Those Suffering From Schizophrenia Must Have Medical Records That Show How They Are Limited In Functioning Socially Focusing On Tasks Or In Other Ways
Schizophrenia is a serious, psychotic mental disorder that may make it difficult to think logically, interact socially in a normal way, control behavior, and distinguish between reality and delusions/hallucinations. Schizophrenia is a spectrumdisorder, meaning that the types and severity of symptoms may vary greatly between individuals, especially taking into account different responses to treatment. Although some people with schizophrenia respond well enough to medications to perform some type of work, there are many others who cannot.
While schizophrenia is a common psychotic disorder seen by Social Security, there are similar disorders involving different degrees of psychosis that may also quality for disability benefits, such as:
- schizotypal disorder
- substance/medication-induced psychotic disorder, and
- psychotic disorder due to another medical condition.
As with all mental impairments, Social Security is more interested in what functional limitations a disability applicant has, after trying medical treatment, than what specific psychotic diagnosis the applicant has been given.
What Are The Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia has a large variety of symptoms and can seem very different in one person from another. If its not treated, schizophrenia may lead to long-term psychosis.
The main symptoms of schizophrenia are:
- hallucinations
- delusions
- confused thinking: thoughts are jumbled and the person cant make sense of what other people are saying.
Someone with schizophrenia will have symptoms for more than 6 months. They may have unusual ideas or beliefs about themselves or the world around them, which may be frightening.
What Triggers Schizophrenia
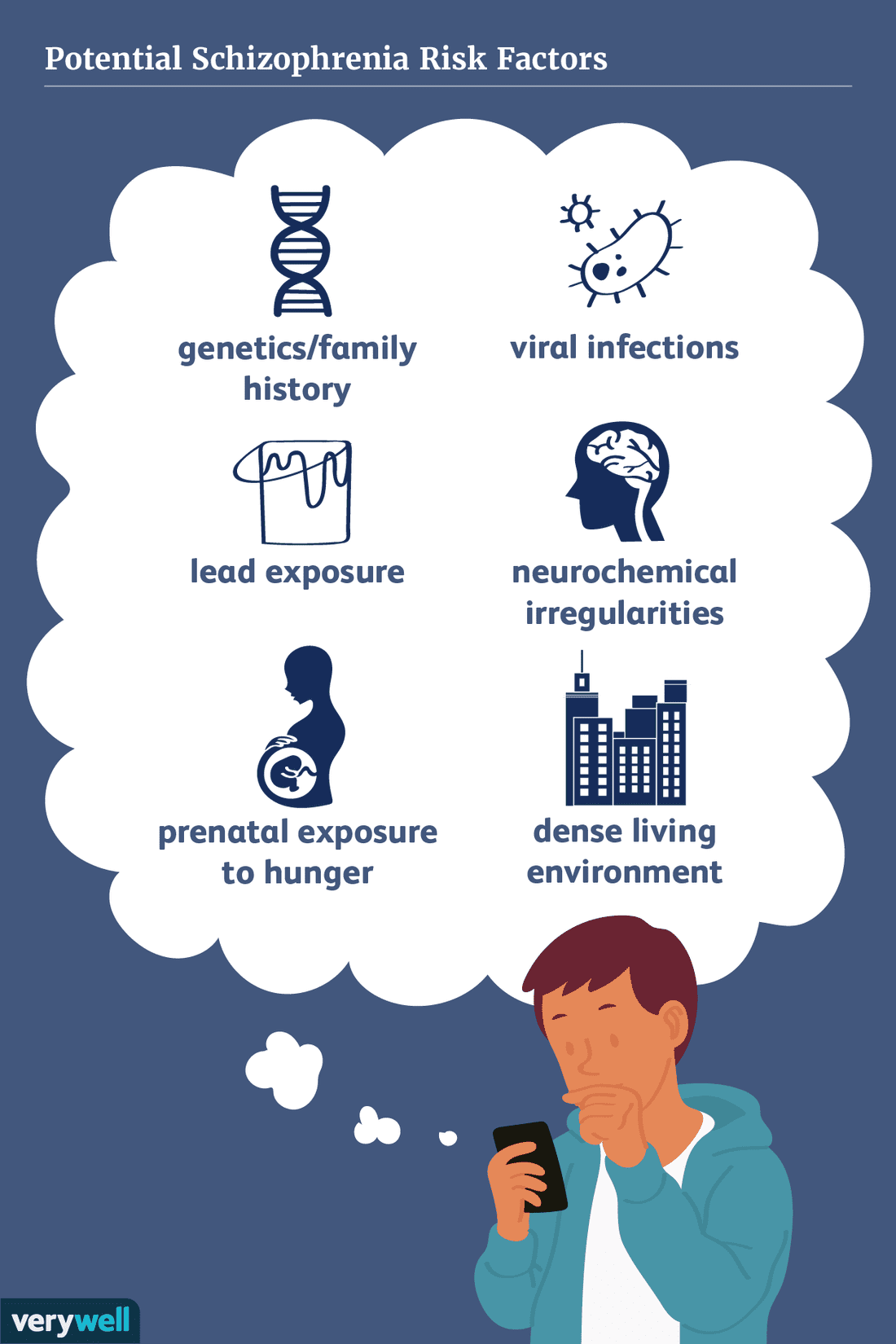
The exact causes of schizophrenia are unknown. Research suggests a combination of physical, genetic, psychological and environmental factors can make a person more likely to develop the condition. Some people may be prone to schizophrenia, and a stressful or emotional life event might trigger a psychotic episode.
Don’t Miss: Late Onset Schizophrenia
When Should I See My Doctor
Some people with schizophrenia do not realise they have a problem or avoid health professionals if they have paranoid thoughts. Its important to get professional help to manage schizophrenia. If you or someone you know seems to be experiencing signs of schizophrenia, see your doctor as soon as possible.
It can be hard to recognise signs of schizophrenia at first, but over time the changes in someones thinking and behaviour may get worse.
See a doctor if you or someone you know:
- gets very preoccupied with something
- starts talking or writing very fast, or is talking much less than normal
- seems muddled, irrational or is hard to understand
- withdraws from normal activities
- is hyperactive or starts behaving recklessly
- laughs or cries inappropriately, or cannot laugh or cry or express happiness
- doesnt look after their personal hygiene
- develops depression or anxiety
Although the majority of people with schizophrenia are not violent, severe symptoms can cause some people to have thoughts of suicide or harming others. If you think someone may be at risk of suicide or violence, call triple zero .
ASK YOUR DOCTOR Preparing for an appointment? Use the Question Builder for general tips on what to ask your GP or specialist.
Where To From Here
- Contact an Early Psychosis Intervention program in your region. Note you do not need a referral and can contact the program directly.
- If there is no early psychosis intervention program in your area, then call and ask for the number of your local mental health team. They can also help you.
For additional information about options for support and treatment in BC, visit our interactive Ask Kelty Mental Health tool, where you can type in the questions you have about accessing services and supports.
Read Also: What Is The General Population’s Risk Of Developing Schizophrenia
Here Are Some Things You Can Do To Help Your Loved One:
- Help them get treatment and encourage them to stay in treatment
- Remember that their beliefs or hallucinations seem very real to them
- Tell them that you acknowledge that everyone has the right to see things their way
- Be respectful, supportive, and kind without tolerating dangerous or inappropriate behavior
- Check to see if there are any support groups in your area
Some symptoms require immediate emergency care. If your loved one is thinking about harming themselves or others or attempting suicide, seek help right away:
- Call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 1-800-273-TALK or text the Crisis Text Line .
Genetic Causes Of Schizophrenia
Many genes play a role in your odds of getting schizophrenia. A change to any of them can do it. But usually, itâs several small changes that add up and lead to a higher risk. Doctors arenât sure how genetic changes lead to schizophrenia. But theyâve found that people who have the disorder may be more likely to have problems in their genes that may interfere with brain development.
You May Like: When Does Schizophrenia Develop In Females
Is There A Specific Window Of Vulnerability During Pregnancy That Increases Schizophrenia Risk
In terms of brain development, pregnancy has an orderly sequence of definable stages. Therefore, an important factor to consider is whether there are specific stages of pregnancy that are more vulnerable? In respect to obstetric complications, most studies have focused on adverse events during labour. Far fewer have examined adverse events earlier in pregnancy. Although prenatal hypoxia induced by maternal smoking is a well-described schizophrenia RF, there is no convincing study indicating any particular pregnancy stage is the most vulnerable. However, it is likely that maternal smoking may diminish once pregnancy is confirmed, suggesting that smoking induced prenatal hypoxia may be more common in the earlier stages of pregnancy.
With respect to influenza, the risk of schizophrenia is increased sevenfold if the mother was exposed in the first trimester with no increase at later gestational ages, however, this was only statistically significant when the first half of pregnancy was considered. Reproductive tract infections also increase the incidence of schizophrenia in offspring but only when infection occurs either at conception or in the first few weeks of pregnancy as infection at later stages did not increase risk.
Disturbances Of Early Development
Prospectively collected measures of premorbid function have consistently revealed neuromotor abnormalities and developmental delays. In the British 1946 Birth Cohort pre-schizophrenic children were found to have delayed motor and speech development by the age of 2 years. In the Northern Finland 1966 Birth Cohort the ages that children learned to stand, walk and become potty-trained were related to subsequent risk for schizophrenia and other psychoses earlier milestones reduced the risk, whereas later milestones increased it. Cannon et al.showed, in a birth cohort from New Zealand, that children who went on to develop schizophreniform disorder had persistently poor motor function over repeated measurements in childhood. In an innovative study using home movies filmed during childhood, pre-schizophrenic individuals could be differentiated from their healthy siblings by viewers who were blind to the psychiatric outcomes.
Recommended Reading: Faint From Anxiety
What Role Do Epigenetic Factors Play In Schizophrenia And Could This Affect Brain Development
As previously mentioned most genetic variance in schizophrenia is in non-coding, potentially regulatory areas of the genome. In general, during development the more well-studied epigenetic processes such as DNA methylation and histone acetylation control the availability of the local chromatin environment for transcription and along with small non-coding RNA species help cells to maintain a differentiated state,. Here, I will discuss the epigenetic factors implicated in schizophrenia which may also have implications for developing brains.
In general, the genome becomes progressively more methylated with age. This has been recently confirmed for genes related to brain development, i.e. neuron differentiation and axonogenesis in the human prefrontal cortex . However more importantly when these authors examined CpG sites within schizophrenia GWAS-implicated variants, this CpGs were more highly methylated and this finding was driven by sites that were more heavily methylated in foetal compared with adult life. Importantly, reanalysis of such methylation patterns in adult PFC from patients with schizophrenia showed no such association. This work was largely replicated by a separate group that found the GWAS-significant loci were more than four times likely to be methylated in the foetal brain compared to regions unrelated to schizophrenia.
What Is The Root Cause Of Schizophrenia
The exact causes of schizophrenia are unknown. Research suggests a combination of physical, genetic, psychological and environmental factors can make a person more likely to develop the condition. Some people may be prone to schizophrenia, and a stressful or emotional life event might trigger a psychotic episode.
You May Like: Can Anxiety Cause High Blood Sugar
How Likely Are You To Get Schizophrenia
schizophrenia
If one parent has the condition, it raises your chances of developing schizophrenia by about 13 percent. If your identical twin has the illness, you have a roughly 50 percent chance of developing schizophrenia. If both of your parents have schizophrenia, you have a 40 percent likelihood of developing the illness.
Beside above, how does schizophrenia start? Symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions usually start between ages 16 and 30. Men tend to experience symptoms earlier than women. Most of the time, people do not get schizophrenia after age 45.
People also ask, how do you know if you are susceptible to schizophrenia?
The most common early warning signs include:
What percentage of the population has schizophrenia?
1 percent
How Do Validated Genomic Variants In Schizophrenia Affect Brain Development

Schizophrenia is clearly familial. The heritability of schizophrenia is estimated to be as high as . Early studies on small, genetically homogenous populations produced findings suggesting single nucleotide polymorphisms, copy errors or splicing variants were increased in genes that could be plausibly associated with schizophrenia. These became known as candidate gene studies. Perhaps the most famous of these candidates was a translocation error in Disrupted in Schizophrenia 1 . Much interest was generated regarding this gene due to its numerous functions in neuronal development. While much has been learnt regarding the role of candidate genes in brain development and function, follow up studies in broader patient populations invariably failed to replicate any such association. Following many such false dawns with other such candidates the field had to recognise that schizophrenia was a polygenetic disorder of multiple variants of small effect.
Finally, one group has now used deep sequencing technology to assess gene transcript variants induced by gene splicing and shown that the isoforms of commonly expressed genes in brain change from foetal to adult life. Importantly it would appear that the isoforms expressed in the adult brains of patients with schizophrenia more closely resemble the foetal state. The genes with these isoform shifts were significantly enriched for neurodevelopmental and cellular signalling processes.
Also Check: Effects Of Phobia
Premorbid Cognitive And Scholastic Performance
Schizophrenia patients, when considered as a group, have intellectual impairments, some of which predate the onset of psychotic symptoms. Individuals who later develop schizophrenia have been found to perform below average on standardized measures of intelligence in childhood, adolescence and young adulthood, and to show lower premorbid IQ than the general population The lower the IQ, the higher is the risk for later development of schizophrenia.
Poor school performance can be seen as a premorbid sign. Repeating a grade, difficulties in completing the final level of schooling, and social and behavioural difficulties have also been found to be risk factors for developing schizophrenia. In the Northern Finland 1966 Birth Cohort, 14-year-olds who were below their expected normal grade were three times more likely to develop schizophrenia than those in their normal grade, but low school marks did not predict schizophrenia. Developmental continuity, indicated by early developmental deviation in the first year of life associated with lower school performance at age 16 years, has been found to be stronger among children who develop psychoses later in life than among normal controls and those admitted to hospital for non-psychotic psychiatric disorder.
What Are The Different Types Of Schizophrenia
Prior to 2013, schizophrenia was divided into five subtypes as separate diagnostic categories. Schizophrenia is now one diagnosis.
Although the subtypes are no longer used in clinical diagnosis, the names of the subtypes may be known for people diagnosed prior to the DSM-5 . These classic subtypes included:
- paranoid, with symptoms such as delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized speech
- hebephrenic or disorganized, with symptoms such as flat affect, speech disturbances, and disorganized thinking
- undifferentiated, with symptoms displaying behaviors applicable to more than one type
- residual, with symptoms that have lessened in intensity since a previous diagnosis
- catatonic, with symptoms of immobility, mutism, or stupor
According to the DSM-5, to be diagnosed with schizophrenia, two or more of the following must be present during a 1-month period.
At least one must be numbers 1, 2, or 3 on the list:
Also Check: What Is Phobia Mean
Animal Models Of Obstetric Complications/hypoxia: Impact On The Developing Brain
Pre-natal hypoxia can be modelled in terms of severity and duration using specially designed chambers. Acute perinatal hypoxia is mimicked by brief exposure of rat newborns to 100% nitrogen atmosphere, whereas perinatal hypoxia-induced by prolonged labour has been modelled by caesarean section followed by immersion of the uterus in a water bath for a prescribed time. Placental insufficiency or pre-eclampsia have been modelled in guinea pigs by inducing intrauterine artery restriction to reduce nutrient flow to the placenta. Such models also induced widespread growth restriction and have now fallen out of favour.
Both pre- and peri-natal hypoxia models produce impairments in pre-pulse inhibition, social behaviours and cognitive deficits i.e. working memory and consistent with other developmental RF models, sensitivity to DA-releasing agents. They also appear to produce generalised cellular loss across the brain, diminished neuronal branching, alterations in DA release in response to psychomimetics, increases in tyrosine hydroxylase the rate-limiting enzyme in DA synthesis and other indices of DA dysfunction . Currently, there is a paucity of data on embryonic brains subjected to pre- or peri-natal hypoxia.
The Dopamine Theory Of Schizophrenia
The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia is a model used by scientists to explain many schizophrenic symptoms. The model claims that a high fluctuation of levels of dopamine can be responsible for schizophrenic symptoms. The simplest version of this theory suggests that schizophrenia is associated with an increase of dopamine in the central nervous system.
Additional research has identified two dopamine pathways in particular that are associated with the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. The first is the mesolimbic system, which affects areas regulating reward pathways and emotional processes the second is the mesocortical system, which affects the prefrontal cortex, areas that regulate cognitive processing, and areas involved with motor control. Excess activity in the mesolimbic pathway and lack of activity in the mesocortical pathway are thought to be responsible for positive and negative symptoms, respectively.
The dopamine hypothesis has helped progress the development of antipsychotics, which are drugs that stabilize positive symptoms by blocking dopamine receptors. The fact that these medications have been shown to treat psychosis supports the dopamine theory.
Also Check: Clown Phobia Definition
Some Models Produce Early Alterations In Gaba/glutamatergic Systems
Many of these developmental RFs also affect GABA and glutamate function in adult offspring. However, there is minimal data on how these RFs affect the early development of these neurotransmitter systems. Perhaps the best evidence comes from studies of prenatal hypoxia. Prenatal hypoxia alters embryonic cortical GABA cell number and positioning up to P2 in the cortex but this reverses from P4. Prenatal hypoxia at GD17 in mice also induces an immediate reduction in foetal cerebral cortex levels of the GABA synthesising enzyme, glutamate decarboxylase. Prenatal hypoxia also upregulates the NR1 subunit of the NMDA receptor for up to 3 days post exposure in white matter microglia but this is reversed from 7 days post exposure.
There is no evidence of effects of MIA on glutamate and GABA systems in the developing brain. Effects on adult brain however are clearly dependent on the timing of exposure. While MIA has no long lasting effect on glutamate or GABA levels, exposure at later gestational ages such as GD17 leads to alterations in GABA and NMDA NR1 subunit expression in juveniles and adult offspring,,. Earlier gestational exposures, however, have little to no effect on this neurotransmitter systems.
Epidemiologically Validated Rfs: Convergent Processes Affecting Brain Development
The developmental animal models discussed here all produce robust behavioural phenotypes of relevance to the positivenegative and cognitive symptoms of the disease in adult animals. These overlapping phenotypes suggest an early common pathogenic mechanism/s. Unfortunately, apart from a concentrated effort to understand early brain changes in the MIA and DVD-deficient models, there has been far less focus on the developing brain in the other models. However, certain themes are emerging.
Also Check: Depression Appetite Loss
Cannabis And Other Substance Use
Substance use is highly prevalent in psychotic patients . There is good evidence that psychostimulants can induce psychosis . There also have been a few suggestions that alcohol misuse and psychosis might be associated , and recently, a meta-analysis raised the question of whether tobacco use could be a risk factor for psychosis . However, much greater evidence points to an important aetiological role for cannabis use. Prospective epidemiological studies consistently report an association between cannabis use and schizophrenia with an estimated two- to threefold increased risk . A doseresponse relationship between extent of use and risk of psychosis has been shown in a meta-analysis . The association is stronger in those individuals who used cannabis earlier , and who used high potency tetrahydrocannabinol cannabis or/and more frequently . Indeed, the EU-GEI study has found that if high-potency cannabis was no longer available, around 12% of first-episode psychosis cases across 11 Europe-wide sites could be prevented, rising to 30% in London and 50% in Amsterdam . The age at which cannabis use begins appears to correlate with the age at onset of psychosis while persistent cannabis use after a first episode is associated with poorer prognosis , higher relapse rates, longer hospitalizations, and severe positive symptoms .