What Is A Major Depressive Episode
Major depression is a mood state thats characterized by low energy levels, low mood, and feelings of despair or hopelessness. Depression is one of the most common mental health issues in the United States after anxiety disorders.
When it comes to bipolar disorder, major depression is identified by a set of symptoms similar to a manic episode. The DSM outlines nine symptoms of depression, and you need to experience five or more of them for it to be considered a major depressive episode. The symptoms include:
In addition to experiencing at least five of these symptoms, one of them has to be the first or second symptom. A low mood and the loss of interest in activities are definitive symptoms of a major depressive episode.
Recommended Reading: What Bipolar Medications Cause Weight Loss
What Causes Bipolar Disorder
The cause of bipolar disorder isnt clear. Research suggests that a combination of different things can make it more likely that you will develop bipolar disorder.
Genetic factors
There is a 13% chance you will develop bipolar disorder if someone in your immediate family, like a parent, brother or sister has bipolar disorder.
This risk is higher if both of your parents have the condition or if your twin has the condition.
Researchers havent found the exact genes that cause bipolar disorder. But different genes have been linked to the development of bipolar disorder.
Brain chemical imbalance
Different chemicals in your brain affect your mood and behaviour. Too much or too little of these chemicals could lead to you developing mania or depression.
Environmental factors
Stressful life events can trigger symptoms of bipolar disorder. Such as childhood abuse or the loss of a loved one. They can increase your chances of developing depressive episodes.
You can find more information about Does mental illness run in families? by clicking here.
How Do I Get Help If I Think I Have Bipolar Disorder
The usual first step to getting help is to speak to your GP.
It can help to keep a record of your moods. This can help you and your GP to understand your mood swings. Bipolar UK have a mood diary and a mood scale on their website. You can find their details in the Useful contacts section at the bottom of this page.
Your GP cant diagnose bipolar disorder. Only a psychiatrist can make a formal diagnosis. Your GP may arrange an appointment with a psychiatrist if you have:
- depression, and
- ever felt very excited or not in control of your mood or behaviour for at least 4 days in a row.
They might refer you to a psychiatrist at your local NHS community mental health team .
Your GP should make an urgent referral to the CMHT if they think that you might have mania or severe depression. Or there is a chance that you are a danger to yourself or someone else.
Your GP should refer you to your local NHS early intervention team if you have an episode of psychosis and its your first one.
Bipolar disorder can be difficult to diagnose because it affects everyone differently. Also, the symptoms of bipolar disorder can be experienced by people who have other mental illness diagnoses. It can take a long time to get a diagnosis of bipolar disorder.
You can find more information about:
- NHS mental health teams by clicking here.
Also Check: What Is The Most Common Eating Disorder In America
Recommended Reading: Phobia Psychology Definition
Does Someone With Schizoaffective Disorder Need To Be Hospitalized
Most people with this disorder can get outpatient treatment. They go to a clinic or hospital for treatment during the day and then return home. Sometimes, people have severe symptoms, though, or theyre in danger of harming themselves or others. They may need to be hospitalized to stabilize their condition.
Read Also: What Is A Phobia Of Spoons Called
Symptoms Of Schizoaffective Bipolar Type
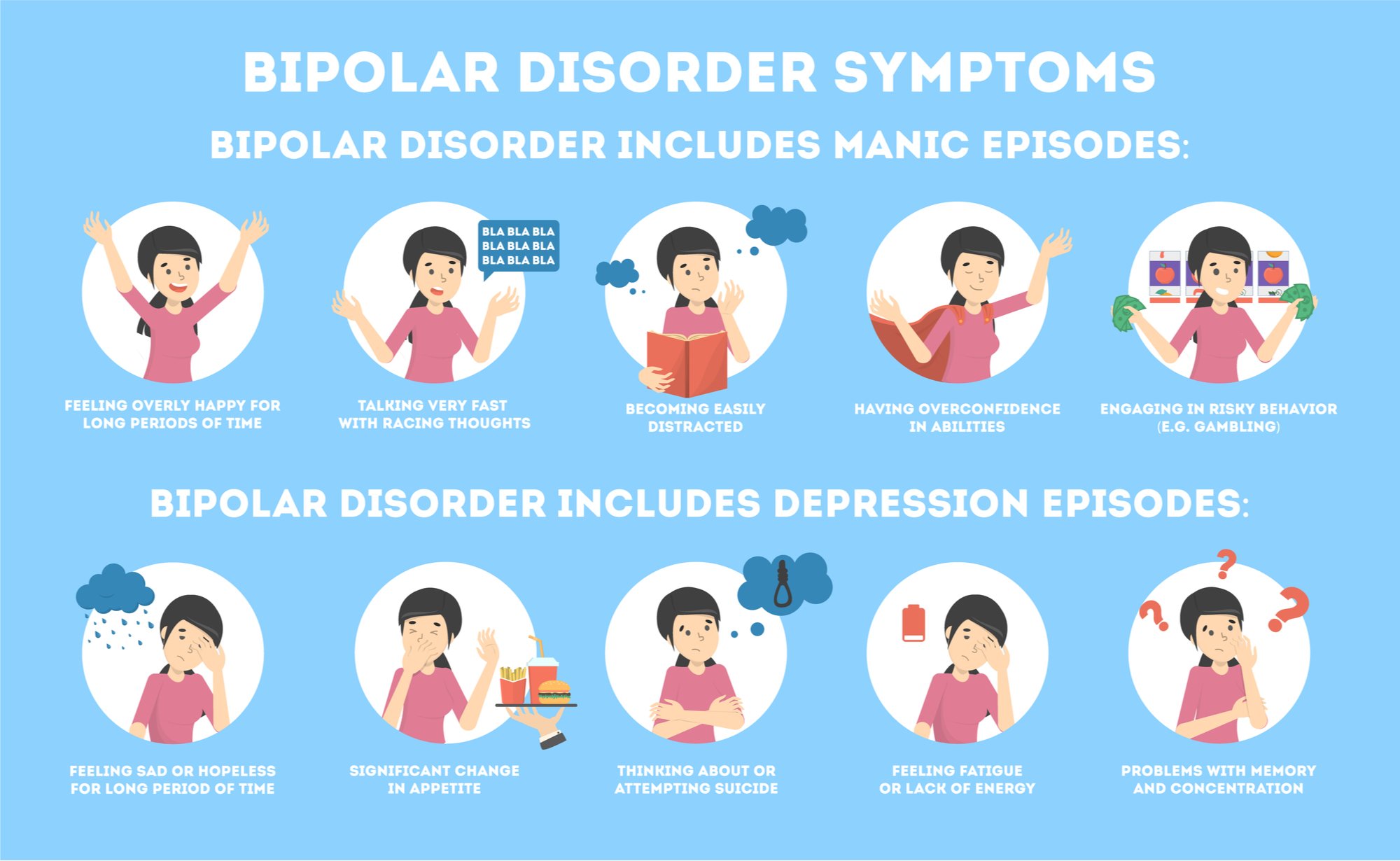
In terms of schizoaffective disorder vs. schizophrenia, the difference lies in the mood disorder symptoms. Someone diagnosed with schizophrenia will only experience the aforementioned symptoms of this mental illness. But, someone diagnosed with schizoaffective disorder experiences those symptoms as well as symptoms of a mood disorder, depression or bipolar disorder. Symptoms of bipolar disorder include:
- Mania or manic episodes. During a manic period a person has an extreme amount of energy and feels exaggerated self-confidence and an ability to keep going without much sleep. The high that someone experiences during mania is not normal and goes to the extreme, often resulting in irritability, anger, aggression, risky behaviors, and even suicide in some cases.
- Depressive episodes. In a depressive episode the symptoms are the same as major depression: hopelessness, sadness, guilt, shame, changes in sleeping and eating patterns, weight loss or weight gain, lack of energy, loss of interest in activities, and sometimes suicidal thoughts or attempts at suicide.
Someone diagnosed with schizoaffective disorder depressive type will only experience the symptoms of major depression along with schizophrenic symptoms. He or she does not experience manic episodes or symptoms of mania.
Also Check: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
Differences Between Bipolar Disorder And Schizophrenia
Psychosis, which includes hallucinations and delusions, is a hallmark symptom of schizophrenia. People with bipolar I disorder can have psychotic symptoms during mania and/or depression, and those with bipolar II can have them during an episode of depression. So while bipolar disorder and schizophrenia can share a set of serious symptoms, when distinguishing between the two disorders, doctors look at the differences between symptoms and also give different weight to some of the shared symptoms.
Also Check: Whatâs The Phobia Of Long Words
Symptom Of Mania And Hypomania
Euphoria
Euphoria can be described as a heightened, exaggerated, or extremely positive sense of happiness or well-being. It is considered to represent an abnormally extreme degree of happiness or contentment beyond that which occurs in normal emotional responses. It can be described as a sense of intense joy or happiness that is beyond what would be expected under the normal circumstances. Euphoria may be experienced by those who suffer from bipolar depression in the manic phase. It may occasionally be seen in other psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, in which emotional responses and perceptions of reality are abnormal.
- more talkative than usual or feeling pressured to continue talking
- expresses ideas rapidly â quickly changes topics or feels that thoughts are racing
- trouble focusing
- restlessness or increased participation in goal-oriented activities and
- excessively engaging in activities that have a high likelihood of having negative consequences .
While mania and hypomania have many symptoms in common, mania results in more severe problems compared to hypomania.
Read Also: Depression Appetite Loss
How Should I Take Care Of Myself When It Comes To Schizoaffective Disorder
Perhaps youve noticed signs of schizoaffective disorder in yourself or a loved one. Those symptoms may include prolonged hallucinations, delusions, depression or manic episodes. The first step is to talk to a healthcare provider. Getting diagnosis and treatment as soon as possible helps improve symptoms and promote a good quality of life. Be sure to follow your providers treatment instructions:
- Attend therapy sessions, including individual and family therapy.
- Stay in contact with your provider, who can help manage and adjust your treatments as necessary.
- Take medications as directed. Talk to your provider to help manage side effects from the medications.
- Treat substance use disorders, if necessary.
Donât Miss: Feritriphobia
How Are Bipolar And Schizophrenia Related
Although bipolar and schizophrenia are still, for the most part, thought to be two distinct psychiatric diseases, they are related in many ways. Both diseases usually develop in late adolescence or early adulthood. The genetic causal factors have been found to be highly similar in the two brain diseases both disorders often appear in the same families. Some people are diagnosed with symptoms of both diseases. Schizophrenia and bipolar, or manic-depressive, disorder also share common symptoms and treatments.
Some medications prescribed for both bipolar and schizophrenia lower levels of protein kinase C in the brain. High levels of this brain protein are thought to increase the severity of symptoms related to both diseases such as hearing or seeing things that arenât there, having racing thoughts and experiencing grandiose, or false beliefs, relating to oneâs personal power. In what is called the dysphoric mood in schizophrenia, schizophrenics often experience severe irritability, anxiety and depression similar to what bipolars, or manic-depressives, tend to have in their depressive periods. If not treated, both bipolars and schizophrenics are extremely likely to abuse drugs or alcohol as a way of âself medicating.â
Recommended Reading: Can You Faint From A Panic Attack
When To See A Doctor
If a person notices mood changes that seem to be stronger than normal, they should see a healthcare professional. Bipolar disorder can be difficult to diagnose, but a comprehensive health history, physical exam, and discussion of moods and symptoms can help.
If a friend or family member appears to have symptoms of mania or hypomania, those closest to them may want to talk to them about seeing a doctor and getting treatment.
How Can I Tell If Im Having A Manic Or Hypomanic Episode
It can be difficult to recognize if youre having a manic or hypomanic episode, especially if you havent been diagnosed with a mental disorder associated with it. If you suspect that you may be experiencing either hypomania or mania, start a mood journal to keep track of your moods, and talk to your loved ones.
Read Also: Schizophrenia Cycles
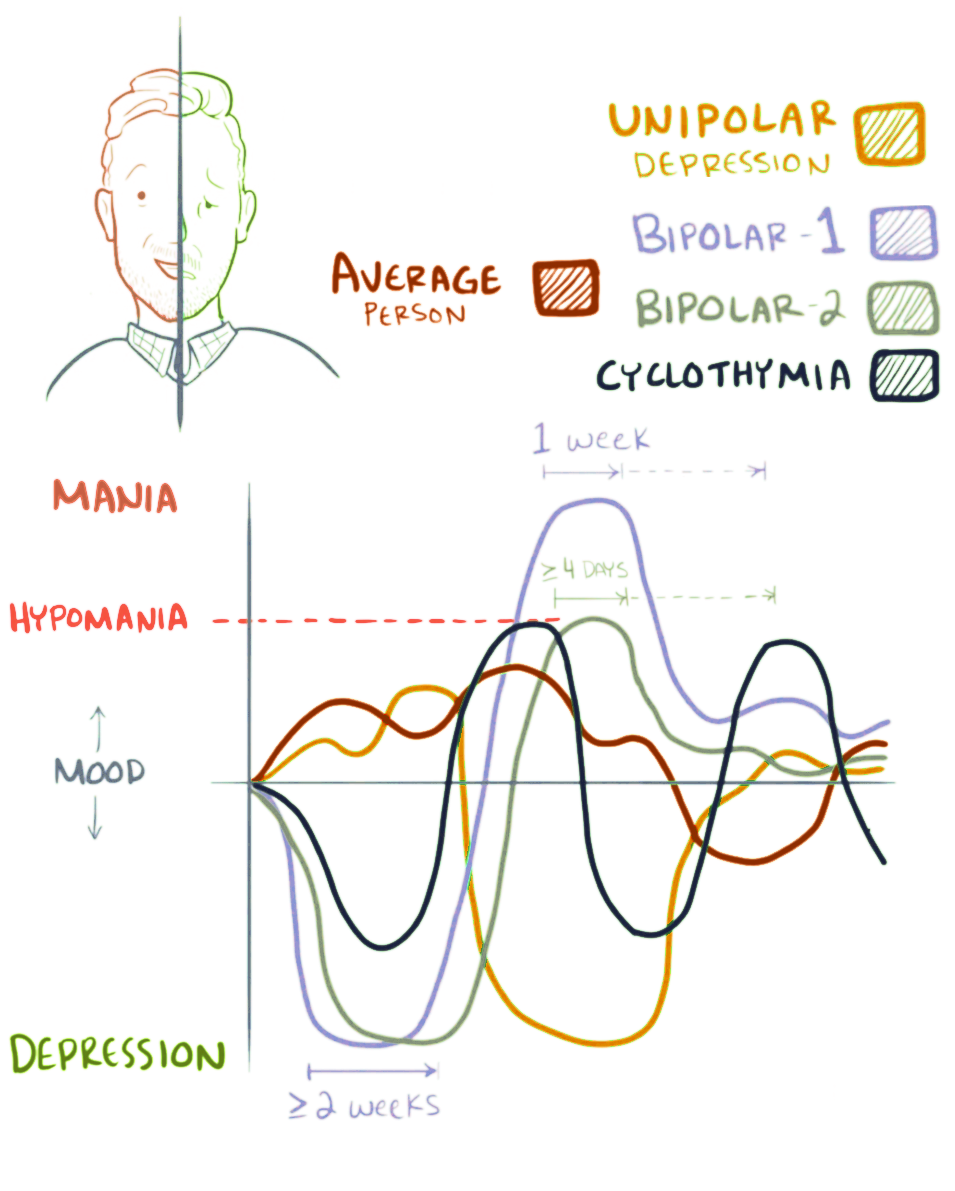
What Is Bipolar Ii Disorder
Bipolar II disorder is a type of bipolar disorder in which people experience depressive episodes as well as hypomanic episodes , but never mania. People with bipolar II disorder tend to have longer and more frequent depressed episodes than people with bipolar I disorder.
If the severity of your symptoms never rises to the level of mania, you have bipolar II disorder. If you have even a single episode of what is considered mania or one psychotic event during a hypomanic episode, your diagnosis would change to bipolar I disorder.
Whats The Difference Between Feeling Good Vs Hypomania
It takes time to know the difference. Everyone enjoys being happy and feeling good. But feeling good doesnt always mean you are good. Over time, youll start to understand yourself and learn the warning signs that you may be starting to have an elevated mood that is different than just feeling good.
Ask family and close friends who you trust, and have frequent contact with, to give you feedback. Ask them to tell you when they see beyond normal changes in your mood or behaviors.
Read Also: Phobia Of Spoons
Symptoms That Lead To A Diagnosis
If youre suffering from any kind of mental health disorder, its important that you identify and understand your symptoms in order for our doctors to correctly diagnose you. Bipolar disorder consists of both manic and depressive episodes that create an unstable mood.
Mania can be extreme changes in mood, or you can have hypomania which is typically less severe. Symptoms of mania include:
Difficulty sleeping Extreme energy Increased self-esteem Difficulty concentrating Racing thoughts
On the opposite end of the spectrum, depression can change your emotional highs to hopeless lows. If you have bipolar disorder with depression, symptoms you may experience include:
Fatigue Sadness Decreased energy Overeating or loss of appetite Suicidal thoughts
Our team at Boston MindCare take a detailed history to decipher your symptoms and give you a definitive diagnosis. With that, we can also form a customized treatment plan for you.
How To Manage Mania And Hypomania
The good news is that there are effective ways to manage manic and hypomanic episodes through treatment and coping strategies.
Episodes of mania and hypomania will be different for each person, so your treatment plan and management strategy will be unique to you.
When you feel the early symptoms starting, there are ways to prevent them from getting worse. The International Bipolar Foundation recommends the following:
- Remember that having bipolar is not your fault. You are not broken in any way.
- Pay attention to the warning signs that a mood episode is coming on. Noticing the symptoms early can help you prevent an episode from escalating.
- Avoid using drugs and alcohol.
- Make use of support networks, including healthcare professionals, family, and friends.
- Try to get enough sleep and keep up consistent sleeping patterns.
- Use stress management techniques, like therapy or exercise.
- Continue to take your medication, even if you feel well during a manic episode.
For long-term management, research shows that medication paired with psychotherapy results in more successful treatment than just having one form of treatment.
Medications prescribed often include mood stabilizers, antidepressants, and atypical antipsychotics. These are given to reduce the extreme changes in mood.
Some therapy options to help with difficult emotions or thoughts are:
Recommended Reading: The Phobia Of Bees
Is Bipolar Affective Disorder The Same As Bipolar 1
Bipolar Affective DisorderIdepression
. Besides, is bipolar disorder and bipolar affective disorder the same?
The combination of the two episodes, which are at the opposite poles of the range of mood, is called bipolar disorder or bipolar affective disorder. Rarely, some people show features of both mania and depression at the same time. They are hyperactive while experiencing depressive mood. The term ‘affect’ means mood.
One may also ask, what are the 4 types of bipolar disorder? Or the cycles can be much longer, lasting up to several weeks or even months. According to the American Psychiatric Association, there are four major categories of bipolar disorder: bipolar I disorder, bipolar II disorder, cyclothymic disorder, and bipolar disorder due to another medical or substance abuse disorder.
Also, is Bipolar 1 or 2 worse?
Bipolar II only involves hypomanic and depressive episodes. The manic episodes in bipolar I can be more dangerous than the hypomanic ones in bipolar II, but depressive episodes can be longer in people with bipolar II, the Mayo Clinic. One is not better or worse than the otherthey’re just different.
What is a bipolar 1 disorder?
Bipolar I disorder is a form of mental illness. A person affected by bipolar I disorder has had at least one manic episode in his or her life. Most people with bipolar I disorder also suffer from episodes of depression.
Can Bipolar Disorder Be Prevented
While theres no guaranteed way to prevent someone from developing bipolar disorder, many people successfully manage it with the right treatment and support. A successful strategy may include medication, therapy and other self-help strategies.
If you have a family history of bipolar disorder, its important to be aware of early warning signs, and for friends and family to be aware of them too. Avoid taking substances that can trigger manic or hypomanic episodes such as:
- recreational drugs such as cocaine, ecstasy and amphetamines
- excessive amounts of caffeine
Other ways to prevent relapses or episodes include learning to manage your stress and getting enough sleep.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Phobia Of Long Words
Can Hypomania Be Prevented
Episodes of hypomania cant always be prevented. However, you can learn ways to better manage your symptoms and prevent them from getting worse.
Suggestions on your to-do list might include:
- Keeping a mood diary to become more self-aware of events that trigger an oncoming episode of hypomania. These events are unique to you. Sometimes you cant recognize your own triggers. Ask your trusted, close family and friends to help identify when they see changes in your mood, behavior and energy level that is different from your usual self.
- Following other coping strategies.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hypomania
Symptoms of a hypomanic episode are the same but less intense than mania. Hypomanic symptoms, which vary from person to person, include:
- Having an abnormally high level of activity or energy.
- Feeling extremely happy, excited.
- Not sleeping or only getting a few hours of sleep but still feel rested.
- Having an inflated self-esteem, thinking youre invincible.
- Being more talkative than usual. Talking so much and so fast that others cant interrupt.
- Having racing thoughts having lots of thoughts on lots of topics at the same time .
- Being easily distracted by unimportant or unrelated things.
- Being obsessed with and completely absorbed in an activity youre focus on.
- Displaying purposeless movements, such as pacing around your home or office or fidgeting when youre sitting.
- Showing impulsive behavior that can lead to poor choices, such as buying sprees, reckless sex or foolish business investments.
Recommended Reading: Dehydration Panic Attacks
Acute Mania Or Hypomania
Treatment is summarized inBox 25.27. Acute mania is treated with an atypical antipsychotic, sodium valproate or lithium.
-
The atypical antipsychotics olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone and aripiprazole are recommended, especially with behavioural disturbance. The behavioural excitement and overactivity are usually reduced within days, but elation, grandiosity and associated delusions often take longer to respond.
-
Lithium may be used in instances where compliance is likely to be good however, the screening necessary prior to its prescription may prohibit its use in these circumstances as a first-line agent.
Andrew M. McIntosh, … Guy M. Goodwin, in, 2010
What Does Hypomania Feel And Look Like
What hypomania feels like and looks like will be different for each person. Some examples of things you might feel and/or do include:
- Get into an intense cleaning frenzy and clean all surfaces of every room in your house.
- Stay up until 3 a.m. or dont go to bed at all and not feel tired the next morning.
- Start a project, or more than one project, and work non-stop on these projects for 20 hours straight.
- Feel that you cant fail at anything you want to do, even if you have no training or experience.
- Quickly jump from subject to subject when talking, and talking very fast.
Don’t Miss: Can Anxiety Cause Blurry Vision