First Episode Of Psychosis
The first episode of psychosis refers to when you first show signs of being unable to distinguish whats real from what isnt. It typically involves hallucinations and delusions, which can seem very real to the person experiencing them.
Experts say the average age at which people first experience psychosis is 24 years old. The oldest age of onset was 63 years and the youngest age was 3 years.
Acting quickly to connect yourself or your loved one with the right treatment during early psychosis can help dramatically. If you are a family member or friend, consider reaching out to a healthcare professional on behalf of the person you care about.
Schizophrenia Voices Or Thoughts
Hearing voices that aren’t there is a common sign of severemental illness. These experiences, however, may be frequent in thenon-help-seeking population, prompting some to argue the existence of apsychotic continuum from health to sickness.
A data synthesis from 100 clinical cases, 80 percent ofwhich had a diagnosis of schizophrenia or another psychotic disease, isprovided.
In 94 percent of instances, it was possible to clearly define theunderlying emotional conflicts reflected by the voices e.g., low self-worth,anger, shame and guilt.
In 78 percent of instances, representations for voiceidentity e.g., disowned elements of self, a family member, a former abuser weredeveloped.
It is suggested that many people hear voices that makepsychological sense in the context of life events, and that this knowledge maybe professionally used to help them recover.
Why Sex Differences In Schizophrenia
1Beijing Key Laboratory of Mental Disorders, Beijing Anding Hospital Capital Medical University, Beijing 100088, China
2Center of Schizophrenia, Beijing Institute for Brain Disorders, Beijing 100069, China
3Center for Hormone Advanced Science and Education, Roskamp Institute, Sarasota, FL 34243, USA
You May Like: What Is A Phobia Of Spoons Called
Early Warning Signs And Symptoms
Usually, a person with schizophrenia has gradual changes in their thoughts and perceptions. Families are often the first to see early signs of psychosis and schizophrenia in a loved one.
Before the first episode of psychosis, you go through what is known as a premorbid period. This is the 6 months before the first symptoms of psychosis. During this period, you might experience gradual changes.
Although sleep disturbances are not included in the diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia, people with the condition consistently report them.
Early warning signs include:
Social And Environmental Factors
Social cognition and social functioning
Premorbid social functioning and social cognition, robust predictors of relapse in this population, differ significantly between men and women. Men have poorer overall premorbid social functioning and social cognition, which is associated with higher rates of isolation, loneliness, and lower quality of life. Social cognitive and functional deficits are also related to the increased expression of negative symptoms observed in men. Additionally, these factors are also associated with reduced social network size and lower marriage rates in men with schizophrenia compared to women. Younger age at onset in men may also negatively impact community reintegration following the illness onset by delaying the development of life skills necessary to develop strong social support networks and foster self-perceptions of efficacy and agency.
Substance abuse and dependence
Read Also: Celine Dion Anorexic
The Phases And Recovery Of Schizophrenia
Recovery from psychotic episodes is not something that can be predicted. Some people may only experience one psychotic episode that is full-blown. Others have several different episodes. Some people may recover completely, however it is recommended that patients continue with lifelong treatment and support so as to avoid relapsing.
The Age Of Onset In Men And Women
Its hard to pinpoint the exact onset of schizophrenia because people may have cognition problems or trouble in social relationships long before they are officially diagnosed. In general, schizophrenia is diagnosed in late adolescence through the early 30s.
Men are usually diagnosed between the late teens and early 20s, with a peak at 21-25 years of age. Women are diagnosed a few years later, at 25-30 or again after menopause.
The ages are just a guide. No matter when you notice any of the signs or symptoms of schizophrenia in yourself or a loved one, its important to get diagnosed and treated as soon as possible. Symptoms include confusion, disorganized speech, and hallucinations .
At Allied Psychiatry & Mental Health, board-certified psychiatrist Dr. Hadi Estakhri helps his patients live better quality lives through symptom management.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Women Tend To Develop Symptoms Of Schizophrenia Later Than Men And Often Exhibit Different Symptoms
Article by:SymptomsChallengesTreatment
There is no disparity in the occurrence and prevalence of schizophrenia between men and women, though schizophrenia is more closely associated with younger men. This may be due to the fact that women are more likely to experience the onset of schizophrenia later than men. Women tend to develop symptoms in their late 20s whereas the onset in men is typically in their early 20s.1 Also, because women with schizophrenia tend to be more socially active, their schizophrenia may be less detectable.
Early Warning Signs Of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia can be hard to diagnose for a few reasons. One is that people with the disorder often don’t realize they’re ill, so they’re unlikely to go to a doctor for help.Another issue is that many of the changes leading up to schizophrenia, called the prodrome, can mirror other normal life changes. For example, a teen who’s developing the illness might drop their group of friends and take up with new ones. They may also have trouble sleeping or suddenly start coming home with poor grades.
Some research suggests that if a doctor strongly thinks someone is getting the disorder while still in this early phase, low doses of antipsychotic medication might delay it. More studies need to be done to know whether these drugs work for young people at risk for the disease. Cognitive behavioral therapy, family therapy, and social skills training appear to have clearer benefits for them, at least in the short term, when used early on. Learn more about the prodrome phase of schizophrenia.
Read Also: Can Depression Make You Lose Your Appetite
Life Challenges For Women With Schizophrenia
Typically, women with schizophrenia function better socially than men, often because a later age of onset indicates a less severe form of mental illness. Women with schizophrenia are likely to experience fewer hospitalizations and shorter visits while in the hospital compared to men. Some researchers believe that this later onset is because hormones like estrogen have a protective effect.4 However, this disparity in the age of onset is not present in all ethnic groups. For example, multiple studies in the country of India have found no difference in the mean age of onset between men and women.5
Sex Differences In Age At Onset
While men and women have similar prevalence of Schizophrenia, most of studies demonstrated that female onset is typically 3â5 years later than males. It is now accepted that men has a single peak age for onset which is between 21 and 25 years old and women have two peaks age of onset, one between 25 and 30 years old and another one is after 45 years old as shown in . It is also observed that women with schizophrenia are more associated with seasonality of first admissions as compared to schizophrenic men. The delayed two peaks of onset ages in women have been consistent with other studies which reported that women make up 66%â87% of patients with onset after the age of 40â50 years.
Sex differences in onset age of schizophrenia
Note: Men have a notable peak of incidence in late adolescence and a subsequent sharp decline into middle age. The peak age of incidence rates in women appears in adolescence as well as after 45 years old.
Read Also: The Definition Of Phobia
How You Get A Diagnosis
If you or someone you love shows any of these signs, see a doctor right away. The symptoms of prodrome are subtle and easy to miss. Many also overlap with other mental health issues, like depression and substance misuse.
To rule out other health problems, your doctor may order lab tests and imaging tests. You’ll also be asked to answer detailed questions about your health, feelings, thoughts, and daily habits. How you respond will help your doctor decide if you are in a schizophrenia prodrome and if so, what kind.
To reach the right diagnosis, your family doctor may refer you to a psychiatrist who treats schizophrenia.
Sex Differences In Schizophrenia
Sex differences in schizophrenia are widely reported. Men and women exhibit different rates of incidence and prevalence, age at onset, symptom expression, course of illness, and response to treatment. Reviews of the literature suggest that understanding the implications of sex differences on schizophrenia may help inform individualized treatment and positively affect outcomes.
Read Also: Spasmenagaliaphobia
Cognitive Symptoms & Thinking Problems
These symptoms reflect how well the personâs brain learns, stores, and uses information.
Someone with schizophrenia might have a hard time with their working memory. For example, they may not be able to keep track of different kinds of facts at the same time, like a phone number plus instructions.
Along with having trouble paying attention, it can be hard for them to organize their thoughts and make decisions.
Latest Mental Health News
In the 1990’s, new antipsychotic medications were developed. These new medications are called second generation, or “atypical” antipsychotics.
One of these medications, clozapine is an effective medication that treats psychotic symptoms, hallucinations, and breaks with reality. But clozapine can sometimes cause a serious problem called agranulocytosis, which is a loss of the white blood cells that help a person fight infection. People who take clozapine must get their white blood cell counts checked every week or two. This problem and the cost of blood tests make treatment with clozapine difficult for many people. But clozapine is potentially helpful for people who do not respond to other antipsychotic medications.
Other atypical antipsychotics were also developed. None cause agranulocytosis. Examples include:
- Skin rashes
- Menstrual problems for women.
Atypical antipsychotic medications can cause major weight gain and changes in a person’s metabolism. This may increase a person’s risk of getting diabetes and high cholesterol. A person’s weight, glucose levels, and lipid levels should be monitored regularly by a doctor while taking an atypical antipsychotic medication.
Typical antipsychotic medications can cause side effects related to physical movement, such as:
- Rigidity
- Tremors
- Restlessness.
How are antipsychotics taken and how do people respond to them?
How do antipsychotics interact with other medications?
Psychosocial treatments
Also Check: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
When Does Schizophrenia Start And Who Gets It
Schizophrenia affects men and women equally. It occurs at similar rates in all ethnic groups around the world. Symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions usually start between ages 16 and 30. Men tend to experience symptoms a little earlier than women. Most of the time, people do not get schizophrenia after age 45. Schizophrenia rarely occurs in children, but awareness of childhood-onset schizophrenia is increasing.
It can be difficult to diagnose schizophrenia in teens. This is because the first signs can include a change of friends, a drop in grades, sleep problems, and irritability — behaviors that are common among teens. A combination of factors can predict schizophrenia in up to 80 percent of youth who are at high risk of developing the illness. These factors include isolating oneself and withdrawing from others, an increase in unusual thoughts and suspicions, and a family history of psychosis. In young people who develop the disease, this stage of the disorder is called the “prodromal” period.
Hospitalizations Before And After Diagnosis
Psychiatric hospitalizations in patients later diagnosed with SSD were assessed during five years before diagnosis. The number and durations of hospitalizations for SSD and prevalence of other psychiatric diagnoses was also determined up to ten years after the index diagnosis. Psychiatric diagnoses were defined on ICD-10 basis . Information on diagnoses were collected from Hospital Discharge Register data and these diagnoses are recorded during hospitalization. Therefore, we use psychiatric diagnoses made during hospitalization as a reflection of total diagnoses.
Recommended Reading: Meaning Of Phobic
Signs That A Teen Has Schizophrenia
Before teenagers show the classic signs of schizophrenia, they often go through whats known as the prodromal period. During this time, teens may exhibit signs such as:
- Steadily increasing the amount of unusual thoughts and actions
- Hanging out with a new group of friends and leaving old friends behind
- Withdrawing from normal social activities
- Making lower grades than usual
- Seeming depressed or irritable
- Sleeping too much or too little
These symptoms are too general to base any diagnosis on. For example, low grades can indicate a number of different problems and irritability can be a normal part of teenage development. However, these symptoms can act as warning signs for parents and other caregivers, who should stay alert for the symptoms of full-blown schizophrenia, including:
- A lack of personal hygiene
- Disorganized communication
- Social skills classes
- Support groups
In some cases, teenagers with schizophrenia need temporary residential treatment. During this time, the teen lives in the treatment facility and professionals monitor them around the clock. They also receive medication management and daily therapy sessions.
You can help your teen by seeking professional help you should not go it alone. First and foremost, you should seek immediate medical attention if your teen has suicidal thoughts or poses a risk to others.
Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia: Things That Might Stop Happening
Negative symptoms refer to an absence or lack of normal mental function involving thinking, behavior, and perception. You might notice:
- Lack of pleasure. The person may not seem to enjoy anything anymore. A doctor will call this anhedonia.
- Trouble with speech. They might not talk much or show any feelings. Doctors call this alogia.
- Flattening: The person with schizophrenia might seem like they have a terrible case of the blahs. When they talk, their voice can sound flat, like they have no emotions. They may not smile normally or show usual facial emotions in response to conversations or things happening around them. A doctor might call this affective flattening.
- Withdrawal. This might include no longer making plans with friends or becoming a hermit. Talking to the person can feel like pulling teeth: If you want an answer, you have to really work to pry it out of them. Doctors call this apathy.
- Struggling with the basics of daily life. They may stop bathing or taking care of themselves.
- No follow-through. People with schizophrenia have trouble staying on schedule or finishing what they start. Sometimes they can’t get started at all. A doctor might call this avolition.
Depression has some of the same symptoms, too. They can be hard to spot, especially in teens, because even healthy teens can have big emotional swings between highs and lows.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Motivated To Exercise When Depressed
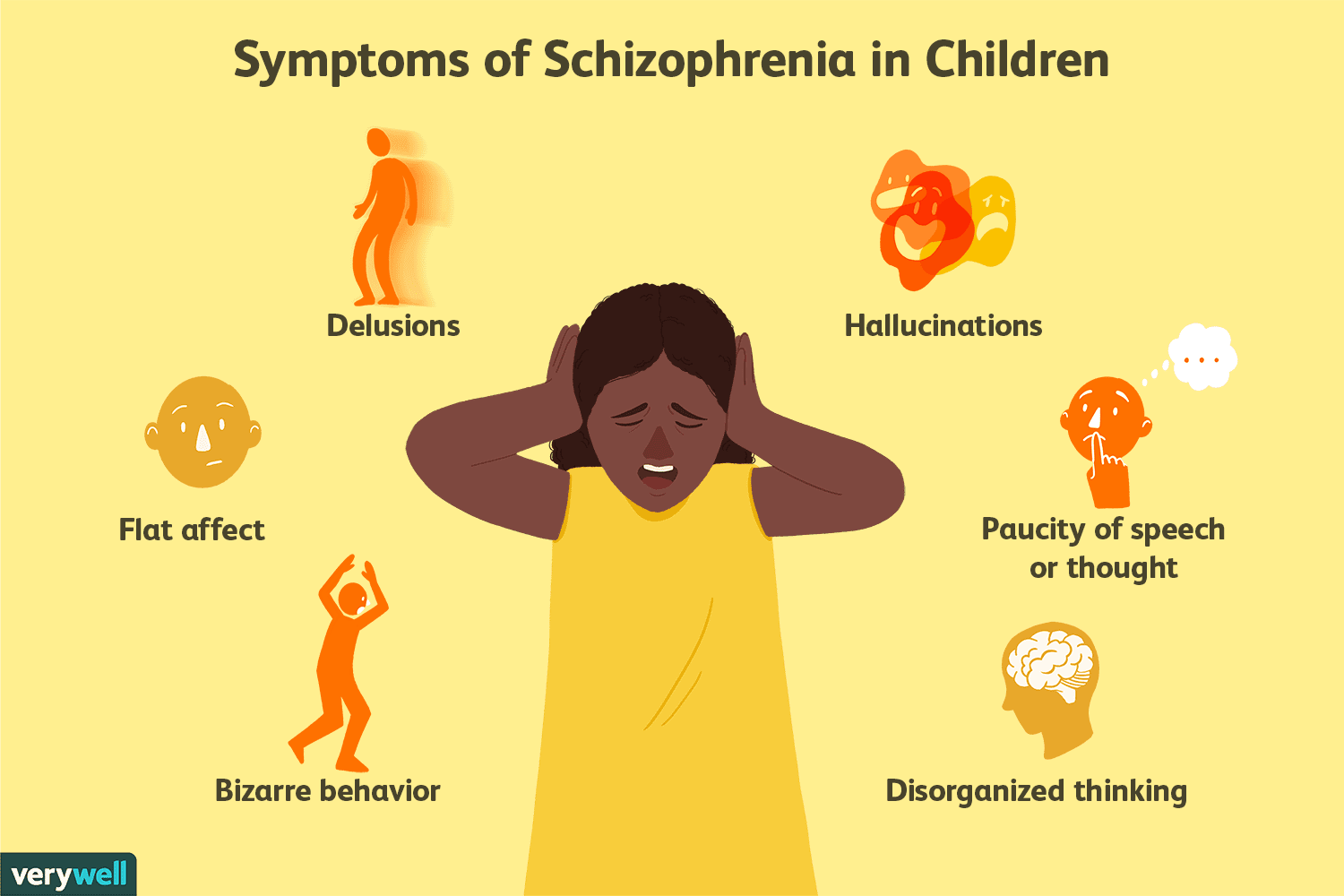
Childhood Schizophrenia Signs And Symptoms
Some children who develop schizophrenia first go through a period called the prodrome or the prodromal phase. They might withdraw from daily life, with more anxiety and less interest in school or friends. Not all children who show these signs will have a psychotic disorder, so itâs important to talk to your doctor if you notice any issues.
Early childhood schizophrenia symptoms
A baby or toddler may have signs of schizophrenia that are different from those in older children, teens, and adults.
The disorder affects how your child develops. You may notice things like:
- Long periods in which theyâre sluggish or not active
- Floppy arms or legs
- Delays in crawling, walking, or talking
- Odd movements such as rocking or flapping their arms
- A limp or slumped posture
Some of these symptoms show up in children with other problems besides schizophrenia. And some happen in kids without any mental health conditions. Only your child’s doctor can figure out what’s really going on.
Later childhood schizophrenia symptoms
In older kids, you might notice the behavior changes of schizophrenia over time or suddenly, as if out of nowhere. Your child may act withdrawn and clingy, or they may talk about strange and disturbed ideas and fears.
Tell your doctor as soon as you see symptoms of schizophrenia. It’s important to get a diagnosis and start treatment before your youngster shows signs of a break from reality, called psychosis.
Symptoms in older children include:
Can Schizophrenia Appear Even Later In Life

While the majority of cases are diagnosed between a persons late teens to early 30s, schizophrenia can still occur later. This is called late-onset schizophrenia.
While research is still limited, more and more people are being diagnosed with schizophrenia later in life. In fact, its believed that a quarter of people with schizophrenia develop it after age 40.
Many researchers currently believe these later diagnoses happen because the person had untreated cognitive obstacles and a small or poor network of support and camaraderie.
You May Like: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
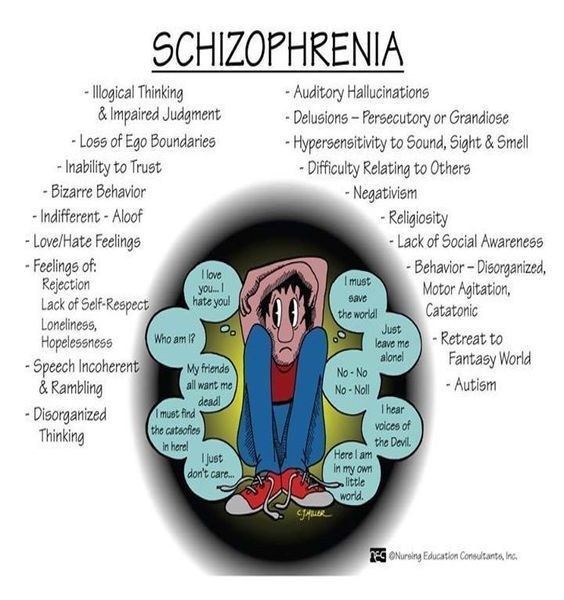
What Are The Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia generally has certain symptoms which must be present for at least 6 months before a diagnosis can be made. These symptoms fall into two main categories: positive symptoms and negative symptoms. Positive symptoms are changes in the way you think or perceive things. Negative symptoms represent a loss of functioning. Examples of each are as follows:
Positive symptoms:
- Hallucinations: Having sensations that others dont have. For example:
- Hearing your name called when no one is around
- Hearing static when you arent near a radio
- Hearing a voice or voices that are not your own
- Seeing things that arent there
- Delusions: Having ideas that are not based in reality. For example:
- Believing you can read peoples minds or they can hear your thoughts
- Believing someone else is controlling your thoughts
- Believing you are extremely special or a gift to the world
- Confused thinking:
- Often losing your train of thought when speaking
- Trouble following conversations
- Trouble paying attention to others because of the thoughts or noises in your head
Negative symptoms:
- New and severe trouble with motivation or getting started on activities
- Loss of interest in social activities, people or the world around you
- Drop in ability to focus, understand or remember things