Treatment And Medical Options For Schizophrenia
Over the past 30 years, researchers have identified more than 100 genes that may increase the risk of schizophrenia, and they have begun finding novel pathways and making other discoveries that may help identify new targets for drug therapy.
There is no cure for schizophrenia, and as with many diseases that can be managed but not cured, early detection and treatment are important.
Seek medical treatment if you or someone you know might be experiencing signs of psychosis or schizophrenia. Early treatment can improve a persons chance for a successful recovery. Whats more, proper treatment helps minimize symptoms and improve quality of life. Yet even after symptoms have ceased and schizophrenia is managed, most people with schizophrenia require ongoing drug and nondrug treatment.
Genetic Counseling Issues And Schizophrenia
With increasing attention in the media to issues relating to genetics and particularly the role of genetic factors in mental illness, an increasing number of individuals will likely be seeking genetic counseling for issues related to schizophrenia. In our experience, by far the most common situation is a married couple who are contemplating having children and the husband or wife has a family history of schizophrenia. They typically ask any combination of three questions: First, is there a genetic test that can be performed on us to determine whether we have the gene for schizophrenia and whether we might pass it on to our children? Second, is there an in utero test that can be given that would determine the risk of the fetus to develop schizophrenia later in life? Third, what is the risk for schizophrenia to our children?
Unfortunately, given the current state of our knowledge, answers to the first two questions are no, we are not yet in the position of having a genetic test that can usefully predict risk for schizophrenia. We would also often add a statement to the effect that this is a very active area of research and there is hope that in the next few years, some breakthrough might occur that would allow us to develop such a test. But, right now we really do not know when or even if that will be possible.
What Are The Early Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
The condition usually shows its first signs in men in their late teens or early 20s. It mostly affects women in their early 20s and 30s. The period when symptoms first start and before full psychosis is called the prodromal period. It can last days, weeks, or even years. It can be hard to spot because thereâs usually no specific trigger. You might only notice subtle behavioral changes, especially in teens. This includes:
- A change in grades
- Difficulty sleeping
Read Also: Phobia Of Bees And Wasps
What Psychiatric Disorders Are Transmitted Within Families Of Individuals With Schizophrenia
Since the earliest genetic studies of schizophrenia, a major focus of such work has been to clarify more precisely the nature of the psychiatric syndromes that occur in excess in relatives of schizophrenic patients. To summarize a large body of evidence, relatives of schizophrenia patients are at increased risk for not only schizophrenia but also schizophrenia-like personality disorders and other psychotic disorders . However, there is good evidence that relatives of schizophrenia patients are not at increased risk for other disorders, such as anxiety disorders and alcoholism. The most active debate in this area is the relationship between schizophrenia and mood disorders. Most evidence suggests little if any genetic relationship between these two major groups of disorders, but some research does suggest a relationship particularly between schizophrenia and major depression.
The evidence that other disorders in addition to schizophrenia occur at greater frequency in the close relatives of individuals with schizophrenia has led to the concept of the schizophrenia-spectruma group of disorders that all bear a genetic relationship with classic or core schizophrenia.
Emotional Signs Of Schizophrenia:

- Emotional dullness the person becomes indifferent to their family.
- Inadequacy in particular cases, the patient is hypersensitive to certain stimuli: a mere trifle can cause unmotivated aggression, anger, jealousy. And those who are closest to the patient are first to suffer. The less close the person is to someone, the less pronounced the negative reaction is. The attitude to strangers will hardly change.
- The loss of interest in usual activities.
- The dullness of sensations reduced instinctive needs, such as appetite, hygiene.
- Delusion distorted perception of reality. The patient sees unusual, colored dreams, is obsessed by the idea that someone is watching them, wants to kill them, is affecting them in some way, etc. Often, the affected person believes that their spouse cheats on them. Unlike normal jealousy, such delusions take the form of obsessive thoughts.
- Hallucinations the most common are auditory hallucinations: the person hears the voices telling them what to do, controlling them. The patient also can have visual colored hallucinations, such as bright dreams.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
Schizophrenia: The 7 Keys To Self
Seek social support. Friends and family vital to helping you get the right treatment and keeping your symptoms under control. Regularly connecting with others face-to-face is also the most effective way to calm your nervous system and relieve stress. Stay involved with others by continuing your work or education. If thats not possible, consider volunteering, joining a schizophrenia support group, or taking a class or joining a club to spend time with people who have common interests. As well as keeping you socially connected, it can help you feel good about yourself.
Manage stress. High levels of stress are believed to trigger schizophrenic episodes by increasing the bodys production of the hormone cortisol. As well as staying socially connected, there are plenty of steps you can take to reduce your stress levels. Try adopting a regular relaxation practice such as yoga, deep breathing, or meditation.
Get regular exercise. As well as all the emotional and physical benefits, exercise may help reduce symptoms of schizophrenia, improve your focus and energy, and help you feel calmer. Aim for 30 minutes of activity on most days, or if its easier, three 10-minute sessions. Try rhythmic exercise that engages both your arms and legs, such as walking, running, swimming, or dancing.
Schizophrenia Through The Ages
What does schizophrenia mean?
In 1910, the Swiss psychiatrist Paul Eugen Bleuler coined the term ‘schizophrenia from the Greek words schizo and phren . Bleuler had intended the term to denote a loosening of thoughts and feelings, but, unfortunately, many people read it to mean a split personality.
What does schizophrenia not mean?
Robert Louis Stevensons novel The Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde did much to popularize the concept of a split personality, which is sometimes also referred to as multiple personality disorder . However, MPD is a vanishingly rare condition that is entirely unrelated to schizophrenia. The vast majority of psychiatrists, myself included, have never seen a case of MPD, and many if not most suspect that such a condition does not exist. Yes, schizophrenia sufferers may hear various voices, or harbour strange beliefs, but this is not the same as having a split personality. Unlike Dr Jekyll, schizophrenia sufferers do not suddenly mutate into a different, unrecognizable person.
Who discovered schizophrenia?
How was schizophrenia thought of in antiquity?
But the spirit of the Lord departed from Saul, and an evil spirit from the Lord troubled him And it came to pass, when the evil spirit from God was upon Saul, that David took an harp, and played with his hand: so Saul was refreshed, and was well, and the evil spirit departed from him.
When did people first start thinking of schizophrenia as an illness?
How did beliefs change?
Read Also: Simple Phobia Definition
Types Of Treatments In Addiction Rehabs
What Is Schizophrenia? Definition & Diagnosis of the Disorder
Schizophrenia belongs to severe mental disorders leading to the distorted perception of reality. The affected person is acting inadequately, and their ideas and explanations are illogical .
The scientific views on the causes of schizophrenia remain a controversial position. The underlying risk factor is heredity, secondary factors various diseases and traumas. They are triggering the latent processes. The first signs of schizophrenia are diagnosed, as a rule, in adolescence. This mental disorder is more common among youngsters and less widespread among elderly people. Nowadays almost 1% of the worlds population is familiar with it.
How Is Schizophrenia Treated
The goal of schizophrenia treatment is to ease the symptoms and to cut the chances of a relapse, or return of symptoms. Treatment for schizophrenia may include:
- Medications: The primary medications used to treat schizophrenia are called antipsychotics. These drugs donât cure schizophrenia but help relieve the most troubling symptoms, including delusions, hallucinations, and thinking problems.
- Older antipsychotic medications used include:
Note: Clozapine is the only FDA-approved medication for treating schizophrenia that is resistant to other treatments. Itâs also used to lessen suicidal behaviors in those with schizophrenia who are at risk.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Early Warning Signs Of Schizophrenia
In some people, schizophrenia appears suddenly and without warning. But for most, it comes on slowly, with subtle warning signs and a gradual decline in functioning, long before the first severe episode. Often, friends or family members will know early on that something is wrong, without knowing exactly what.
In this early phase of schizophrenia, you may seem eccentric, unmotivated, emotionless, and reclusive to others. You may start to isolate yourself, begin neglecting your appearance, say peculiar things, and show a general indifference to life. You may abandon hobbies and activities, and your performance at work or school can deteriorate.
The Signs And Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
Steven Gans, MD is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
The symptoms of schizophrenia can seem peculiar to people who observe them. However, when people are experiencing symptoms, they may have little or no insight that their thoughts or behaviors are strange. The lack of insight can make schizophrenia very frustrating and frightening for loved ones.
Read Also: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
Here Are Some Things You Can Do To Help Your Loved One:
- Help them get treatment and encourage them to stay in treatment
- Remember that their beliefs or hallucinations seem very real to them
- Tell them that you acknowledge that everyone has the right to see things their way
- Be respectful, supportive, and kind without tolerating dangerous or inappropriate behavior
- Check to see if there are any support groups in your area
Some symptoms require immediate emergency care. If your loved one is thinking about harming themselves or others or attempting suicide, seek help right away:
- Call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 1-800-273-TALK or text the Crisis Text Line .
What’s It Like Living With Schizophrenia

Watch Miles talk about his experience of living with schizophrenia.
Positive and negative symptoms
Professionals sometimes talk about schizophrenia symptoms as being ‘positive’ and ‘negative’. But this doesn’t mean ‘good’ or ‘bad’.
- Positive symptoms are experiences or behaviours that the condition adds to your life. Like hearing or seeing things that others don’t, or having a belief that something is real or true when it isn’t.
- Negative symptoms are experiences or behaviours that the condition takes away from your life. Like finding things less interesting or enjoyable, moving your body less, or having less motivation.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia Myths And Facts
Myth: People with schizophrenia have split, or multiple, personalities.
One of the biggest myths about schizophrenia is that people with schizophrenia have split, or multiple, personalities.
Fact: Having multiple personalities, or split personalities, is a symptom of a different mental illness called dissociative identity disorder.
Experts say that the media is partially responsible for some public misconceptions about schizophrenia.
Myth: People who have schizophrenia are dangerous.
Movies and television shows often perpetuate the myth that all people with schizophrenia are dangerous. This type of misunderstanding can be harmful for people with schizophrenia.
Fact: Most people with schizophrenia are not dangerous to others.
Some people with schizophrenia may have violent outbursts, and theres a small subset of people with schizophrenia who can be dangerous.
The risk of harm to others is increased in people who are not currently in treatment, as well as people who are acutely psychotic, often with paranoid or other delusions involving others potentially harming them in some way.
Overall, the rate of violence committed by people with schizophrenia is very small in fact, people with schizophrenia are more likely to be victims of violence as opposed to perpetrators.
When people with schizophrenia use drugs or alcohol, the risk of violence directed toward others is increased.
How Common Is Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is more common than most people think. About 1 in 200 of the people in the United States will develop schizophrenia over the course of their lives. It’s also important to know that schizophrenia has many different symptoms and can show up in many different ways.
Schizophrenia is not the same as a “split personality.” A split personality is another type of mental illness. Split personality is much less common than schizophrenia.
Recommended Reading: Feretrophobia Definition
Brain Circuitry In Schizophrenia
Information processing in the brain is a complex task, and even simple sensory information, such as recognizing a sight or a sound, engages circuits of cells in multiple regions of the brain. Scientists early in the 20th century imagined that brain function occurred in discrete steps along a linear stream of information flow. However, the recent emergence of brain imaging as an important tool for understanding the neuroscience of cognition and emotion has demonstrated that the brain operates more like a parallel processing computer with feed-forward and feedback circuitry that manages information in distributed and overlapping processing modules working in parallel. Thus, abnormal function in one brain region will have functional ripple effects in other regions, and abnormal sharing of information between regions, perhaps because of problems in the connectional wiring, can result in abnormal behavior even if individual modules are functionally intact.
Challenges In Reaching Out
It can be challenging for people with schizophrenia to reach out to a doctor or other health professional about their concerns. This can be particularly tough for people who may be experiencing symptoms that leave them feeling suspicious of others.
Reassurance from people they trust can be helpful in encouraging and prompting someone to speak with a doctor or other mental health professional.
You May Like: The Definition Of Phobia
Are People With Schizophrenia Dangerous
Popular books and movies often depict people with schizophrenia and other mental illnesses as dangerous and violent. This usually isnât true. Most people with schizophrenia are not violent. More typically, they prefer to withdraw and be left alone. When people with mental illness do take part in dangerous or violent behaviors, itâs generally a result of their psychosis and the fear that theyâre being threatened in some way by their surroundings. Drug or alcohol use can make it worse.
On the other hand, people with schizophrenia can be a danger to themselves. Suicide is the top cause of premature death among people with schizophrenia.
The Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia Include:
- Avolition: A total lack of motivation, to the point of not being able to pursue any sort of goal, including seemingly simple things like making or taking a phone call
- Anhedonia: An inability to experience pleasure from social situations or physical activities like eating, touching, or sex
- Social withdrawal: Lack of interest in being with other people
- Difficulty paying attention: Staring off aimlessly while someone is speaking, for example
- Apathy: This might show up as lack of personal hygiene, or a lack of concern for yourself or others.
- Affective flattening: An absence of affect or emotional expression, such as unresponsive facial expressions or vocal tones and very little body language or movement
- Alogia: Difficulty speaking, which might mean a significant reduction in the amount of words spoken or in the ability to speak with ease or use detail when communicating
Also Check: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
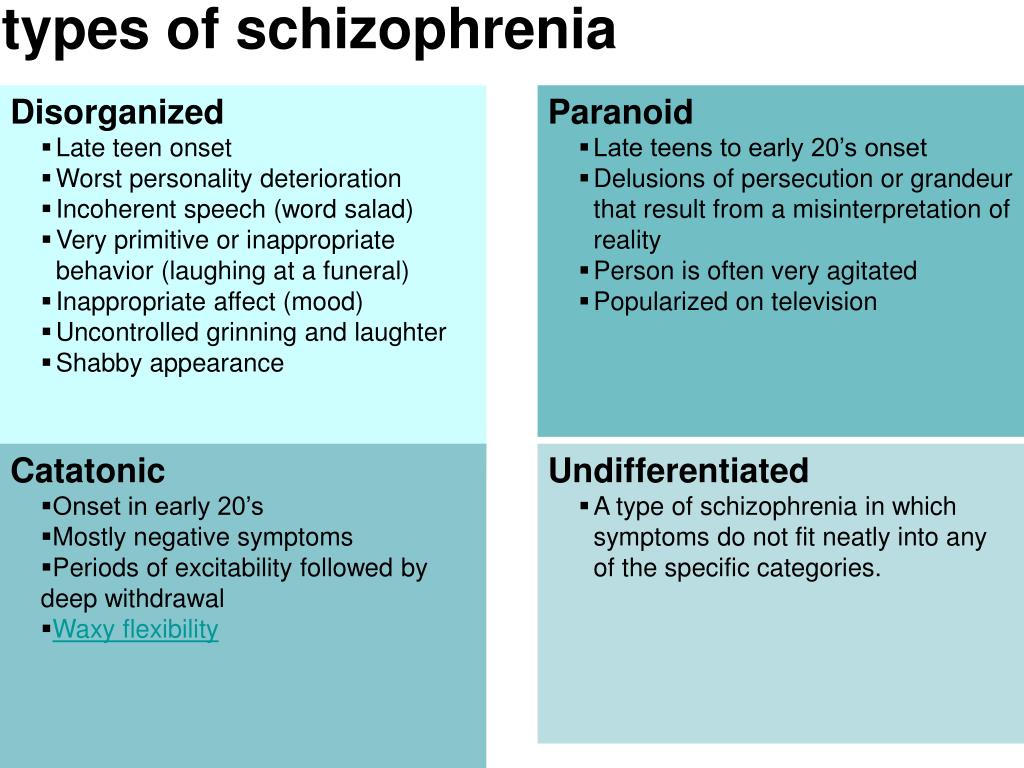
What Are The Types Of Schizophrenia
There are different types of schizophrenia. The International Classification of Diseases manual describes them as below.
Paranoid schizophrenia
- Pranks, giggling and health complaints.
- Usually diagnosed in adolescents or young adults.
Catatonic schizophrenia
- Unusual movements, often switching between being very active and very still.
- You may not talk at all.
Simple schizophrenia
- Negative symptoms are prominent early and get worse quickly.
- Positive symptoms are rare.
Undifferentiated schizophrenia
Your diagnosis may have some signs of paranoid, hebephrenic or catatonic schizophrenia, but doesnt obviously fit into one of these types alone.
Residual schizophrenia
This type of schizophrenia is diagnosed in the later stages of schizophrenia. You may be diagnosed with this if you have a history of schizophrenia but only continue to experience negative symptoms.
Other schizophrenia
There are other types of schizophrenia according to the ICD-10, such as.
- Cenesthopathic schizophrenia. This is where people experience unusual bodily sensations.
- Schizophreniform. Schizophreniform disorder is a type of psychotic illness with symptoms similar to those of schizophrenia. But symptoms last for a short period.
Unspecified schizophrenia
Symptoms meet the general conditions for a diagnosis, but do not fit in to any of the above categories.
Schizophrenia Research And Statistics
The exact prevalence of schizophrenia is hard to measures, but the NIMH estimates that schizophrenia affects between 0.25 and 0.64 percent of U.S. adults, while the NAMI has put it closer to 1 percent.
Men typically start to show symptoms of schizophrenia in their late teens or early twenties. Women tend to show symptoms a bit later, usually in their late twenties or early thirties.
Men are about 1.4 times more likely to be diagnosed with schizophrenia than women.
Schizophrenia can occur at any age, but it’s less commonly diagnosed for the first time in a person older than 40 or younger than 12.
Recommended Reading: Can Dehydration Cause Panic Attacks