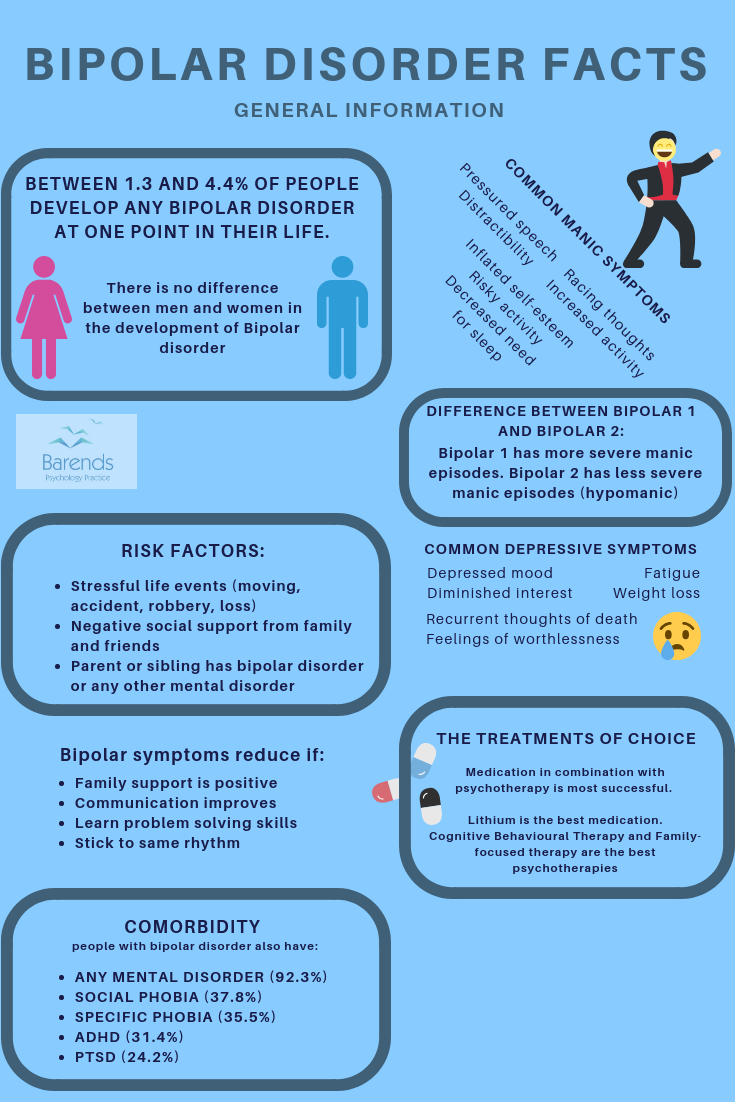
What Is Bipolar I Disorder
Bipolar I disorder is a form of mental illness. A person affected by bipolar I disorder has had at least one manic episode in their life. A manic episode is a period of abnormally elevated or irritable mood and high energy, accompanied by abnormal behavior that disrupts life.
Most people with bipolar I disorder also suffer from episodes of depression. Often, there is a pattern of cycling between mania and depression. This is where the term “manic depression” comes from. In between episodes of mania and depression, many people with bipolar I disorder can live normal lives.
Type : Bipolar 2 Disorder
For those who are diagnosed with Bipolar 2 Disorder, they will not experience the mania that is a hallmark symptom of Bipolar 1 Disorder. Rather, people living with Bipolar 2 Disorder experience hypomania, which is a milder form of mania. Hypomania symptoms are similar to those of mania, and can include rapid, loud speech, racing thoughts, increased energy and a decreased need to sleep.
Instead, those with Bipolar 2 Disorder will more often experience symptoms of major depression, and cycle in and out of depressive episodes. This can sometimes lead to a misdiagnosis of depression.
Complete List Of Bipolar Medications: Types Uses Side
The list of bipolar disorder medications is long and complex, but it’s important to understand your options when it comes to treating this condition. The majority of people diagnosed with bipolar disorder take some form of medication to manage their symptoms. There is, however, a surviving stigma around psychiatric medicines, and many people are dangerously misinformed. Here, you can discover the official list of bipolar disorder medications as well as their common side-effects.
Read Also: Can Dehydration Cause Anxiety
Bipolar Ii: What To Expect
Bipolar II is sometimes erroneously referred to as a milder form of bipolar I. But although patients with bipolar II do not develop the most severe symptoms of full-blown mania, they tend to have symptoms more of the time. Long periods of depression are typical of bipolar II disorder and can be even more debilitating than the dramatic but shorter-lived episodes of bipolar I illness.
Persons with bipolar II are more likely to have a seasonal variation in their symptoms, meaning that they tend to get depressed in the fall and winter and feel betteror even develop hypomaniain the spring and summer. Whereas patients with bipolar I frequently have irritable manic symptoms, the hypomanic periods of bipolar II patients are characterized by an elated mood.
Concerning depressive symptoms, patients with bipolar II disorder more often suffer from psychomotor agitation, guilty feelings, and thoughts of suicide. Bipolar II patients also have a higher incidence of phobias and eating disorders. Typically, hypomanic episodes taper off as the bipolar II patient ages. When they reach middle age, depression is usually the predominant mood.
Different Types Of Bipolar Disorder
- Bipolar I disorder: involves at least one manic or mixed episode. Most people experience depression as well.
- Bipolar II disorder: involves at least one episode of hypomania and an episode of depression.
- Cyclothymia: involves hypomania and mild symptoms of depression experienced most of the time over at least a two-year period.
- When bipolar disorder does not fit into the above categories: For example, a person may experience mild depressive or hypomanic symptoms that last less than the two years specified for cyclothymia. Another example is when a person has depressive episodes, but their symptoms of mood elevation are too mild or brief to be diagnosed as mania or hypomania.
Read Also: Acrophobia Medical Definition
Type : Bipolar 1 Disorder
People living with Bipolar 1 Disorder generally experience some cycling between periods of depression, and periods of mania, and have already experienced at least one manic episode in their life. Manic episodes last at least a week and have psychotic features, which means that the person will experience hallucinations, delusions or another significant disconnect from reality. This could result in hospitalisation.
Depressive episodes, which usually last around two weeks, also typically occur in Bipolar 1 Disorder. Both manic and depressive episodes can also have elements of the other for example, you can have some symptoms of depression while experiencing mania and vice versa. In between these phases, life will feel relatively normal.
Are There Other Types Of Bipolar Disorder
There are two other types of bipolar disorder, but they are far less common than bipolar I and II.
Cyclothymic Disorder is a milder form of bipolar. Moods fluctuate between short-but-distinct periods of hypomania and low levels of depression. In order for a diagnosis of cyclothymic disorder, symptoms must be evident for at least two years. People with cyclothymic disorder can have stable moods for long periods of time, then experience cyclical mood swings of peaks and dips.
Other Specified and Unspecified Bipolar and Related Disorders has no specific criteria for diagnosis. Its more of a catch-all phrase of symptoms that are similar to bipolar disorder but do not meet the full criteria. People with this diagnosis experience signs of mania or hypomania and depression but the episodes are too short to be considered bipolar I or II or cyclothymic disorder.
Remember: No matter what type of bipolar you or someone you know has been diagnosed with, there is hope. With the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments, most people with bipolar can be happy and productive.
Also Check: Can You Go To Urgent Care For Panic Attacks
Bipolar I: What To Expect
Many excellent clinical studies about bipolar disorder were done in the years before effective treatments were available. How many episodes of illness did patients have in the days before treatment was available? How long did their episodes last? What was the length of time between episodes?
In a 1942 study, researchers looked at the medical records of 66 patients with manic-depressive psychosis. A few patients had only one episode of illness in the study period. About one-third had 2 to 3 episodes, about one-third had 4 to 6 episodes, and about one-third had more than 7. A few had 20 or more episodes. Unfortunately, there is no way to know whether the individual will have another 2 or 3 episodes during his lifetime or more than 20.
Subsequent studies have shown that, if untreated, episodes of bipolar disorder often occur more frequently as patients age, and episodes seemed to be triggered more easily.
Many patients with bipolar I disorder have nearly complete remission of their symptoms between episodes. This illness pattern often predicts that an individual will have an excellent response to treatment with lithium.
Types Of Bipolar Disorder: Type Ii
The main characteristic of this typology is that it includes the mildest version of mania: hypomania. However, recurrent episodes of major depression are also more common. In order to diagnose this type, the person needs to have experienced:
- At least one hypomanic episode and more than one major depressive episode.
- Sleep problems: either insomnia or excessive sleep .
- Intense exhaustion.
You May Like: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
Different Types Of Pitfalls Bipolar
- School
- 100%1 out of 1 people found this document helpful
This preview shows page 8 – 10 out of 18 pages.
We have textbook solutions for you!
The document you are viewing contains questions related to this textbook.The document you are viewing contains questions related to this textbook.Research Methods for the Behavioral Sciences
Literature Study Guides
Learn more about characters, symbols, and themes in all your favorite books with Course Hero’s FREE study guides and infographics!
Music Sales assignment instructions and questions.docx
Texas State University
Kent State University COMM 35860
Interviewing Final Exam
Texas State University CS 3358
Music Sales assignment instructions and questions.docx
homework
Kent State University COMM 35860
Interviewing Test 2
West Chester University PHI 101
Daniel P assignment 3
We have textbook solutions for you!
The document you are viewing contains questions related to this textbook.The document you are viewing contains questions related to this textbook.
What Are The Types Of Bipolar Disorder
Because people often just say they have bipolar disorder, many dont know there are several types of bipolar disorder. Indeed, the type of bipolar disorder that a person has matters when it comes to understanding the illness. Read on to learn about how many types of bipolar disorder there are, what theyre like, and which type of bipolar disorder is most severe.
Recommended Reading: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
Bipolar I Vs Bipolar Ii: What Are The Differences
The two most common types are bipolar I and bipolar II. What differentiates them is the intensity of the manic episodes.
The mania for a person with bipolar I is obvious to everyone around them. Its usually so debilitating that the person is unable to function and may even need to be hospitalized.
Mania for bipolar II, called hypomania, is less severe and sometimes even mild enough that the person experiencing it may still be able to function day to day. Occasionally it can even be so subtle that nobody around them notices that anything is significantly off.
Another difference between bipolar I and II: A person with bipolar I may or may not experience a depressive state in fact, one episode of mania is all thats required for a diagnosis of bipolar I. But if the person does have depressive episodeswhich most dothey usually last at least two weeks.
For a diagnosis of bipolar II, you must have experienced at least one major depressive episode as well as a manic episode.
How Bipolar Disorder Affects A Marriage
For many people, getting married is a positive experience and aspiration. Being married provides an emotional connection and partnership in life.
However, every relationship has its challenges. When one partner in a marriage has bipolar disorder, the relationship can become complicated when they are unwell.
You May Like: What Is A Phobia Of Spoons Called
What Are The Treatments For Cyclothymia
Cyclothymia frequently goes undiagnosed and untreated. Most people’s symptoms are mild enough that they do not seek mental health treatment. In fact, some people resist the idea of treatment, which reduces their “up” episodes as well as “down.”
The depressive symptoms of cyclothymic disorder are typically more frequent, unpleasant, and disabling than the hypomanic symptoms. Feelings of depression or instability are usually what cause people with cyclothymia to seek help.
No medicines are specifically approved for the treatment of cyclothymia, although mood stabilizers such as lithium or lamotrigine are sometimes recommended as a possible strategy to reduce mood fluctuations. Antidepressants such Prozac, Paxil, or Zoloft are generally not recommended unless someone develops a full major depression, which, by definition, does not occur in cyclothymic disorder. There is also a small risk that antidepressants could trigger or worsen mania symptoms in a subgroup of vulnerable people. Antidepressants alone also are not known to improve fluctuations in mood, which are hallmark characteristics of cyclothymic disorder.
Technically speaking, when elevated or depressed moods become severe, a person no longer has cyclothymia, but rather has bipolar disorder. This progression to more severe symptoms can happen, and this is when many people first receive treatment.
What To Do When Youre Depressed
The most important step you can take is to start and stay on a bipolar treatment plan. Most include a mix of medicine and talk therapy.
Your doctor might prescribe a few different kinds of medication, including mood stabilizers, antidepressants, and antipsychotic drugs. Talk therapy can also help you control stress and recognize your symptoms sooner. Another type of therapy, called cognitive behavioral therapy, teaches you good ways to handle the negative thoughts that come with depression.
You can take other steps to fight depression, too:
- Donât drink alcohol or use drugs. They can make your mood worse and keep your medications from working.
- Stick to a routine. Try to go to bed, wake up, exercise, and take your medicines at the same time every day.
- Donât make major life changes while youâre depressed. Your doctor or therapist may be able to help you schedule absences from work if you need them.
- Ask a family member or friend for support. They can help you keep up with your appointments and medications.
If you are thinking about suicide or hurting yourself:
- Tell someone who can help you right now
Also Check: Phobia Root Words
Types Of Bipolar Disorder
The APA classifies bipolar disorder according to the duration and severity of these mood episodes. According to APA’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , there are four different types of bipolar disorder your doctor may diagnose you with:
Caring For Your Needs
You must also remember to take care of yourself. Some ways to do that include:
- Cultivate self-care and coping skills.
- Set boundaries by expressing what is acceptable or unacceptable.
- Be clear about what will happen if a boundary is violated.
- Reach out for help if you need it .
- Be gentle and compassionate toward yourself.
Also Check: Schizophreniform Vs Brief Psychotic Disorder
How Often Do Bipolar Episodes Occur
This can depend on a lot of things, such as:
- your exact diagnosis
- how well you’re able to manage your symptoms
- whether certain situations or experiences can trigger your episodes (for example, you might find that getting very
- little sleep while going through a stressful life event could trigger an episode of mania)
- how you define an episode personally
What’s normal for you can also change over time. However, many people find that:
- mania can start suddenly and last between two weeks and four or five months
- depressive episodes can last longer sometimes for several months
Rapid cycling
You may be told your bipolar is rapid cycling if you have experienced four or more depressive, manic, hypomanic or mixed episodes within a year. This might mean you feel stable for a few weeks between episodes, or that your mood can change as quickly as within the same day, or even the same hour.
Currently, rapid cycling is not officially considered a separate type of bipolar disorder, but more research is needed to know for sure or to better understand it.
For more information on rapid cycling, see the Bipolar UK website.
“It’s a lot harder coming to terms with being stable than I could have imagined. I’ve had to struggle with a ‘new’ identity and way of life after spending so many years thinking the ups and downs of bipolar are ‘normal’.”
What Are The Different Types Of Bipolar Disorder
There are three main types of bipolar disorder bipolar I, bipolar II, and cyclothymic disorder.
Bipolar I disorder
Bipolar I diagnosis involves having severe manic episodes that last at least seven days or require hospitalization. Depressive episodes are also seen and last for two weeks. There may be periods of normal moods between these two episodes.
Bipolar II disorder
Bipolar II involves a current or past major depressive episode lasting for at least two weeks. The person must also have had a current or past episode of hypomania. Women have a higher risk than men to develop bipolar II disorder.
Cyclothymic disorder
Patients may experience ongoing bipolar symptoms that do not meet the full criteria for a bipolar I or bipolar II diagnosis. Cyclothymic disorder is a less severe form of bipolar disorder. It may cause frequent episodes of hypomanic and depressive symptoms, but they are not severe. Symptoms generally persist for around two years.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
Potential Causes And Risk Factors
Experts do not know exactly what causes bipolar disorder, although they believe that several factors play a role. These include:
- Genetics. People with bipolar disorder seem to have variations in genes that may have increased their risk of developing the condition. However, it is unclear exactly how these variations lead to the onset of the disorder.
- Family history. If a sibling or parent has bipolar disorder, a person is more likely to develop it themselves.
- Environmental factors. Experiencing periods of high stress, such as bereavement, can trigger bipolar symptoms. A traumatic head injury or abusing alcohol or drugs may also increase the risk.
Most likely, a combination of heredity and environmental factors plays a role in bipolar development.
Considering Your Spouses Feelings
Compassion from both partners toward each other can go a long way in a marriage in which one spouse has bipolar disorder.
The partner with the condition may have feelings of guilt, shame, and fear because of the impact of a mood episode on the relationship. Meanwhile, the spouses partner may experience a range of emotions, including anxiety, resentment, loneliness, or feeling stuck.
Learning how to take care of themselves and support each other can strengthen the relationship.
Don’t Miss: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
What Is Bipolar 1 Disorder
You must have had at least one manic episode to be diagnosed with bipolar 1 disorder. A person with bipolar 1 disorder may or may not have a major depressive episode. The symptoms of a manic episode may be so severe that you require hospital care.
Manic episodes are usually characterized by the following:
- exceptional energy
The symptoms of a manic episode tend to be so obvious and intrusive that theres little doubt that something is wrong.
If Your Spouse Has Diagnosed Bipolar Disorder
Recurrent or extreme changes in mood can have a significant impact on the spouses of people living with bipolar disorder. There can be a level of unpredictability in the relationship that causes distress.
On the one hand, the partner experiencing the mood episode is affected by their symptoms, leading to changes in behavior and level of functioning. On the other hand, their spouse may feel responsible for their partner and the family, and may begin to feel burnt out.
These dynamics create challenges in marriages that can be difficult to overcome. Research indicates divorce rates are higher in couples in which one partner has the condition.
Read Also: Phobia Mean