Clinical Efficacy Of Fga Versus Sga
The introduction of SGAs was thought to be a revolution in the treatment of schizophrenia. Initially, claims were made that the SGAs had better efficacy for positive and negative symptomatology and cognitive deficits as well as improved tolerability. However, over time, this initial enthusiasm and optimism for therapeutic advantages for the SGAs as a class have diminished.
The Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness and the Cost Utility of the Latest Antipsychotic Drugs in Schizophrenia Study , which compared FGAs and SGAs, failed to show a difference between FGAs and SGAs in rates of treatment discontinuation, improvement in psychotic symptoms or quality of life., CATIE further failed to demonstrate that SGAs were more effective in the reduction of negative or cognitive symptoms than FGAs. The results of CATIE and CUtLASS demonstrated similarities in treatment response, though with SGAs carrying a lower risk of tardive dyskinesia. Further evidence for clozapine’s unique position among antipsychotics was provided, with it found to be superior to other SGAs in both CATIE and CUtLASS.
Study Design Sample And Data Sources
This naturalistic retrospective study at the Seoul National University Hospital compared the effectiveness of oral antipsychotic medications in patients with schizophrenia. SNUH is a large urban tertiary hospital in Seoul, South Korea. Data were obtained from a Clinical Data Warehouse totally synchronized with the electronic medical records system generated as part of the usual clinical practice. The SNUH CDW encompasses all routine clinical information, such as the demographics, diagnosis, medication profiles, and laboratory results, from each visit since 2001. Approval from the Institutional Review Board at SNUH was obtained prior to collecting and analyzing the data. Written informed consent is not required for CDW-based studies using anonymized data.
The study population included all patients who were treated in the inpatient and/or outpatient setting at SNUH from 1 March 2005 to 28 February 2014, with a diagnosis of schizophrenia or schizophreniform disorder . For the homogeneity of the study population, patients with schizoaffective disorder or bipolar disorder were excluded. From this sample, we selected patients prescribed any one of the following antipsychotic medications: amisulpride, aripiprazole, clozapine, haloperidol, olanzapine, paliperidone, quetiapine, risperidone, and ziprasidone. Here, we included only the oral form of the above drugs and not the LAI formulation.
Efficacy Of Antipsychotics Versus Placebo In Multi
The analysis included 167 randomized controlled trials published between 1955and 2016 .9 The mean age of participants was 38.7 years and the mean duration of illnesswas 13.4 years. The analysis did not include any studies that exclusively recruitedpatients with a first episode of psychosis . Therefore, the placebo-controlled findings relate to patientswith multi-episode schizophrenia. The median duration of the studies was 6 weeks. About half the studies, for which sponsorship could beidentified, were industry sponsored.
Effect size [expressed as standardized mean difference betweenantipsychotic treatment versus placebo) for variousoutcomes as reported in a comprehensive meta-analysis of placebo-controlledantipsychotic drug trials in acute schizophrenia .
95% CrI = 95% credible interval.
Table 1 shows thepercentage of patients in the antipsychotic- and placebo-treated groups who wereresponders, according to two definitions, as well as those leaving the study for anyreason or inefficacy. It is sobering that only a minority of those treated withantipsychotics achieved a good response .Those treated with antipsychotics were significantly more likely to experiencemovement disorders, sedation, weight gain, prolactin increase and QTc prolongationthan those treated with placebo.9
Don’t Miss: Does Schizophrenia Affect The Brain
What Does Current Guidance Say On This Issue
The NICE guideline on schizophrenia in adults published in 2014 states: Offer clozapine to people with schizophrenia whose illness has not responded adequately to treatment despite the sequential use of adequate doses of at least two different antipsychotic drugs. At least one of the drugs should be a non-clozapine second-generation antipsychotic.
If the illness does not respond to an adequate dose of clozapine, clinicians are advised to review the diagnosis, check adherence, consider other possible causes of non-response and measure therapeutic drug levels before adding a second antipsychotic to augment treatment with clozapine.
Clozapine: A Special Case
Clozapine is unique among antipsychotic medications and can be viewed as a standalone third class of antipsychotic. It is the only antipsychotic medication that has proven effectiveness in treatment-resistant schizophrenia . The precise mechanism of clozapine’s superior effectiveness in TRS has not been established, but some 5060% of patients with schizophrenia refractory to other antipsychotics will respond to clozapine. Clozapine produces robust antipsychotic effect at < 65% threshold of striatal D2 receptor blockade, suggesting that beyond D2 receptor blockade in the striatum, other receptors or mechanisms also contribute to its therapeutic effect.
Clozapine and TRS are considered in greater detail in the following text.
Don’t Miss: Can Bipolar Turn To Schizophrenia
How Is Schizophrenia Treated
The treatment for schizophrenia is a combination of therapy and drugs. Schizophrenia drugs are a lifelong commitment at best, they control the outbursts of psychosis. Antipsychotic schizophrenia drugs have actually been used considering that the 1950s to cut psychosis and to prevent relapses. A few of these were fluphenazine, haloperidol, and chlorpromazine. These drugs were infamous for their degenerative side effects. Considering that the 1990s, lots of newer generation schizophrenia drugs have actually been developed. Fortunately, these drugs do not have a number of the side effects of the older generation of schizophrenia drugs.
Also Check: The Suffix Phobia Means
Relative Efficacy Of Different Approaches To Psychosocial Intervention
From the literature reviewed between 1995 and 2008, the estimated efficacy of the five main approaches to psychosocial intervention for schizophrenia is presented in terms of the effect sizes on two of their most commonly reported patient outcomes. The effect sizes of CBT in terms of relapse and positive symptoms are 0.200.52 and 0.190.50, respectively,, and those of psychoeducation are 0.250.50 and 0.210.48, respectively. For family intervention, the effect sizes in terms of mental state and family burden are 0.210.45 and 0.280.50, respectively., In addition, the effect sizes of social skills training based on improvements in interpersonal skills and community functioning are 0.581.12 and 0.450.89, respectively, whereas those of cognitive remediation in terms of cognitive functioning and social behaviors are 0.130.70 and 0.280.50, respectively.,
Also Check: When Does A Diet Become An Eating Disorder
Side Effects Of Antipsychotics
While the first-generation, older meds usually cost less, they can have different side effects than the newer antipsychotics. Some can cause higher levels of the hormone prolactin. This can affect sex drive, mood, menstrual cycles, and growth of breast tissue in both men and women.
One of the common side effects of many of the newer antipsychotics is weight gain. You may also have trouble keeping your blood sugar and cholesterol levels under control.
One of the more serious side effects from long-term use of both the older and newer medications is a movement disorder called tardive dyskinesia. It makes your facial, tongue, and neck muscles move uncontrollably and can be permanent.
While both older and newer antipsychotics can cause tardive dyskinesia, researchers believe that the odds are higher with the older antipsychotics.
Antipsychotics come with other side effects as well. You could have any of the following:
Be sure you see your doctor regularly while taking antipsychotic medication. And talk to your doctor if you have any concerns about side effects.
Managing Medication Side Effects
If you are worried about any side effects you may be experiencing, talk to your treating doctor. To manage or reduce side effects, your doctor may:
- change the dose of the medication
- prescribe a different medication
- suggest that you take the medication at a different time of day
- try non-medication intervention to reduce side effects. For example, diet and exercise programs can be helpful in addressing weight gain.
Read Also: Which Organization Sets The Standards For Diagnosing Eating Disorders
Antipsychotic Medication For Schizophrenia: What Was Studied
Researchers who performed the analysis, published in the journal JAMA Psychiatry in August 2021, looked at how effectively different doses of medication prevented symptoms of schizophrenia over time.
They also studied how common side effects were among people taking these medications and how frequently people wanted to stop taking the medications due to side effects.
Can I Drive When Taking Antipsychotics
Antipsychotics can affect your concentration and make you feel drowsy. This could affect how well you are able to drive especially when you first start taking the medication. You should consider stopping driving during this time if you are affected.
You have to tell the DVLA if you live with certain mental health conditions including psychosis, paranoid schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
You can find more information about Driving and mental illness by clicking here.
Don’t Miss: Can Bipolar People Tell They Are Bipolar
A Combination Is The Best Treatment For Schizophrenia
According to the American Psychiatric Association, the best practices for treating schizophrenia include using a combination of strategies. Unfortunately, there is no one treatment that is always effective. A combination of approaches, including medications, psychotherapy, social support and family education, vocational and housing support, treatment for co-occurring issues, and sometimes electroconvulsive therapy, is most effective for most patients.
Most people being treated for schizophrenia will respond to this combination, but the specific type of each treatment that is used depends on the individual. For instance, some patients may do better with a first generation antipsychotic than a second generation drug. Some may respond well to cognitive behavioral therapy, while others prefer group therapy. Effective treatment depends on finding the right combination of approaches for each patient.
A patient can be best guided through an effective treatment plan when in a residential setting. Most patients with schizophrenia benefit from intensive inpatient treatment because it provides a safe environment and a period of time in which individuals can dedicate themselves to treatment. It also provides a social setting in which patients can work together and rely on social support.
Types Of Antipsychotic Medications
NOTE: medications are referred to in two ways: by their generic name and by their brand or trade names. Brand names available in Canada appear in brackets.
Antipsychotic medications are generally divided into two categories:
- atypical antipsychotics
- typical antipsychotics
The main difference between the two types of antipsychotics is that the first generation drugs block dopamine and the second generation drugs block dopamine and also affect serotonin levels. Evidence suggests that some of the second generation drugs have milder movement-related side-effects than the first generation drugs.
Both categories of drugs work equally well overall, although no drug or type of drug works equally well for everyone who takes it. When the same drug is given to a group of people, one-third of that group will find that it works well another third will find that the drug helps only with some symptoms and the final third will find that it does not help at all. For this reason, people may need to try different antipsychotics before finding the one that works best for them.
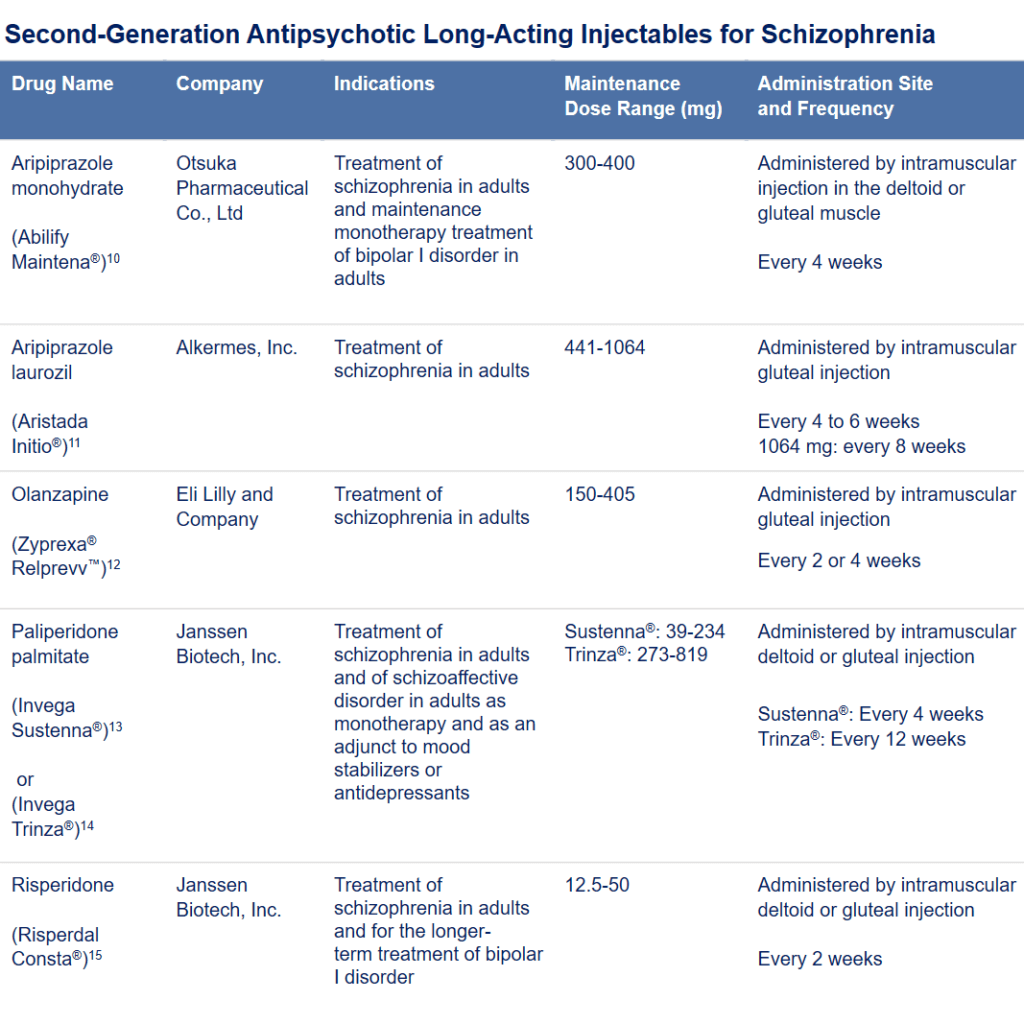
Most of these drugs are given in tablet form, some are liquids and others are given as injections. Some are available as long-lasting injections, which may be given anywhere from once a week to once a month.
Most people who take antipsychotics over a longer term are now prescribed the second generation drugs.
Atypical antipsychotics
Possible side-effects of atypical antipsychotics include:
Typical antipsychotics
Don’t Miss: Why Eating Disorders Are Classified As Mental Illnesses
Whats The Standard Treatment For Schizophrenia
Anti-psychosis drugs administered orally or through injections have transformed schizophrenia treatment. These drugs work on chemicals in the brain, such as dopamine and serotonin. These newer medications are less likely to cause certain side effects that the first-generation antipsychotics incite. Thanks to them, most patients can live in the community, rather than stay in a hospital.
Some of the common schizophrenia medications are:
The primary schizophrenia treatment is medication. However, oftentimes, compliance can be a major problem. People with schizophrenia often come off their medication for long periods during their lives at significant personal costs to themselves and those around themnonadherence rates in schizophrenia range from 37% to 74%.
Doctors decide which medication is best by looking at several factors, including:
- How effectively it alleviates symptoms
- How much it will cost
- How easily the medication is to procure
- How often the patient has to take it
Getting a diagnosis of schizophrenia doesnt mean you cant live a full and meaningful life. Despite the widespread misconception that people with schizophrenia have no chance of recovery or improvement, the reality is much more hopeful. Currently, there is no cure for schizophrenia, but you can treat and manage it with medication, self-help strategies, and supportive therapies.
What Did The Researchers Find
The studies showed that the effectiveness of antipsychotic medication in preventing symptoms of schizophrenia levels off at what experts consider relatively low doses of medication.
For example, the antipsychotic drug Risperdal is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use in doses of up to 16 milligrams . When someone comes to a psychiatrist for help with active symptoms of schizophrenia, the dose most psychiatrists aim for to treat ongoing symptoms is 4 to 8 mg, based on currently available research.
However, the researchers found that, although doses of up to 8 mg may help in treating active symptoms of schizophrenia, a dose of Risperdal didnt provide much additional benefit in preventing symptoms after surpassing the equivalent of 5 mg. Additionally, even lower doses the equivalent of 2.5 mg of Risperdal were effective in preventing significant symptoms for some people.
Its also important to note that the number and severity of side effects people experienced increased with higher doses of antipsychotic medication. As a result, more people on higher doses stopped taking their medication due to side effects than people on lower doses.
The researchers concluded that higher doses of antipsychotic medication may have limited usefulness in preventing symptoms of schizophrenia when compared with lower doses. And lower doses of medication came with lower long-term risks and were better tolerated by the body than higher doses.
Also Check: Which Magnesium Is Best For Anxiety
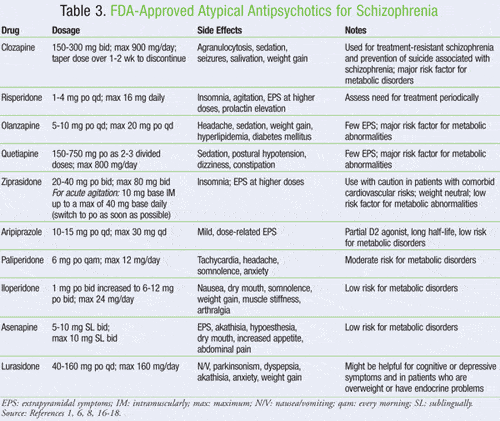
Common Atypical Antipsychotics For Schizophrenia
Below is a list of common atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia, their side effects, indications, and dosage recommendations. Keep in mind that you should follow your doctors dosage guidelines and never adjust the dosage of your medication without speaking with your treatment team first.
Common atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia include:
- aripiprazole / aripiprazole lauroxil
Aripiprazole may be prescribed off-label for borderline personality disorder or drug-induced hyperprolactinemia .
How Was This Studied
The researchers performed whats called a meta-analysis. This means they combined and studied the results of many different clinical trials.
Twenty-six clinical trials were included in the analysis. All of these trials had compared how effectively different doses of antipsychotic medication prevented future symptoms of schizophrenia among people with stable schizophrenia who did not currently have significant symptoms of their illness.
The researchers also kept track of side effects associated with treatment.
Since the researchers wanted to look at the long-term effects of these medications, they included only studies that lasted at least three months in their analysis. The average length of these studies was about one year.
Don’t Miss: Does Hugging Dogs Give Them Anxiety
Discontinuation Versus Maintenance Therapy: Emotional And Cognitive Functioning
In the context of functional recovery, the impact of continuation on emotional and cognitive functioning needs to be evaluated. Blockade of the dopamine D2 receptors, the main mediator of efficacy of antipsychotic medication , can produce adverse subjective experiences or neuroleptic dysphoria , encompassing a variety of unpleasant subjective changes in arousal, mood, thinking, and motivation . Severity of these mental adverse effects depends on individual variability of sensitivity and proportion of D2 receptors blocked. Individuals with lower baseline dopamine function are at increased risk for dysphoric responses during treatment with dopaminergic blocking drugs . With regard to dosage of antipsychotic medication, most mental adverse effects occur at D2 receptor occupancy higher than 6570% . In addition to dysphoria, dopamine blockade may reduce functioning by exerting negative effects on cognition. Dopamine plays an important role in learning and motivation, as it enables associative learning, especially of aversive stimuli . Approximately 50% of men and up to 70% of women report difficulty in concentrating or tiredness with the use of antipsychotic medication . Blockade of this system reduces the cognitive capacity to learn new associations, which may hinder study or work . Blockade of the mesolimbic reward system also reduces motivation and drive, which can be expected to hamper professional and social success .
Time Course Of Antipsychotic Response
For decades it was believed that antipsychotics had a delayed onset of action. In2003, a meta-analysis by Agid and colleagues,28 assessing response over 4 weeks of antipsychotic treatment, showed that thiswas incorrect and that the reduction in PANSS/BPRS scores seen during the first 2weeks of treatment was significantly greater than the improvement seen inthe third and fourth weeks . This finding has been confirmed by many studiessince, but inconsistencies in methodology, in particular in defining early and lateresponse, have prevented this research from being translated into clear guidance forclinicians. Given this, it is not surprising that clinical guidelines produced bydifferent organizations vary in their recommendations as to how long a trial ofantipsychotic medication should continue before consideration is given toswitching.
The diagnostic test remained accurate when it was applied to data for individualdrugs, namely amisulpride, haloperidol, olanzapine and risperidone. The consistencyof the results, despite the pharmacological differences between these drugs,suggests that the results can be generalized to other antipsychotics.
Don’t Miss: Is Bipolar Inherited From Mother Or Father
Delivery Of Antipsychotic Medications
Most antipsychotic medications are taken in tablet form, but can also be taken in syrup or liquid form, or as an injection . Depot injections contain the same medications as those found in pill or liquid form. They are given in a carrier liquid that releases the medication slowly, so it lasts a lot longer. This can occur over several weeks. Not all antipsychotics are available as depot injections.Depot injections might be helpful where:
- a person has difficulty remembering to take their medication regularly or may take the wrong dose
- a person might have difficulty swallowing medication in tablet form
- the person would prefer not to have to think about taking medication every day
- medication might be a condition of a court community-treatment order.
It is important to discuss with your doctor the different treatment options available, and which of them might be the best for you.
Whichever delivery method you choose, do not suddenly stop taking antipsychotic medication without speaking with a mental health professional, as psychotic symptoms may return.