovered three areas of the schizophrenic brain that differed from normal brains two areas in the frontal lobes and one very small area of the hippocampus, known as CA1. Weve always known that schizophrenics have a more active hippocampus, the area used for memory and learning, but this study pinpoints the exact spot of hyperactivity in patients with the illness.
This discovery brings new hope and promise to those at risk for developing a schizophrenic brain and for those already suffering from it. Doctors hope that once researchers further develop the findings, that they can use this as a diagnostic marker to predict whether certain high-risk patients will go on to develop full-blown psychosis after prodrome. They also hope to use the CA1 subfield marker in the hippocampus to indicate the efficacy of treatments. For example, a decreased amount of activity in the area could indicate the success of treatment strategies.
Box : Symptom Groups In Schizophrenia
-
Positive symptoms
: Positive symptoms include delusions and hallucinations, linked to aberrant salience. These symptoms are most recognisable during periods of acute psychosis.
-
Cognitive symptoms
: Impairments in learning, memory, attention and executive functioning are all included as cognitive symptoms.
-
Negative symptoms: Negative symptoms include blunting of affect , avolition and social withdrawal.
It is widely acknowledged that we cannot recreate the complicated symptom profile of schizophrenia in animal models. However, animal models provide an avenue to invasively explore the role of neurotransmitters and circuitry in psychiatric diseases. To improve the poor predictive validity of treatments in animal models, it is critical that our understanding and the use of animal models evolves alongside our knowledge of schizophrenia neurobiology. The delayed incorporation of new clinical findings to develop better animal models highlights the need for better communication between clinical and basic research communities.
In this article, we discuss the challenges clinicians and researchers are facing in understanding the neurobiology of positive symptoms and psychosis in schizophrenia. We discuss the implications this has for current assessments of positive symptoms in rodents and propose a more relevant set of tests for future study. Finally, the need for a joint focus on bi-directional translation between clinical and basic research is outlined.
Recommended Reading: Can Eating Disorders Cause Acne
Studying The Brain Of Someone With Schizophrenia
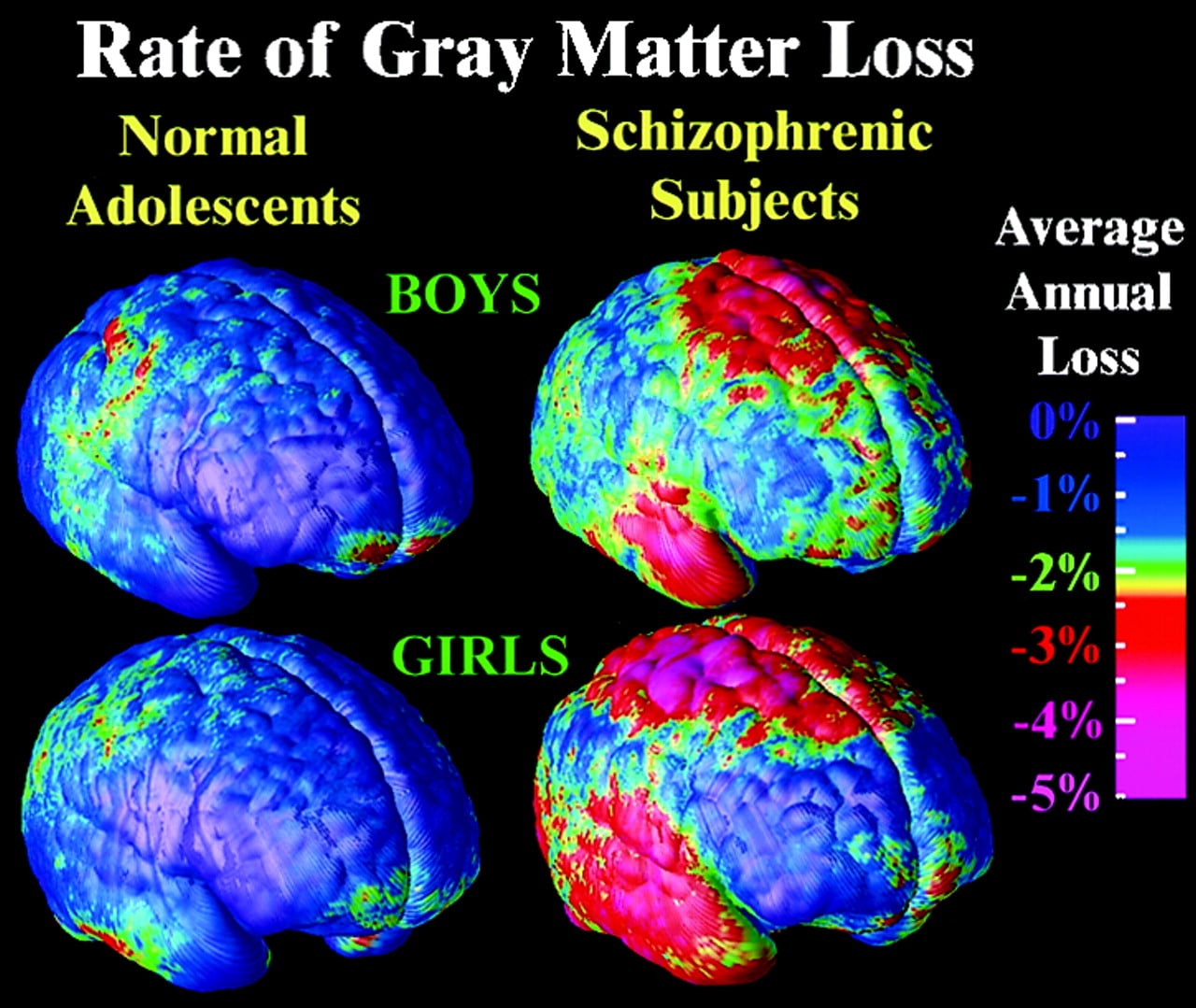
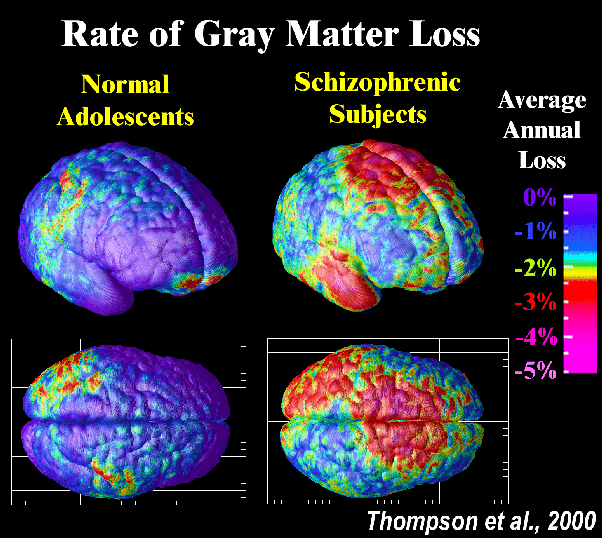
Over the past decade, several brain-imaging studies have shown evidence of structural abnormalities in patients with schizophrenia, providing researchers with clues to the root biological causes of the disease and how it progresses.
One 15-year study, partly funded by and published in the American Journal of Psychiatry, revealed that patients at the first episode of psychosis had less brain tissue than healthy individuals. Although the loss appeared to plateau over time, long relapses of psychosis were associated with additional shrinkage.
We knew from earlier post-mortem studies of the brains of people with schizophrenia that they have fewer synapses and neuron branches, which allow neurons to communicate, explains Scott W. Woods, M.D., a professor of psychiatry and the director of the PRIME Psychosis Prodrome Research Clinic at Yale University. So we believe that this is what accounts for the shrinkage of brain tissue were seeing in scans.
While everyone undergoes a normal loss of some gray matterwhich contains neurons and their short branchesduring adolescence, experts theorize that the process may become too fast or aggressive in some people at high risk of schizophrenia, triggering psychosis.
Share
The Broken Brain Circuit At Fault
First, Dr. Brady and team worked with 44 participants who had received a schizophrenia diagnosis. The participants underwent functional MRI scans, which the researchers analyzed to look for changes in brain connectivity that might have an association with schizophrenia symptoms.
After looking at the scans, the team found that people with severe negative symptoms had poorer connectivity between the brains prefrontal cortex, which scientists believe to play a role in determining personality and social behavior, and the cerebellum, which helps control movement.
The researchers did not, however, find any links between a breakdown in this brain circuit and the presence of so-called psychotic symptoms, such as hallucinations and delusions.
Following this initial finding, the investigators were interested in seeing whether they could target and reset this brain network to improve negative symptoms in schizophrenia.
We wanted to find out if we could restore that brain circuit through noninvasive brain stimulation, and if we could, would people get better?, explains co-author Mark Halko, adding, The answer is they absolutely do get better. Its a very provocative finding.
Halko specializes in noninvasive brain stimulation. In this study, he worked with Brady and his team, applying this method specifically to treat the faulty brain network.
Also Check: How Much Disability For Bipolar Disorder
Mental Illness In Children And Adolescents
Mental illness is not uncommon among children and adolescents. Approximately 12million children under the age of 18 have mental disorders. TheNational Mental Health Association has compiled some statisticsabout mental illness in children and adolescents:
- Mental health problems affect one in every five young people at anygiven time.
- An estimated two-thirds of all young people with mental healthproblems are not receiving the help they need.
- Less than one-third of the children under age 18 who have a seriousmental health problem receive any mental health services.
- As many as 1 in every 33 children may be depressed. Depression inadolescents may be as high as 1 in 8.
- Suicide is the third leading cause of death for 15- to 24-years-oldsand the sixth leading cause of death for 5- to 15-year-olds.
- Schizophrenia is rare in children under age 12, but it occurs inabout 3 of every 1,000 adolescents.
- Between 118,700 and 186,600 youths in the juvenile justice systemhave at least one mental illness.
- Of the 100,000 teenagers in juvenile detention, an estimated 60percent have behavioral, cognitive, or emotional problems.
Early Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
Because early treatment is thought to be most effective for schizophrenia, researchers are continually looking for ways to detect it before symptoms fully develop.
Hallucinations and delusions are the hallmark symptoms of psychosis and must be present for a diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Although psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations or delusions are the most common aspects that present in schizophrenia, there are several symptoms involved. People with schizophrenia experience:
- Positive symptoms: The appearance of things that should not be there, like hallucinations, delusions, and thought disorder .
- Negative symptoms: The absence of things that should be there, like loss of motivation, disinterest or lack of enjoyment in daily activities, social withdrawal, difficulty showing emotions, and difficulty functioning normally.
- Cognitive symptoms: Problems with attention, concentration, and memory.
Assessment of these symptoms is typically how schizophrenia is diagnosed, but the discovery of brain differences in people with schizophrenia could potentially mean an earlier diagnosis and more effective treatment.
While schizophrenia is usually diagnosed in the late teens to early thirties, subtle changes in cognition and social relationships may be noticeable before the actual diagnosis, even during adolescence. Often these early symptoms are apparent years before a person is diagnosed with schizophrenia.
Some of these early symptoms include:
Read Also: Is Bipolar Genetic Or Developed
How Are Schizophrenic Brains Different
Brain imaging shows that people with schizophrenia have less gray matter volume, especially in the temporal and frontal lobes. These areas of the brain are important for thinking and judgment. Whats more, gray matter loss continues over time.
How does schizophrenia affect memory?
Researchers have long hypothesized that memory problems in schizophrenia stem from disruptions in the brains dorsolateral prefrontal cortex . This area of the brain plays a key role in working memorythe system for temporarily storing and managing information required to carry out complex cognitive tasks.
Economic And Social Impacts
Not all consequences of untreated schizophrenia take place inside the persons body and mind. This serious disorder can affect the patients relationships, financial security, and social standing. People with schizophrenia are more likely to:
- Social withdrawal: One of the symptoms of schizophrenia is isolating oneself from others. Without a concentrated effort from loved ones, it can be impossible for people with schizophrenia to maintain healthy, meaningful relationships.
- Become a victim: Although many people believe that those with schizophrenia are more likely to perpetrate violent crime, the opposite is true. While some people with the disorder act out in violence, they are much more likely to become the victims of violent crime than the general population.
- Experience homelessness: Several schizophrenia symptoms can make it hard to get and keep a job. As such, people with the disorder often find it difficult to pay their bills and can end up without a home of their own. Some such people stay with friends and family. However, others end up living in homeless shelters or on the streets.
- Abuse alcohol and drugs: Schizophrenia can be difficult to live with, even when a person is on medication and seeking treatment. Without this help, patients may try to self-medicate and use substances to drown out the symptoms. This can lead to dependence on alcohol and illicit substances.
You May Like: How To Avoid Social Phobia
The Default Mode Network
When weâre just hanging out — the dishes are done, weâve finished our homework, or we’ve completed a tough project at work — our thoughts are free to roam. This âdefault modeâ allows us time to daydream, reflect, and plan. It helps us to process our thoughts and memories. Scientists call this the default mode network. When weâre not focused on a given task, it âlights up.”
If you have schizophrenia, your default mode network seems to be in overdrive. You may not be able to pay attention or remember information in this mode, one study shows.
Chemical Changes In The Brain
A series of complex interrelated chemicals in the brain, called neurotransmitters, are responsible for sending signals between brain cells.
Low levels or imbalances of these chemicals are believed to play a role in the development of schizophrenia and other mental health conditions.
Dopamine, in particular, seems to play a role in the development of schizophrenia.
Researchers have found evidence that dopamine causes an overstimulation of the brain in people with schizophrenia. It may account for some of the symptoms of the condition.
Glutamate is another chemical thats been linked to schizophrenia. Evidence has pointed toward its involvement. However, there are a number of limitations to this research.
Complications before and during birth may increase the likelihood a person will develop mental health disorders, including schizophrenia.
These complications include:
Because of the ethics involved in studying pregnant women, many of the studies that have looked at the connection between prenatal complications and schizophrenia have been on animals.
Women with schizophrenia are at an increased risk for complications during pregnancy.
Its unclear if their children are at an increased likelihood for developing the condition because of genetics, pregnancy complications, or a combination of the two.
Recommended Reading: Can Birth Control Make You Depressed And Anxious
Brain Volume Abnormalities In Schizophrenia
Cerebral tissue of the brain is also impacted by a diagnosis of schizophrenia. Significant shrinkage or enlarged fluid-filled areas in the cerebral cortex are common in the brains of those with schizophrenia.
Studies involving brain images of those diagnosed with schizophrenia show decreased gray matter brain volume and enlarged lateral and third ventricles. These brain abnormalities can cause issues with judgment and decision-making since they involve the areas of the brain that control these tasks.
Gray matter is theneural tissue of the brain that contains nerve-cell bodies and nerve fibers.
Lateral and third ventricles, wikimedia.commons.com
Increased fluid in the brain is part of the reason for these changes in brain volume and size in those with schizophrenia. Excess fluid in the brain can cause issues that range from headaches to more severe issues such as alterations to the immune system.
Brain scans, Wikimedia Commons
The Stigma Of Mental Illness7
“The last great stigma of the twentieth century is the stigma of mentalillness.”
âTipper Gore, wife of the former U.S. Vice President
Words can hurt. Many derogatory words and phrases are used in relation tomental illness. However, these words maintain the stereotyped image and notthe reality about mental illness. Try not to use these words, and encouragestudents not to use them.
“Mentally ill people are nuts, crazy, wacko.” “Mentally ill people are morally bad.””Mentally ill people are dangerous and should be locked in an asylum forever.””Mentally ill people need somebody to take care of them.” How often have we heardcomments like these or seen these types of portrayals in movies, television shows,or books? We may even be guilty ofmaking comments like them ourselves. Is there any truth behind these portrayals, oris that negative view based on our ignorance and fear?
Stigmas are negative stereotypes about groups of people. Common stigmasabout people who are mentally ill are
- Individuals who have a mental illness are dangerous.
- Individuals who have a mental illness are irresponsible and can’t makelife decisions for themselves.
- People who have a mental illness are childlike and must be taken care ofby parents or guardians.
- People who have a mental illness should just get overit.
Providing accurate information is one way to reduce stigmas about mentalillness.
Read Also: How To Treat Depression Naturally
What Is Schizophrenia Or Paranoid Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a challenging brain disorder that often makes it difficult to distinguish between what is real and unreal, to think clearly, manage emotions, relate to others, and function normally. It affects the way a person behaves, thinks, and sees the world.
The most common form is paranoid schizophrenia, or schizophrenia with paranoia as its often called. People with paranoid schizophrenia have an altered perception of reality. They may see or hear things that dont exist, speak in confusing ways, believe that others are trying to harm them, or feel like theyre being constantly watched. This can cause relationship problems, disrupt normal daily activities like bathing, eating, or running errands, and lead to alcohol and drug abuse in an attempt to self-medicate.
Many people with schizophrenia withdraw from the outside world, act out in confusion and fear, and are at an increased risk of attempting suicide, especially during psychotic episodes, periods of depression, and in the first six months after starting treatment.
Take any suicidal thoughts or talk very seriously
If you or someone you care about is suicidal, call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline in the U.S. at 1-800-273-TALK, visit IASP or Suicide.org to find a helpline in your country, or read Suicide Prevention.