Causes & Risk Factors
It is not known for certain what causes schizophrenia, but like most other mental health problems, researchers believe that a combination of biological and environmental factors contribute to its development. Research has shown that:
- The risk is higher when a close family member has the illness.
- Schizophrenia may be influenced by brain development factors before and around the time of birth, and during childhood and adolescence.
- People who have experienced social hardship or trauma, particularly during childhood, have a higher risk.
- Cannabis use increases the risk of developing schizophrenia in youth and of triggering an earlier onset of the illness in people who are genetically vulnerable.
- Being born or spending ones childhood in an urban environment, rather than a rural one, increases the risk.
- Particular immigrant and refugee groups in Ontario may have a higher risk of developing psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia.
Exactly how these risk factors interact to cause schizophrenia is not yet fully understood.
What Myths Are There About Schizophrenia
There are some myths or mistaken beliefs about schizophrenia which come from the media. For example,
- Schizophrenia means someone has a split personality
This is not the case. The mistake may come from the fact that the name ‘schizophrenia’ comes from two Greek words meaning ‘split’ and ‘mind’.
- Schizophrenia causes people to be violent
Research shows that only a small number of people with the illness may become violent. The same way as a small minority of the general public may become violent.
People with schizophrenia are far more likely to be harmed by other people than other people are to be harmed by them. But as these incidents can be shocking, the media often report them in a way which emphasises the mental health diagnosis. This can create fear and stigma in the general public.
What Causes Schizophrenia
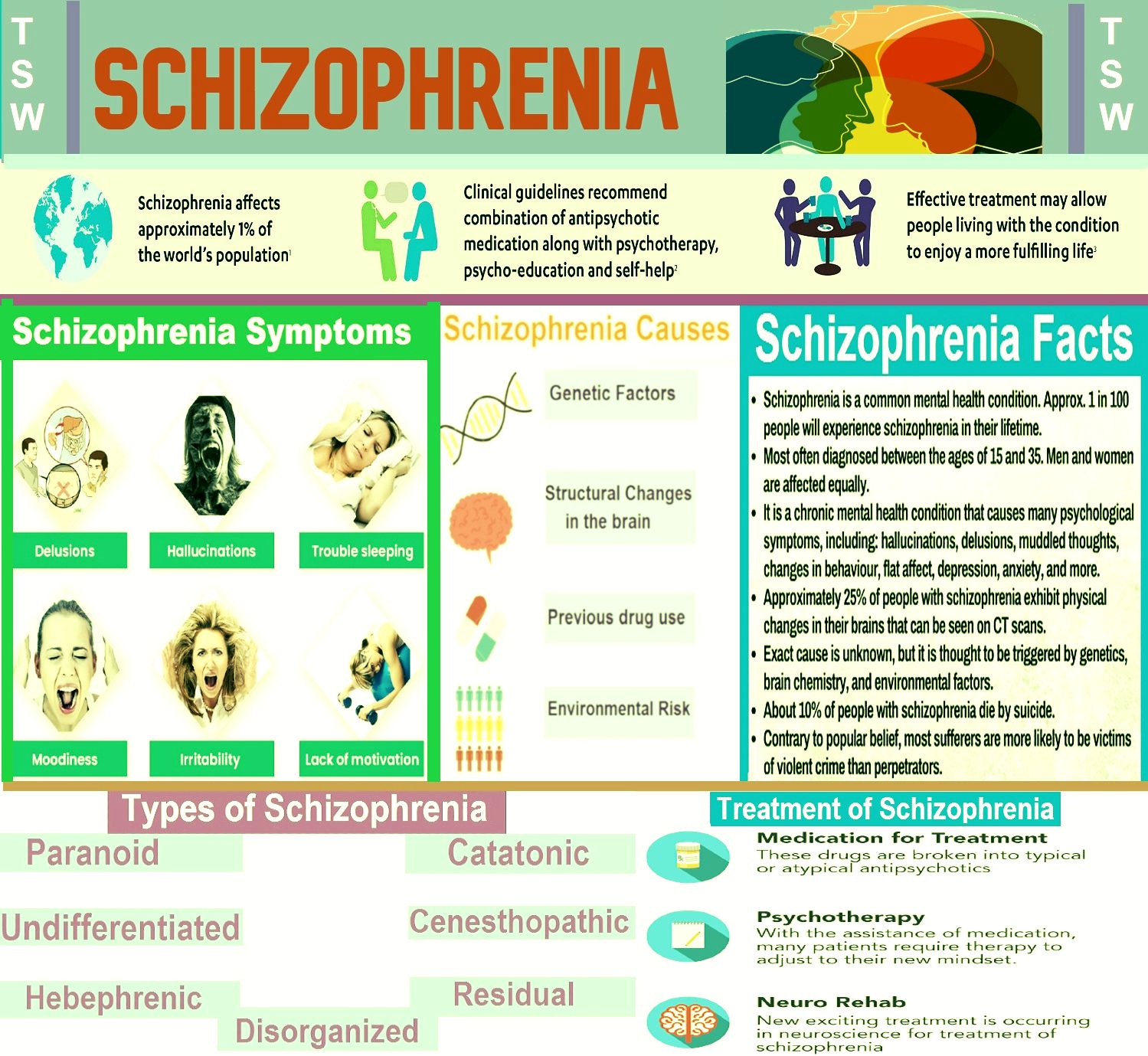
The exact cause of schizophrenia isnât known. But like cancer and diabetes, schizophrenia is a real illness with a biological basis. Researchers have uncovered a number of things that appear to make someone more likely to get schizophrenia, including:
- Genetics : Schizophrenia can run in families, which means a greater likelihood to have schizophrenia may be passed on from parents to their children.
- Brain chemistry and circuits: People with schizophrenia may not be able to regulate brain chemicals called neurotransmitters that control certain pathways, or “circuits,” of nerve cells that affect thinking and behavior.
- Brain abnormality: Research has found abnormal brain structure in people with schizophrenia. But this doesnât apply to all people with schizophrenia. It can affect people without the disease.
- Environment: Things like viral infections, exposure to toxins like , or highly stressful situations may trigger schizophrenia in people whose genes make them more likely to get the disorder. Schizophrenia more often surfaces when the body is having hormonal and physical changes, like those that happen during the teen and young adult years.
You May Like: What Are The Three Stages Of Schizophrenia
What Is The Long
Without ongoing care, people with schizophrenia can be hospitalized multiple times, lose jobs and fall out of touch with their families.
Early treatment in whatever setting works best for the patient is important, says Dr. Bowers. If they are in the hospital, we want to be sure they have a good aftercare plan.
Patients need to have a clear idea about how to maintain their health by taking their meds, staying sober and getting community support.
This will help them maintain their independence and function better in society.
The road to diagnosis, treatment and stability is a challenging one. Along the way, she recommends getting education and support from national organizations like the National Alliance on Mental Illness , Recovery International and Emotions Anonymous.
To learn about local services, families can reach out to their county mental health board, local hospital or mental health center.
What Causes Schizoaffective Disorder

Researchers dont know the exact cause of schizoaffective disorder. They believe several factors are involved:
- Genetics: Schizoaffective disorder might be hereditary. Parents may pass down the tendency to develop the condition to their children. Schizoaffective disorder can also occur in several members of an extended family.
- Brain chemistry: People with the disorder may have an imbalance of brain chemicals called neurotransmitters. These chemicals help nerve cells in the brain communicate with each other. An imbalance can throw off these connections, leading to symptoms.
- Brain structure: Abnormalities in the size or composition of different brain regions may be associated with developing schizoaffective disorder.
- Environmental factors: Certain environmental factors may trigger schizoaffective disorder in people who inherited a higher risk. Factors may include highly stressful situations, emotional trauma or certain viral infections.
- Drug use: Using psychoactive drugs, such as marijuana, may lead to the development of schizoaffective disorder.
You May Like: Pheritriphobia
How Common Is Schizoaffective Disorder
Schizoaffective disorder is rare. Research estimates that 3 in every 1000 people will develop schizoaffective disorder in their lifetime.Still, its difficult to know exactly how many people have the condition because of the challenging diagnosis. People with schizoaffective disorder have symptoms of two different mental health conditions. Some people might get misdiagnosed with schizophrenia. Others might get misdiagnosed with a mood disorder.
Psychotic Disorders & Schizophrenia Causes
While the exact cause of psychotic disorders, including schizophrenia, is unknown, researchers believe several a combination of physical, genetic, psychological and environmental factors play a role.
Like other mental health conditions, psychotic disorders are often genetic. There is evidence linking schizophrenia and genetic, however, no single gene is thought to be responsible. People with family members who have these psychotic disorders are at an increased risk.
Overactivity in brain chemicals that regulate normal functioning can also cause psychotic disorders. Additionally, studies suggest that people with psychotic disorders, including schizophrenia, have subtle differences in brain structures.
Some experts believe childhood schizophrenia could be linked to factors affecting mothers during pregnancy including drug or alcohol use, extreme stress, poor nutrition and exposure to some hormonal or chemical agents
Schizophrenia is more common in adults, but it also affects children and adolescents. When it occurs before the age of 18, its considered early-onset schizophrenia. Like adults, children with schizophrenia often inherit the condition. If a parent has the illness, a child has about a 10% to 15% chance of developing it. If more than one family member has the disorder, the risk is even higher.
Also Check: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
At What Age Is Schizophrenia Diagnosed
Schizophrenia usually develops after puberty, with most people being diagnosed with schizophrenia in their late teens to early 30s. The typical age of onset and diagnosis also varies between males and females. Males are more likely to be diagnosed in their late teens to early 20s, while females are more likely to be diagnosed in their late 20s to early 30s.
Donât Miss: How To Lose Weight If You Have Binge Eating Disorder
What Is Paranoid Schizophrenia
Paranoid schizophrenia is one type of schizophrenia. In this type, the person’s false beliefs are mainly about being persecuted or being punished by someone. The person may hear the voice of someone he or she believes is punishing them. The person may believe that he or she has been specially chosen to complete a secret mission. These are just a few examples of any number of false beliefs a person with this disorder may have.
Other types of schizophrenia include “catatonic” schizophrenia and “disorganized” schizophrenia. Different types of schizophrenia may have some of the same symptoms.
You May Like: Can You Be Bipolar And Have Bpd
What Are The Types Of Schizoaffective Disorder
There are two types of schizoaffective disorder: bipolar schizoaffective disorder and depressive schizoaffective disorder. The two types are based on the associated mood disorder the person has:
- Bipolar disorder type: This condition features one or two types of different mood changes. People with bipolar disorder have severe highs alone or combined with lows .
- Depressive type: People who have depression have feelings of sadness, worthlessness and hopelessness. They may have suicidal thoughts. They may also experience concentration and memory problems.
How Common Is Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is more common than most people think. About 1 in 200 of the people in the United States will develop schizophrenia over the course of their lives. It’s also important to know that schizophrenia has many different symptoms and can show up in many different ways.
Schizophrenia is not the same as a “split personality.” A split personality is another type of mental illness. Split personality is much less common than schizophrenia.
You May Like: How To Cure Schizophrenia Permanently
Schizophrenia Test & Diagnosis
If you or a loved one shows signs of psychosis, visit your doctor right away for a physical exam and review of your medical history. If physical reasons for the behaviors are ruled out, your doctor will consult with a behavioral health professional. Getting help as soon as symptoms arise is important for children and adults alike. Intervening early can make recovery and symptom relief easier.
Before schizophrenia is diagnosed, doctors need to find out if the symptoms are being caused by substance abuse, medication issues or other medical problems. Diagnosing schizophrenia may include:
- Physical examination Doctors look for physical problems that could be causing the symptoms and behaviors.
- Psychiatric evaluation During a psychiatric evaluation, behavioral health professionals ask about thoughts, moods, delusions, hallucinations, substance use, and risks for violence or suicide. This includes discussing personal and family history.
- Using diagnostic criteria Behavioral health professionals refer to the American Psychiatric Associations guidelines for diagnosing schizophrenia.
- Tests and screenings Drug and alcohol screenings and other tests help rule out conditions with similar symptoms. Imaging tests like MRIs and CT scans may be recommended.
Recommended Reading: Is Celine Dion Anorexic
Frequency And Ages Affected

Bipolar disorder affects approximately 2.2 percent of people in the United States. Typically, it first appears between the late teen years and early adulthood. Children can also show signs of bipolar disorder.
Schizophrenia isnt as common as bipolar disorder. It affects 1.1 percent of the U.S. population. People usually learn they have it between the ages of 16 and 30. Schizophrenia isnt usually seen in children.
Read Also: Schizophrenia Cognition Rating Scale
What Risks And Complications Can Schizophrenia Cause
Physical health
Research suggests that people with serious mental illness , such as schizophrenia, have a shorter life expectancy. People with mental illness may die 15 to 20 years earlier than the general population. This may because people who live with SMI are at higher risk of having a range of health issues. Such as being overweight, having heart disease, smoking and diabetes.
Because of these issues, NICE recommends that when you start taking antipsychotic medication, your doctor should do a full range of physical health checks. This should include weight, blood pressure and other blood tests. These checks should be repeated regularly.
Mental health professionals are responsible for doing these checks for the first year of treatment. Responsibility may then pass to your GP. Your doctor or mental health team should offer you a programme which combines healthy eating and physical health checks. You should be supported by a healthcare professional to help stop smoking.
Suicide
The risk of suicide is increased for people with schizophrenia. Research indicates that around 513% of people who live with with schizophrenia die by suicide.
Research has found that the increased risk is not usually because of positive symptoms. The risk of suicide is associated more to affective symptoms, such as low mood.
Key risk factors for suicide include:
- previous suicide attempts,
How Should I Take Care Of Myself When It Comes To Schizoaffective Disorder
Perhaps youve noticed signs of schizoaffective disorder in yourself or a loved one. Those symptoms may include prolonged hallucinations, delusions, depression or manic episodes. The first step is to talk to a healthcare provider. Getting diagnosis and treatment as soon as possible helps improve symptoms and promote a good quality of life. Be sure to follow your providers treatment instructions:
- Attend therapy sessions, including individual and family therapy.
- Stay in contact with your provider, who can help manage and adjust your treatments as necessary.
- Take medications as directed. Talk to your provider to help manage side effects from the medications.
- Treat substance use disorders, if necessary.
Recommended Reading: Bipolar Disorder And Aging
When Should I Go To The Emergency Room
If you or a loved one seems in danger of harming themselves or others, get help right away. Go to an emergency room, call 911, or call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 800.273.8255. This national network of local crisis centers provides free, confidential emotional support to people in suicidal crisis or emotional distress. Its available 24/7.
Schizoaffective Disorder: A Hybrid Condition
The schizoaffective disorder vs. schizophrenia comparison reveals pronounced overlap but clear differences. In fact, schizoaffective disorder is a hybrid condition that combines the characteristics of schizophrenia with those of mood disorders, such as depression and bipolar disorder. It is this blending of different mental health conditions that sets schizoaffective disorder apart from its more well-known cousin, since the standard schizophrenia definition classifies it as a disorder that affects thought, feelings, and behavior but not mood, at least not directly.
Some mental health experts prefer a spectrum model to explain the two conditions, with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder occupying the two extreme ends and schizoaffective disorder found somewhere in the middle. This idea makes some sense, since people with schizoaffective disorder do generally exhibit the same mood swings that are experienced by individuals with bipolar disorder, either the lows of depression or the highs of mania.
However, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar type is only one variety of the condition. Schizoaffective disorder, depressive type includes the symptoms of major depression without the mania, and is just as likely to be diagnosed as bipolar schizoaffective disorder.
Schizoaffective disorder ICD 10 classifications are recognized as authoritative everywhere, including in the United States, even though the American Psychiatric Associations DSM-5 classification system is more well-known.
Read Also: Depression Terrain Feature
What Are The Early Symptoms Of Schizophrenia
The condition usually shows its first signs in men in their late teens or early 20s. It mostly affects women in their early 20s and 30s. The period when symptoms first start and before full psychosis is called the prodromal period. It can last days, weeks, or even years. It can be hard to spot because thereâs usually no specific trigger. You might only notice subtle behavioral changes, especially in teens. This includes:
- A change in grades
- Difficulty sleeping
How Is Schizoaffective Disorder Diagnosed
If someone is showing symptoms of schizophrenia and a mood disorder, see a healthcare provider. The provider will do a medical history and physical examination. There are no lab tests to diagnose schizoaffective disorder. But the provider may use X-rays and blood tests to rule out other illnesses that may be causing the symptoms.
If there is no physical cause for the symptoms, the provider may refer the person to a psychiatrist or psychologist. These professionals specialize in diagnosing and treating conditions tied to mental and behavioral health.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
The Most Common Early Warning Signs Include:
While these warning signs can result from a number of problemsnot just schizophreniathey are cause for concern. When out-of-the-ordinary behavior is causing problems in your life or the life of a loved one, seek medical advice. If schizophrenia or another mental problem is the cause, getting treatment early will help.
Treatment Options For Dual Diagnosis State Of Disorganized Schizophrenia And Addiction
An individual may, for example, hear voices that appear to be accurate but arent. Disorganized schizophrenia speech and thoughts refer to a persons inability to form coherent or rational thoughts, which results in incoherent speech. This symptom may cause a person to jump from one subject to another during a conversation. When the problem is severe, a persons speech can become garbled and difficult to understand by others.
An individual suffering from Disorganized schizophrenia bad symptoms cannot perform basic tasks such as personal hygiene. They may isolate themselves from others and be unable to express emotions, including avoiding eye contact or speaking in a monotone. The unintended actions and expressions that distinguish this type of Schizoaffective problem from the alternative forms of Schizoaffective problem are the hallmark symptoms. When combined with the use of alcohol or narcotics, this component of the condition may become substantially worse.
People who have Disorganized schizophrenia are said to have a mental illness that can be classified as Schizoaffective problem. This condition is often described as an enduring mental disease that involves emotions such as mood swings, obsessive-compulsive disorders , post-traumatic stress disorders , and the traits of several other personality disorders.
The phrases paranoid schizophrenia, Disorganized schizophrenia, and catatonic schizophrenia are no longer used by mental health practitioners.
You May Like: What Is The Phobia Of Bees
What Is Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental illness which affects the way you think. The symptoms may affect how you cope with day to day life.
You could be diagnosed with schizophrenia if you experience some of the following symptoms.
- Hallucinations
- Changes in body language and emotions
- Less interest in social activities
- Low sex drive
Everyones experience of schizophrenia is different. Not everyone with schizophrenia will experience all of these symptoms.
According to the Royal College of Psychiatrists, schizophrenia affects around 1 in 100 people. For some people, schizophrenia can develop during young adulthood and develop slowly. The early stage of the illness is called the prodromal phase. During this phase your sleep, emotions, motivation, communication and ability to think clearly may change.
We have created a video about what is schizophrenia?. You can watch this video by clicking on the following link:www.youtube.com/watch?v=J1s4YCloCbo
What is psychosis, and how is it related to schizophrenia?Psychosis is a medical term. If you live with psychosis you will process the world around you differently to other people. This can include how you experience, believe or view things.
Experiencing psychosis is usually part of schizophrenia. People who live with other mental health conditions can experience psychosis too.
You can find more information about Psychosis by clicking here.