What Should I Know About Participating In Clinical Research
Clinical trials are research studies that look at new ways to prevent, detect, or treat diseases and conditions. Although individuals may benefit from being part of a clinical trial, participants should be aware that the primary purpose of a clinical trial is to gain new scientific knowledge so that others may be better helped in the future.
Talk to your health care provider about clinical trials, their benefits and risks, and whether one is right for you. For more information, visit NIMHs clinical trials webpage.
Recommended Reading: How To Handle Eating Disorders
Whats The Outlook For Children With Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a lifelong condition with symptoms that can be severe at times.
People with schizophrenia may have a higher risk of substance use disorders, depression, anxiety, suicidal thoughts and actions, and relationship challenges. A that includes medication and therapy often leads to better outcomes.
The Stages Of Schizophrenia
The stages of schizophrenia include:
- Prodromal stage:This marks when the initial decline in functioning begins and may involve mild symptoms. If an exam is performed during this stage, a definitive diagnosis will not be made unless/until the symptoms become clearer.
- Active stage:Also known as acute schizophrenia, this stage involves severe symptoms of psychosis such as delusions and hallucinations. This is the period when most people with schizophrenia seek medical intervention and are diagnosed with the disorder.
- Residual stage:This is the period after initial treatment is implemented. During the residual stage, a person with schizophrenia may not have any symptoms of psychosis and the negative symptoms may be the only residual signs of the disorder.
You May Like: How Do You Become Bipolar
You May Like: What Is Good For Anxiety And Depression
What Can Family Friends And Partners Do To Help
Friends, relatives and partners have a vital role in helping people with schizophrenia recover and make a relapse less likely.
It is very important not to blame the person with schizophrenia or tell them to “pull themselves together”, or to blame other people. It is important to stay positive and supportive when dealing with a friend or loved one’s mental illness.
As well as supporting the person with schizophrenia, you may want to get support to cope with your own feelings. Several voluntary organisations provide help and support for carers.
Friends and family should try to understand what schizophrenia is, how it affects people, and how they can help. You can provide emotional and practical support, and encourage people to seek appropriate support and treatment.
As part of someone’s treatment, you may be offered family therapy. This can provide information and support for the person with schizophrenia and their family.
Friends and family can play a major role by monitoring the person’s mental state, watching out for any signs of relapse, and encouraging them to take their medication and attend medical appointments.
If you are the nearest relative of a person who has schizophrenia, you have certain rights that can be used to protect the patient’s interests. These include requesting that the local social services authority ask an approved mental health professional to consider whether the person with schizophrenia should be detained in hospital.
Want to know more?
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
You should see your healthcare provider as recommended. You should also see them if you notice a change in your symptoms, such as symptoms getting worse even if youre taking your medication. You can also see them if side effects of your medication are causing disruptions in your life. Your healthcare provider can sometimes recommend alternative medications or treatments that might better treat your condition without causing those same effects.
When should I go to ER?
You should go to the ER or call 911 if you have thoughts about harming yourself, including thoughts of suicide, or about harming others. If you have thoughts like this, you can call any of the following:
- National Suicide Prevention Lifeline . To call this line, dial 1.800.273.TALK .
- Local crisis lines. Mental health organizations and centers in your area may offer resources and help through crisis lines.
- 911 : You should call 911 if you feel like youre in immediate danger of harming yourself. Operators and dispatchers for 911 lines can often help people in immediate danger because of a severe mental crisis and send first responders to assist.
You May Like: Can Anxiety Cause Panic Attacks
What Conditions Fall Under The Schizophrenia Spectrum
According to the American Psychiatric Associations Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition , the disorders in the schizophrenia spectrum are:
- Schizoaffective disorder.
- Catatonia is a syndrome that can include a lack of movement, unusual movements, unusual repetitive behaviors, not speaking and social withdrawal. It can also complicate schizophrenia, as well as other psychiatric and medical conditions.
- Other schizophrenia spectrum disorders . This diagnosis allows healthcare providers to diagnose unusual variations of schizophrenia.
Who Does It Affect
Schizophrenia typically starts at different ages, depending on sex. It usually starts between ages 15 and 25 for men and between 25 and 35 for women. It also tends to affect men and women in equal numbers.
Schizophrenia in children, especially before age 18, is possible but rare. However, these cases are usually very severe. Earlier onset tends to lead to a more severe, harder-to-treat condition.
About 20% of new schizophrenia cases occur in people over age 45. These cases tend to happen more in women. Delusion symptoms are stronger in these cases, with less-severe negative symptoms and effects on the ability to think and focus.
Also Check: How Many Veterans Seek Help For Ptsd
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better
Your healthcare provider is the best person to tell you how long it will take for medication and therapy to work, as different medications take different amounts of time before their effects are noticeable. They can also tell you about other treatment options that might help if the first attempt isnt effective.
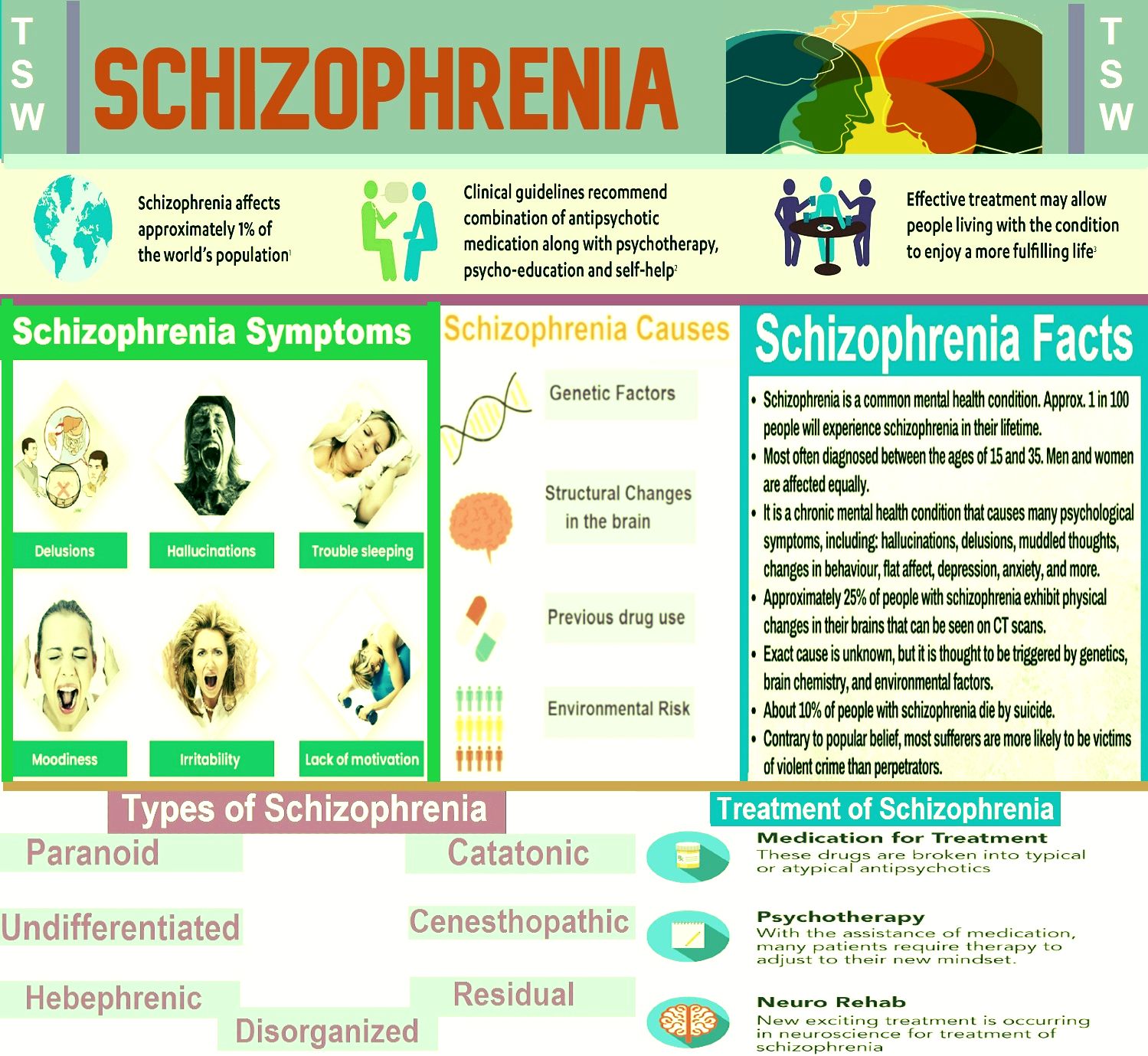
Positive And Negative Symptoms
What psychiatrists call the positive symptoms of schizophrenia are more obvious:
- Abnormal thinking and inappropriate emotions.
- Hallucinations, delusions and odd communication.
What they call the negative symptoms are more subtle and can last longer:
- Not talking much.
- Blunted feelings/little facial expression.
- Staying in bed to avoid people.
Whether their symptoms are positive or negative, people with schizophrenia dont seem to interact with the world in a healthy way, says Dr. Bowers.
Also Check: How To Slow Heart Rate During Panic Attack
Employment And Financial Support
Avoid too much stress, including work-related stress. If you are employed, you may be able to work shorter hours or in a more flexible way.
Under the Equality Act 2010, all employers must make reasonable adjustments for people with disabilities, including people diagnosed with schizophrenia or other mental illnesses.
Several organisations provide support, training and advice for people with schizophrenia who wish to continue working.
Your community mental health team is a good first point of contact to find out what services and support are available for you.
Mental health charities such as Mind or Rethink Mental Illness are also an excellent source of information on training and employment.
If you are unable to work as a result of your mental illness, you are entitled to financial support, such as Incapacity Benefit.
Want to know more?
There are also other places that offer support to people with schizophrenia and other mental illnesses.
Risk Factors For Schizophrenia
Different factors combine to heighten the risk of schizophrenia, says Dr. Bowers:
- Genetics: Having a relative with schizophrenia or one who displays schizophrenic behaviors increases risk.
- Life stressors: Extreme poverty homelessness traumatic events early in life early isolation or deprivation or a constant fight for survival heighten risk.
- Hallucinogens: The use of crystal meth, LSD, PCP or psilocybin mushrooms increases risk in the vulnerable.
Read Also: Can You Get Schizophrenia From Depression
Its Easy To Live In Denial
Even though your loved one isnt functioning well, isnt meeting their own expectations in life, and is using alcohol or drugs to cope, they may not see theres a problem.
Because of the natural urge to protect those you love, families can stay in denial, as well.
Its often the college that sends a young adult to the hospital for the first time because of erratic behavior or an overdose. The parents get involved only because the college requests their child be evaluated by a psychiatrist.
Families often dont seek help on their own, says Dr. Bowers.
They may continue to struggle try to understand their loved ones symptoms. Or ignore those symptoms until they escalate, sometimes into violent behavior.
But early, continuous treatment is critical, she stresses. Without help, a young adults problems will continue especially if they use drugs or alcohol.
If you find them up all hours of the night, or painting their room black, or too irritable without their meds, or scaring their little sister, call the doctor, she says. And encourage them to keep their appointments.
How Is It Diagnosed

Your healthcare provider can diagnose schizophrenia or its related disorders based on a combination of questions they ask, the symptoms you describe or by observing your actions. Theyll also ask questions to rule out causes other than schizophrenia. They then compare what they find to the criteria required for a schizophrenia diagnosis.
According to the DSM-5, a schizophrenia diagnosis requires the following:
- At least two of five main symptoms. Those symptoms, explained above, are delusions, hallucinations, disorganized or incoherent speaking, disorganized or unusual movements and negative symptoms.
- Duration of symptoms and effects. The key symptoms you have must last for at least one month. The conditions effects must also last for at least six months.
- Social or occupational dysfunction. This means the condition disrupts either your ability to work or your relationships .
Don’t Miss: How To Get In A Good Mood When Depressed
What Is Schizophrenia Or Paranoid Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a challenging brain disorder that often makes it difficult to distinguish between what is real and unreal, to think clearly, manage emotions, relate to others, and function normally. It affects the way a person behaves, thinks, and sees the world.
The most common form is paranoid schizophrenia, or schizophrenia with paranoia as its often called. People with paranoid schizophrenia have an altered perception of reality. They may see or hear things that dont exist, speak in confusing ways, believe that others are trying to harm them, or feel like theyre being constantly watched. This can cause relationship problems, disrupt normal daily activities like bathing, eating, or running errands, and lead to alcohol and drug abuse in an attempt to self-medicate.
Many people with schizophrenia withdraw from the outside world, act out in confusion and fear, and are at an increased risk of attempting suicide, especially during psychotic episodes, periods of depression, and in the first six months after starting treatment.
Take any suicidal thoughts or talk very seriously
If you or someone you care about is suicidal, call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline in the U.S. at 1-800-273-TALK, visit IASP or Suicide.org to find a helpline in your country, or read Suicide Prevention.
Causes & Risk Factors
It is not known for certain what causes schizophrenia, but like most other mental health problems, researchers believe that a combination of biological and environmental factors contribute to its development. Research has shown that:
- The risk is higher when a close family member has the illness.
- Schizophrenia may be influenced by brain development factors before and around the time of birth, and during childhood and adolescence.
- People who have experienced social hardship or trauma, particularly during childhood, have a higher risk.
- Cannabis use increases the risk of developing schizophrenia in youth and of triggering an earlier onset of the illness in people who are genetically vulnerable.
- Being born or spending ones childhood in an urban environment, rather than a rural one, increases the risk.
- Particular immigrant and refugee groups in Ontario may have a higher risk of developing psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia.
Exactly how these risk factors interact to cause schizophrenia is not yet fully understood.
Recommended Reading: Are Panic Attacks Common In Pregnancy
Warning Signs Seek Help
It is important to see a doctor if there are any of these warning signs present, or multiple of them. Not all of them will directly diagnose you with schizophrenia, but getting early treatment is key to helping long term with this condition. It can be hard to get someone with schizophrenia to see a doctor especially if there is some paranoia involved. There may also be denial in how they are behaving or acting. There are treatments available that can help manage episodes and symptoms of schizophrenia.
3 million people each year are diagnosed with the brain disorder schizophrenia. Both men and women have the same risk level. #HealthSurgeon
What Is The Typical Age Of Onset For Schizophrenia
Men and women are equally likely to get this brain disorder, but guys tend to get it slightly earlier. On average, men are diagnosed in their late teens to early 20s. Women tend to get diagnosed in their late 20s to early 30s. People rarely develop schizophrenia before they’re 12 or after they’re 40.
You May Like: How To Cure Binge Eating Disorder
Women Tend To Develop Symptoms Of Schizophrenia Later Than Men And Often Exhibit Different Symptoms
Article by:SymptomsChallengesTreatment
There is no disparity in the occurrence and prevalence of schizophrenia between men and women, though schizophrenia is more closely associated with younger men. This may be due to the fact that women are more likely to experience the onset of schizophrenia later than men. Women tend to develop symptoms in their late 20s whereas the onset in men is typically in their early 20s.1 Also, because women with schizophrenia tend to be more socially active, their schizophrenia may be less detectable.
Dont Miss: Apiphobia Definition
How Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
A diagnosis for schizophrenia is often first made in the active stage. This is when symptoms become most obvious. Other people may recognize the disordered thoughts and behavior patterns for the first time.
At that point, a doctor may work with friends and family members to understand when early symptoms began. Symptoms of the first phase are often not recognized until a person is in the active phase.
Once a diagnosis is made, a doctor will also be able to determine when the active phase is over based on symptoms and behaviors.
Where to Find Help
Advocacy organizations can help you find immediate help. They can also connect you with local resources that can help you find sustained, long-term treatment. These mental health resources include:
Most people with schizophrenia arent diagnosed until the second phase, once symptoms worsen and become more obvious.
At this point, treatment options include:
Where to Seek Emergency Care
If you or a loved one is experiencing suicidal thoughts or dangerous behaviors, seek emergency care:
- Dial 911 or your local emergency number
- Visit a hospital or emergency department
Read Also: Are Panic Attacks Bad For You
What Medications Or Treatments Are Used
Treating schizophrenia and related conditions typically involves multiple methods. Those methods can happen in combinations or steps.
Medications
There are two main types of medications that treat schizophrenia.
- Typical antipsychotics. Also known as first-generation antipsychotics, these medications block how your brain uses dopamine, a chemical your brain uses for cell-to-cell communication.
- Atypical antipsychotics. These medications, also called second-generation antipsychotics, work differently from first-generation antipsychotics. These block both dopamine and serotonin, two key communication chemicals in your brain. Clozapine is a particularly effective medication that can treat symptoms of schizophrenia when other drugs dont work. However, it has a rare serious side effect that requires frequent blood monitoring to keep people safe, which is why healthcare providers usually recommend other antipsychotics first.
There are other medications your healthcare provider might also prescribe to treat other symptoms that happen alongside or because of your schizophrenia symptoms. They might also prescribe medications to help reduce side effects of antipsychotic medications such as tremors.
In general, your healthcare provider is the best person to talk to about the medications they might prescribe. They can give you more specific information related to your specific situation, including your life circumstances, medical history and personal preferences.
Psychotherapy
What Is The Difference Between Schizophrenia And Psychosis

Schizophrenia and psychosis are two strongly connected terms, but they also have significant differences.
- Psychosis: This is a grouping of symptoms that involve a disconnection from reality and the world around you . Psychosis can happen with other medical conditions and mental health disorders, such as bipolar disorder.
- Schizophrenia: This is a spectrum of conditions that involve psychotic symptoms.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Are Bipolar
Is It Possible To Recover From Schizophrenia
Many people who live with schizophrenia have recovery journeys that lead them to live meaningful lives.
Recovery can be thought of in terms of:
- clinical recovery, and
- personal recovery.
What is clinical recovery?
Your doctor might have talked to you about recovery. Some doctors and health professionals think of recovery as:
- no longer having mental illness symptoms, or
- where your symptoms are controlled by treatment to such a degree that they are not significantly a problem.
Sometimes this is called clinical recovery.
Everyones experience of clinical recovery is different.
- Some people completely recover from schizophrenia and go on to be symptom free.
- Some who live with schizophrenia can improve a great deal with ongoing treatment.
- Some improve with treatment but need ongoing support from mental health and social services.
What is personal recovery?
Dealing with symptoms is important to a lot of people. But some people think that recovery is wider than this. We call this personal recovery.
Personal recovery means that you can live a meaningful life.
What you think of as being a meaningful life might be different to how other people see it. You can think about what you would like to do to live a meaningful life and work towards that goal.
Below are some ways you can think of recovery.
What can help me recover?
You may want to think about the following questions.
The following things can be important in recovery.