Continue Learning About Schizophrenia
Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.
What Really Happens In The Brain During A Hallucination
A person can experience visual hallucinations for many reasons, including consuming hallucinogenic substances or as a symptom of schizophrenia. But what are the brain mechanisms that explain hallucinations?
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders defines hallucinations as perception-like experiences that occur without an external stimulus, and which are vivid and clear, with the full force and impact of normal perceptions, not under voluntary control.
While we understand some of the circumstances that cause hallucinations often in the context of substance misuse, mental health conditions, or neurological conditions we are yet to find out the specifics of how these phenomena manifest in the brain.
Recently, a team of researchers from the University of Oregon in Eugene has strived to uncover more information about how hallucinations affect brain activity.
Their new study conducted in mouse models has revealed some surprises, which the investigators
What Occurs In The Brain
| The picture below showsmagnetic resonance image brain scans of a pair of twins:one with schizophrenia, one without schizophrenia. Notice that theventricles are larger in the twin withschizophrenia. |
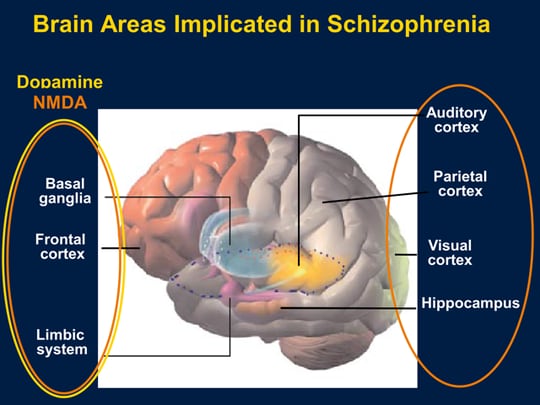
A reduced size of the hippocampus, increased size of the basal ganglia,and abnormalities in the prefrontal cortex are seen in some people withschizophrenia. However, these changes are not seen in all people withschizophrenia and they may occur in people without this disorder.
Recommended Reading: Anxiety From Dehydration
Does My Child Have Schizophrenia
Early signs of schizophrenia can be hard to detect because they often overlap with common adolescent behavior. Moreover, these symptoms in people of any age group do not necessarily mean that a person will develop schizophrenia.
These symptoms can be disruptive though, and they may indicate something worrisome is going on, even if it isn’t schizophrenia. If you or your child are experiencing any of these symptoms, you should make an appointment with a healthcare provider.
How Does Schizophrenia Affect The Body
Schizophrenia is primarily a disease of the mind. Most of its effects are mental or emotional in nature. However, the disease can affect the body in some key ways. Brain modifications cause the disorder to occur, although what causes the brain modifications is unknown. In addition, schizophrenia may cause sufferers to do harm to their physical bodies, as alcohol abuse, violence, and self-destructive behavior are all complications of the disorder.
Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.
Don’t Miss: Feretrophobia Definition
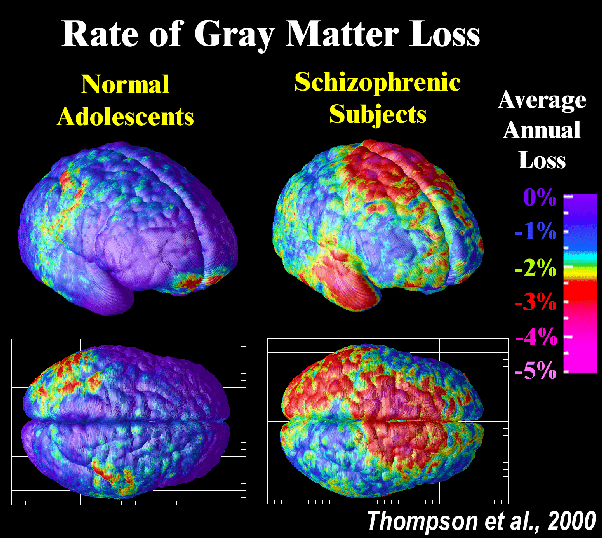
How Schizophrenia Affects The Brain
Its hard to fully understand a mental disease like schizophrenia without peering into the human brain. Now, a study by University of Iowa psychiatry professor Nancy Andreasen uses brain scans to document how schizophrenia impacts brain tissue as well as the effects of anti-psychotic drugs on those who have relapses.
Andreasens study, published in the American Journal of Psychiatry, documented brain changes seen in MRI scans from more than 200 patients beginning with their first episode and continuing with scans at regular intervals for up to 15 years. The study is considered the largest longitudinal, brain-scan data set ever compiled, Andreasen says.
Schizophrenia affects roughly 3.5 million people, or about one percent of the U.S. population, according to the National Institutes of Health. Globally, some 24 million are affected, according to the World Health Organization.
The scans showed that people at their first episode had less brain tissue than healthy individuals. The findings suggest that those who have schizophrenia are being affected by something before they show outward signs of the disease.
The researchers also analyzed the effect of medication on the brain tissue. Although results were not the same for every patient, the group found that in general, the higher the anti-psychotic medication doses, the greater the loss of brain tissue.
This story appeared originally on the Department of Psychiatry website and has been re-purposed for Iowa Now.
Alcohol Drugs Are A Risk
People with schizophrenia are much more likely than other people to abuse alcohol or illicit drugs. Some substances, including marijuana and cocaine, can make symptoms worse. Drug abuse also interferes with treatments for schizophrenia. If you know someone whoâs dealing with that, look for substance abuse programs designed for people with schizophrenia.
Recommended Reading: Schizophrenia Progression
What Happens After You Get The Results From A Schizophrenia Brain Scan
If brain scans are ordered for a person who is showing schizophrenia symptoms, it is usually to rule out or confirm other conditions that could be causing the symptoms.
Whether the scan shows a different condition or plays a part in confirming a diagnosis of schizophrenia, the healthcare provider will discuss treatment options.
Medicines That Treat It
Prescription drugs can reduce symptoms such as abnormal thinking, hallucinations, and delusions. Some people have troubling side effects, including tremors and gaining weight. Drugs may also interfere with other medicines or supplements. But in most cases, medication is a must to treat schizophrenia.
Also Check: Fear Of Long Words Phobia
How Doctors Diagnose It
There are no lab tests to find schizophrenia, so doctors usually base a diagnosis on a personâs history and symptoms. They will first rule out other medical causes. In teens, a combination of family history and certain behaviors can help predict the start of schizophrenia. The period when symptoms first start to arise and before the first episode of psychosis is called the prodromal period. It can last days, weeks or even a years. Sometime it can be difficult to recognize because there is usually no specific trigger. Prodrome is accompanied by what can be perceived as subtle behavioral changes, especially in teens. These behaviors include withdrawing from social groups and expressing unusual suspicions, but thatâs not enough for a diagnosis.
When A Loved One Has It
Relationships can be rocky for people with schizophrenia. Their unusual thoughts and behaviors may keep friends, co-workers, and family members away. Treatment can help. One form of therapy focuses on forming and nurturing relationships. If you are close to someone who has schizophrenia, you may want to join a support group or get counseling yourself, so you can get support and learn more about what they are going through.
Also Check: What Is A Depression Contour
Not The Smoking Gunbut A Piece Of It
The team admits that studying hallucinations in mouse models is not ideal, since, of course, the animals cannot communicate their experience. However, the researchers note that the same types of drugs that cause hallucinations in humans also cause visible movement and behavioral changes in mice.
This, the investigators explain, reasonably suggests that the same drugs alter brain activity in both animals and people. However, future studies should pay closer attention to the animals reactions to visual stimuli in the presence versus the absence of drugs.
I dont feel like weve necessarily found the smoking gun for the entire underlying cause of hallucinations, but this is likely to be a piece of it, Niell says.
The data weve collected will provide a foundation for additional studies going forward. In particular, we plan to use genetic manipulation to study particular parts of this circuit in more detail, the senior researcher adds.
And since previous research has suggested that serotonin 2A receptors which the researchers also targeted in this study are involved in schizophrenia, Niell and team would also like to find out whether their present findings may provide new perspectives regarding the treatment of this and other mental health conditions.
How It Affects Thoughts

People with schizophrenia may have trouble organizing their thoughts or making logical connections. They may feel like their mind is jumping from one unrelated thought to another. Sometimes they have “thought withdrawal,” a feeling that thoughts are removed from their head, or “thought blocking,” when someone’s flow of thinking suddenly gets interrupted.
You May Like: Phobic Definition
Study Reveals How Schizophrenia Affects The Brain
Scientists have discovered how schizophrenia and the use of anti-psychotic drugs can impact brain tissue by reviewing progressive data from brain scans, according to a study published in the American Journal of Psychiatry.
Researchers from the University of Iowa, led by psychiatry professor Nancy Andreasen, analyzed 202 MRI scans of patients who suffer from the mental disorder.
All patients had their scans reviewed from their first schizophrenic episode and at regular 6-month intervals up to a period of 15 years.
The researchers say that as clinical follow-up data was obtained every 6 months, they were able to compute measures of relapse number and duration, and relate these to structural MRI measures.
They note that as higher treatment intensity has previously been linked to smaller brain tissue volumes, this countereffect was measured in terms of dose-years.
Changes In Behaviour And Thoughts
A person’s behaviour may become more disorganised and unpredictable.
Some people describe their thoughts as being controlled by someone else, that their thoughts are not their own, or that thoughts have been planted in their mind by someone else.
Another feeling is that thoughts are disappearing, as though someone is removing them from their mind.
Some people feel their body is being taken over and someone else is directing their movements and actions.
Read Also: Three Phases Of Schizophrenia
Early Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
Because early treatment is thought to be most effective for schizophrenia, researchers are continually looking for ways to detect it before symptoms fully develop.
Hallucinations and delusions are the hallmark symptoms of psychosis and must be present for a diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Although psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations or delusions are the most common aspects that present in schizophrenia, there are several symptoms involved. People with schizophrenia experience:
- Positive symptoms: The appearance of things that should not be there, like hallucinations, delusions, and thought disorder .
- Negative symptoms: The absence of things that should be there, like loss of motivation, disinterest or lack of enjoyment in daily activities, social withdrawal, difficulty showing emotions, and difficulty functioning normally.
- Cognitive symptoms: Problems with attention, concentration, and memory.
Assessment of these symptoms is typically how schizophrenia is diagnosed, but the discovery of brain differences in people with schizophrenia could potentially mean an earlier diagnosis and more effective treatment.
While schizophrenia is usually diagnosed in the late teens to early thirties, subtle changes in cognition and social relationships may be noticeable before the actual diagnosis, even during adolescence. Often these early symptoms are apparent years before a person is diagnosed with schizophrenia.
Some of these early symptoms include:
How Meth Affects The Brain
Methamphetamines increase levels of the neurotransmitters dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine in the brain. Dopamine is associated with pleasure and reward, and the high levels caused by meth encourage you to continue taking the drug.
Many people binge for a short period of time or go on a run, which consists of using it frequently for several days in a row. A meth run is dangerous because people can become malnourished, dehydrated, and sleep-deprived.
Don’t Miss: Fear Of Long Words Phobia Name
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Studies
There is substantial evidence that neurometabolite levels are altered in both schizophrenia and BD. A meta-analysis pooling data from 146 studies suggests decreases in NAA in the frontal lobe, hippocampus, thalamus, and basal ganglia in schizophrenia, but only in the basal ganglia and frontal lobe in BD. Another meta-analysis summarizing findings of glutamatergic abnormalities across 28 studies in schizophrenia revealed a decrease in medial frontal glutamate compared with healthy controls, but the majority of studies were conducted in medicated patients. Contrastingly, several reports do suggest an elevation of glutamatergic indices in unmedicated patients with schizophrenia in the medial prefrontal cortex, striatum, and hippocampus.,,, A smaller meta-analysis in BD including nine studies measuring Glx across different areas of the brain, suggested that this metabolite may be higher in patients with BD compared to controls, irrespective of medication status. Taken together, it appears that some of the neurometabolite alterations, specifically decreased NAA in the frontal cortex and basal ganglia may be shared across the illness spectrum, whereas others may not.
Table 5 Studies examining magnetic resonance spectroscopy
What Are The Symptoms Ofschizophrenia
AmericanPsychiatric AssociationDiagnostic and StatisticalManual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition
When people show any of these five symptoms, they are considered to be inthe “active phase” of the disorder. Oftenpeople with schizophrenia have milder symptoms before and after the active phase.
There are three basic types of schizophrenia. All people who haveschizophrenia have lost touch with reality. The three main types ofschizophrenia are:
Also Check: Define: Phobia
Antipsychotic Medications And The Brain
BACKGROUND PAPER
SUMMARY
Changes in brain structure are caused both by the disease process of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder and by the antipsychotic drugs used to treat these diseases. Different antipsychotic drugs may have different effects.
The structural brain changes caused by antipsychotic drugs used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder are similar in kind to structural brain changes caused by medications used to treat Parkinsons disease, epilepsy and other brain diseases, and it is a mistake to characterize them as an indication that these drugs are dangerous. Many medications widely regarded as beneficial are effective precisely because of their structural impact on the part of the body they treat.
It is also important to study the brain changes caused by antipsychotic drugs because they may shed light on how these drugs work and/or predict the risk of side effects. The merits of antipsychotic use additionally need to be considered within context of the considerable impacts of not using them, which include early mortality and heightened risk for arrest, incarceration, homelessness, victimization and violence, including suicide.
BACKGROUND
Findings that antipsychotic drugs produce structural brain changes should not surprise us. Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder are known to produce structural brain changes as part of the disease process it is reasonable to expect drugs that treat the diseases effectively to do the same.
STRUCTURAL BRAIN CHANGES
Frequently Asked Questions About Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. People with schizophrenia may seem like they have lost touch with reality. Although schizophrenia is not as common as other mental disorders, the symptoms can be very disabling.
Schizophrenia is a severe and debilitating brain and behavior disorder affecting how one thinks, feels and acts. People with schizophrenia can have trouble distinguishing reality from fantasy, expressing and managing normal emotions and making decisions. Thought processes may also be disorganized and the motivation to engage in lifes activities may be blunted. Those with the condition may hear imaginary voices and believe others are reading their minds, controlling their thoughts or plotting to harm them.
While schizophrenia is a chronic disorder, it can be treated with medication, psychological and social treatments, substantially improving the lives of people with the condition.
A moving presentation by Dr. Kafui Dzirasa on Schizophrenia
View Webinar on Identifying Risk Factors and Protective Pathways for Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia affects men and women equally. It occurs at similar rates in all ethnic groups around the world. Symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions usually start between ages 16 and 30.
Learn more about childhood-onset schizophrenia from this expert researcher:
Find answers to more questions about Schizophrenia in our Ask the Expert section.
Read Also: Can You Go To The Er For A Panic Attack
Lack Of Brain Tissue Found In Schizophrenic Patients
Scans from the patients first episode revealed that they had less brain tissue, compared with healthy individuals without the disorder.
The researchers say this finding suggests that something is affecting the brains of those with schizophrenia before they demonstrate obvious symptoms of the conditions.
Prof. Andreasen explains:
There are several studies, mine included, that show people with schizophrenia have smaller-than-average cranial size.
Since cranial development is completed within the first few years of life, there may be some aspect of earliest development perhaps things such as pregnancy complications or exposure to viruses that on average, affected people with schizophrenia.
The brain scans also showed that those who suffer from schizophrenia demonstrated the highest tissue loss in the first 2 years after their first episode, after which point it slowed down significantly.
Prof. Andreasen says that this finding may help doctors to identify the most effective time periods to prevent tissue loss in schizophrenic patients, as well as other effects caused by the disorder.
Additional Consultation Needed For Diagnosis
Following any scans or tests, a healthcare professional may make a referral to a mental health expert who has more specialized knowledge on the subject. It is also common for healthcare professionals to speak with the friends and/or family of a person who is showing signs of schizophrenia.
If schizophrenia is diagnosed, then the person with schizophrenia and their support team will work on a treatment plan together.
Don’t Miss: Prodromal Period Schizophrenia
Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
The negative symptoms of schizophrenia can often appear several years before somebody experiences their first acute schizophrenic episode.
These initial negative symptoms are often referred to as the prodromal period of schizophrenia.
Symptoms during the prodromal period usually appear gradually and slowly get worse.
They include the person becoming more socially withdrawn and increasingly not caring about their appearance and personal hygiene.
It can be difficult to tell whether the symptoms are part of the development of schizophrenia or caused by something else.
Negative symptoms experienced by people living with schizophrenia include:
- losing interest and motivation in life and activities, including relationships and sex
- lack of concentration, not wanting to leave the house, and changes in sleeping patterns
- being less likely to initiate conversations and feeling uncomfortable with people, or feeling there’s nothing to say
The negative symptoms of schizophrenia can often lead to relationship problems with friends and family as they can sometimes be mistaken for deliberate laziness or rudeness.