A Systematic Review On Comorbid Post
Psychiatric comorbidities are common among individuals with mental disorders in particular, post-traumatic stress disorder has been found to frequently co-occur with schizophrenia . Schizophrenia is a chronic mental disorder characterized by positive and negative symptoms . PTSD is a condition of persistent mental and emotional
Can Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Lead To Schizophrenia
Cognition And Mood Symptoms Include:
- Trouble remembering key features of the traumatic event
- Negative thoughts about oneself or the world
- Distorted feelings like guilt or blame
- Loss of interest in enjoyable activities
Cognition and mood symptoms can begin or worsen after the traumatic event, but are not due to injury or substance use. These symptoms can make the person feel alienated or detached from friends or family members.
It is natural to have some of these symptoms for a few weeks after a dangerous event. When the symptoms last more than a month, seriously affect ones ability to function, and are not due to substance use, medical illness, or anything except the event itself, they might be PTSD. Some people with PTSD dont show any symptoms for weeks or months. PTSD is often accompanied by depression, substance abuse, or one or more of the other anxiety disorders.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Depressed Zodiac Sign
Childhood Trauma Linked To Schizophrenia
- Date:
- University of Liverpool
- Summary:
- Researchers have found that children who have experienced severe trauma are three times as likely to develop schizophrenia in later life.
Researchers at the University have found that children who experience severe trauma are three times as likely to develop schizophrenia in later life.
The findings shed new light on the debate about the importance of genetic and environmental triggers of psychotic disorders. For many years research in mental health has focused on the biological factors behind conditions such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and psychotic depression, but there is now increasing evidence to suggest these conditions cannot be fully understood without first looking at the life experiences of individual patients.
The research, conducted by teams at Liverpool and Maastricht University in the Netherlands, is the first of its kind to bring together and analyse the findings from more than 30 years of studies looking at the association between childhood trauma and the development of psychosis. The researchers looked at more than 27,000 research papers to extract data from three types of studies those addressing the progress of children known to have experienced adversity studies of randomly selected members of the population and research on psychotic patients who were asked about their early childhood.
Story Source:
The Relationship Between Ptsd And Psychosis
Frank van Groen / LOOK-foto / Getty Images
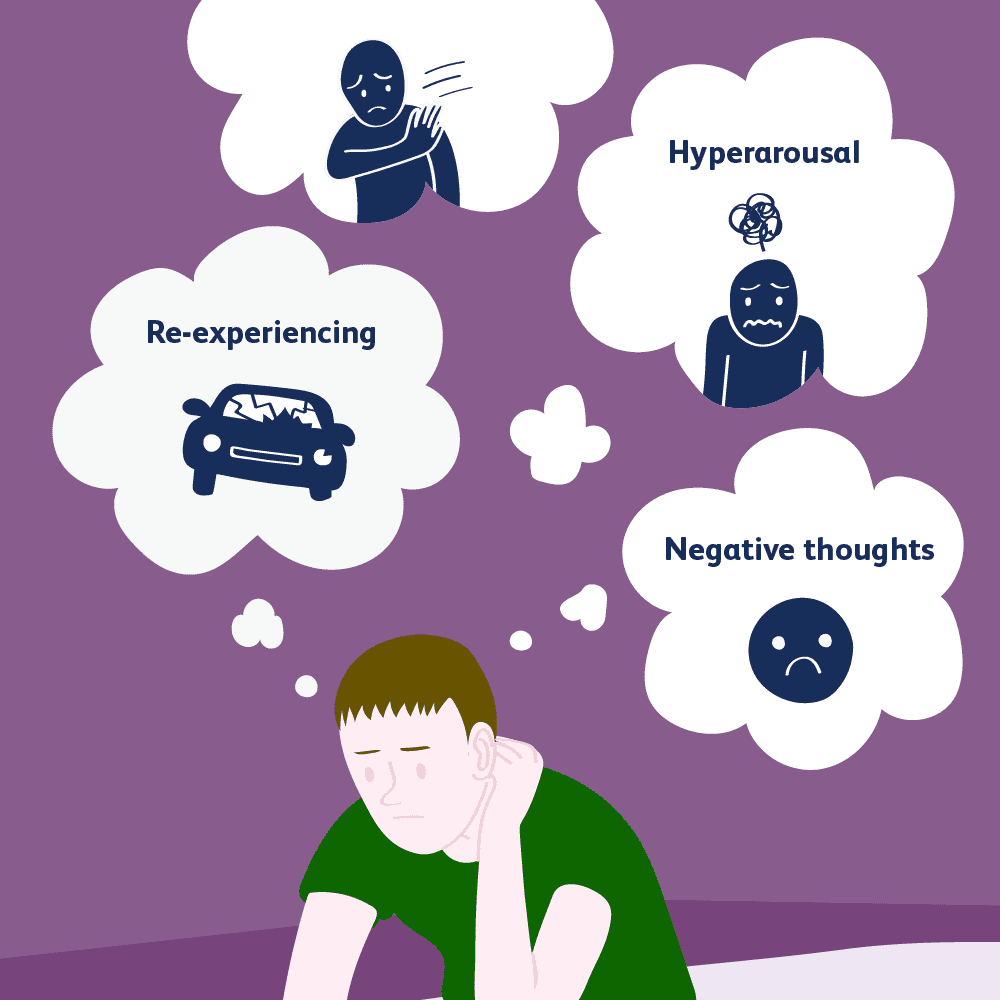
Mental health experts describe post-traumatic stress disorder as consisting of four clusters of symptoms: re-experiencing symptoms, avoidance symptoms, negative changes in mood and brain function, and hyperarousal symptoms.
However, some mental health professionals believe that the experience of psychotic symptoms should be considered as an addition to that list. Symptoms of psychosis, such as hallucinations, often occur with symptoms of PTSD.
Recommended Reading: How To Help During A Panic Attack
Trauma And Ptsd In Severe Mental Illness
Trauma and posttraumatic stress disorder have high prevalence among individuals with severe mental illness, such as schizophrenia. Between 69.5 and 98% of this population experienced a traumatic event in their life , compared to 3956% in the general population . Rates of current PTSD in individuals with a severe mental illness range from 29 to 48% . Rates of current PTSD in studies focusing on schizophrenia specifically found 13, 28 and 29% . These rates are much higher than the prevalence of lifetime PTSD in the general population which ranges from 7.8 to 9.2% and the point prevalence of 2% .
Although trauma and PTSD are common among individuals with a severe mental illness, clinicians frequently overlook trauma and PTSD. A recent study by Howgego et al. found that 33% of their sample of patients of a community mental health setting with a severe mental illness met the diagnostic criteria for PTSD. Only 4% of the sample had a formal diagnosis of PTSD in their medical record. The general lack of recognition and documentation of trauma and PTSD has been demonstrated in a number of studies .
The Relationship Between Ptsd And Schizophrenia
Post-traumatic stress disorder and symptoms of psychosis often occur together. PTSD is described in four clusters. These include avoidance symptoms, re-experiencing symptoms, hyperarousal symptoms, and negative changes in mood and brain function.
Schizophrenia is considered one of the most common psychiatric diagnoses, and its not surprising for people to have both PTSD and schizophrenia. As weve discussed above, PTSD occurs after traumatic experience happen. Still, it has been found that traumatic experiences are more likely to happen to those with schizophrenia than in the general population.
A National Institutes of Health study found that there is a significant genetic overlap between PTSD and schizophrenia.
Treatment for both disorders is imperative, but some physicians are apprehensive about using conventional approaches. When using exposure therapy for PTSD, it may not be the best approach for someone with schizophrenia because therapy will worsen symptoms of schizophrenia. Some evidence has shown that well-thought-out treatment may reduce PTSD symptoms.
If you are struggling with a combination of the two, its crucial that you find a physician who specializes in both treatments. It will allow you to have a tailored experience that helps your specific needs.
Don’t Miss: How Likely Is Schizophrenia To Be Inherited
Mental Health Disorders That Include Psychotic Symptoms
In addition to PTSD, positive and negative psychotic symptoms can occur in other mental health conditions. It can sometimes be difficult to distinguish between them, as the symptoms can overlap.
Mental health conditions that can have positive and negative psychotic symptoms include:
- Schizophreniform disorder
Information For Carers Friends And Relatives
If you are a carer, friend or relative of someone who lives with PTSD, you can get support.
How can I get support?
You can do the following.
- Speak to your GP about talking therapies and medication for yourself.
- Speak to your relatives mental health team about a carers assessment or ask for one from your local social services.
- Join a carers service. They are free and available in most areas.
- Join a carers support group for emotional and practical support. Or set up your own.
What is a carers assessment?A carers assessment is an assessment of the support that you need so that you can continue in your caring role. You might be able to get support from social services.
You can find out more about Carers assessment Under the Care Act 2014 by clicking here.
How do I get support from my peers?You can get peer support through carer support services or carers groups. You can search for local groups in your area by using a search engine such as Google. You can find all of our peer support groups here: www.rethink.org/help-in-your-area/support-groups/.
You can look on the following websites:
How can I support the person I care for?
You can do the following.
You can find out more about:
- Supporting someone with a mental illness by clicking here.
- Responding to unusual thoughts and behaviours by clicking here.
- Worried about someones mental health by clicking here.
- Stress How to cope by clicking here.
You can find out more about:
Also Check: What Does Ed Stand For Eating Disorder
Treating Trauma The Betterhelp Way
Every person needs to feel comfortable with their therapist, but it is particularly important for those living with PTSD. BetterHelp will work to match you with a therapist who makes you feel safe and who you can trust. When you meet with an online counselor who specializes in trauma and recovery, you can be sure that you’re in a secure space where you can speak your truth and begin to process what you’ve been through. The excellent counselors at BetterHelp aren’t here to judge but rather to help you treat your scars and traumatic experiences. BetterHelp therapists will also let you go at your own pace. There’s no timeline on healing from trauma, and your counselor understands this. You can take all the time in the world to sort through your concerns. Read below for some reviews of BetterHelp counselors.
Other Commonly Asked Questions
Is hallucinations a symptom of PTSD?
Can PTSD look like schizophrenia?
Can PTSD trigger psychosis?
Can trauma cause visual hallucinations?
Can PTSD turn into schizophrenia?
Do I have psychosis or is it PTSD?
How do u know if your hallucinating?
Can anxiety cause hallucinations?
What Is Complex Ptsd
The main symptoms of PTSD and complex PTSD are the same. Complex PTSD is sometimes known as c-PTSD, or CPTSD. If you have complex PTSD, you may have extra symptoms such as:
- issues with keeping a relationship,
- finding it difficult to feel connected to other people,
- a belief that you are worthless with deep feelings of shame, guilt or failure that can be related to the trauma, and
- difficulty controlling your emotions.
Youre more likely to develop complex PTSD if your trauma has been an ongoing event. Or series of different traumatic events. The trauma might be very threatening or frightening. Most commonly from a trauma which you werent able to escape from such as:
- a long period of domestic abuse, or
- a long period of sexual or physical abuse as a child or adult.
Don’t Miss: What To Do If Depressed
Risks Of Developing Schizophrenia
- In those with PTSD, psychotic symptoms typical of schizophrenia occur at a higher than expected frequency compared to those without PTSD
- Collections of genes associated with PTSD overlap with genes identified as increasing the risk of developing schizophrenia
Sources: Oconghaile A, DeLisi LE. Distinguishing schizophrenia from posttraumatic stress disorder with psychosis. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2015 28:249-255. | Duncan LE, Ratanatharathorn A, Aiello AE, et al. Largest GWAS of PTSD yields genetic overlap with schizophrenia and sex differences in inheritability. Molec Psychiatry. 2018 23:666-673.
Study Sample And Data Collection
The present analysis was part of a larger study, Japanese Family Violence and Mental Illness . The larger study aimed to examine the prevalence of familial violence and related factors among caregivers and siblings in 866 households belonging to 27 affiliate family groups under a prefectural-level family group association in Japan.
Questionnaires were distributed to 768 of the 866 households in the group association. The distribution of questionnaires was determined by the group leaders. Questionnaires were not distributed to 118 households due to health conditions or family issues. Of the 482 returned caregiver questionnaires , 463 were valid . The present analysis focused on caregiver questionnaires completed by caregivers of patients with schizophrenia. The sample size for this analysis was 353 after the exclusion of questionnaires regarding patients diagnosed with illnesses other than schizophrenia , respondents other than parents , and those with missing IES-R data .
You May Like: What’s The Definition Of Bipolar
Disinhibited Social Engagement Disorder
Disinhibited social engagement disorder occurs in children who have experienced severe social neglect or deprivation before the age of 2. Similar to reactive attachment disorder, it can occur when children lack the basic emotional needs for comfort, stimulation and affection, or when repeated changes in caregivers prevent them from forming stable attachments.
Disinhibited social engagement disorder involves a child engaging in overly familiar or culturally inappropriate behavior with unfamiliar adults. For example, the child may be willing to go off with an unfamiliar adult with minimal or no hesitation. These behaviors cause problems in the childs ability to relate to adults and peers. Moving the child to a normal caregiving environment improves the symptoms. However, even after placement in a positive environment, some children continue to have symptoms through adolescence. Developmental delays, especially cognitive and language delays, may co-occur along with the disorder.
The prevalence of disinhibited social engagement disorder is unknown, but it is thought to be rare. Most severely neglected children do not develop the disorder. Treatment involves the child and family working with a therapist to strengthen their relationship.
Editorial: Trauma Psychosis And Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
- 1Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
- 2Center for Psychiatric Rehabilitation, Boston University, Boston, MA, United States
Editorial on the Research Topic
Exposure to psychologically traumatic experiences has been part of the human condition throughout history, but only within the last half century has research provided insight into the short- and long-term sequelae of trauma, ultimately resulting in the creation of a specific diagnostic category to capture the most common negative consequences. In 1980, posttraumatic stress disorder was included in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , setting the stage for research and clinical practice to more systematically study and treat this mental health problem. Since the inclusion of PTSD in DSM-III, there has been huge growth in the fields understanding of PTSD, and the development of concomitant evidence-based treatments to aid individuals with PTSD in overcoming this disorder and returning to previous levels of functioning.
Also Check: How To Overcome Depression Without Medication
Arousal And Reactivity Symptoms Include:
- Being easily startled
- Feeling tense or on edge
- Having difficulty sleeping
- Having angry outbursts
Arousal symptoms are usually constant, instead of being triggered by things that remind one of the traumatic events. These symptoms can make the person feel stressed and angry. They may make it hard to do daily tasks, such as sleeping, eating, or concentrating.
Psychotic Symptoms In Ptsd
Researchers at the University of Manitoba, Columbia University, and the University of Regina examined data on 5,877 people from across the United States with the goal of determining the rates with which people with PTSD experience different psychotic symptoms.
The researchers found that the experience of positive psychotic symptoms was most common among people with PTSD. Approximately 52% of people who reported having PTSD at some point in their lifetime also reported experiencing a positive psychotic symptom.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Severe Anxiety And Panic Attacks
Paranoia Hallucinations And Delusions
Persons with PTSD may experience one or more of these symptoms, depending on the severity of their trauma exposure.
Paranoia
Paranoia can cause an individual to lose trust in others and withdrawal socially, which can have a circular effect on symptoms of PTSD. Paranoia can make reaching out to others difficult. You may constantly overanalyze the motivations of other people and question whether they are telling you the truth. Children who have experienced child abuse often develop this loss of trust in adults. Paranoia can damage relationships and cause you to become isolated.
Hallucinations
Perhaps the most common symptom of PTSD related to psychosis is hallucinations. You may feel like you are seeing people or hearing voices that aren’t there, but that are related to the trauma. Hallucinations can be correlated with, but are distinct from, flashbacks. These are episodes in which you feel like you’re reliving the trauma.
Dissociation can also be related to these experiences, where you perceive a disconnect between yourself and the world around you.
Delusions
Paranoia can become severe enough to become full-blown delusions. Delusions are usually related to the trauma in some fashion and can keep a person feeling as though they can’t move on from the past. Delusions can be debilitating and difficult to let go of once they have become established.
What Are The Symptoms Of Ptsd
The main symptoms and behaviours associated with PTSD and complex PTSD include:
- Reliving the experience through flashbacks, intrusive memories, or nightmares
- Overwhelming emotions with the flashbacks, memories, or nightmares
- Not being able to feel emotions or feeling numb
- Dissociation, that can include disconnecting from yourself or other people
- Avoidance. This could mean that you try to distract yourself from thinking about the trauma. Or you avoid people and situations that remind you of the trauma.
Other symptoms and behaviours associated with PTSD and complex PTSD include:
- Negative mood and thinking.
You can also try self-help techniques.
How can the NHS help me?
If you have symptoms that are causing you a lot of distress or are affecting your daily life, you can see your GP.
Your GP should carry out an initial assessment using screening tools to decide what care you need.
Your assessment should include information about:
- your physical needs,
- your social needs, and
- any risk to yourself or others.
Your GP will be able to talk to you about treatment options and coping strategies. You’re likely to be offered treatment if you’ve had symptoms of PTSD for more than 4 weeks or your symptoms are severe.
You can choose whether to have treatment and decide about the options your GP offers you. If youre unsure of anything, like the benefits of treatment, then ask your GP.
You can find out more information about NHS mental health teams by clicking here.
Some think:
Don’t Miss: Is The Sound Of Silence About Depression