Arguments Against Complex Ptsd Diagnosis
Though acceptance of the idea of complex PTSD has increased with mental health professionals, the fundamental research required for the proper validation of a new disorder is insufficient as of 2013. The disorder was proposed under the name DES-NOS for inclusion in the DSM-IV but was rejected by members of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders committee of the American Psychiatric Association for lack of sufficient diagnostic validity research. Chief among the stated limitations was a study which showed that 95% of individuals who could be diagnosed with the proposed DES-NOS were also diagnosable with PTSD, raising questions about the added usefulness of an additional disorder.Following the failure of DES-NOS to gain formal recognition in the DSM-IV, the concept was re-packaged for children and adolescents and given a new name, developmental trauma disorder. Supporters of DTD appealed to the developers of the DSM-5 to recognize DTD as a new disorder. Just as the developers of DSM-IV refused to included DES-NOS, the developers of DSM-5 refused to include DTD due to a perceived lack of sufficient research.
One of the primary arguments for a new disorder has been the claim that individuals who experience complex post traumatic stress symptomatology are often misdiagnosed, and as a consequence may be given inappropriate or inadequate treatment interventions.
When Did Ptsd Become A Diagnosis
In 1980, the American Psychiatric Association added PTSD to the third edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders nosologic classification scheme . Although controversial when first introduced, the PTSD diagnosis has filled an important gap in psychiatric theory and practice.
Ptsd During World War Ii
World War II and its resulting psychiatric casualties led to advancements in the understanding of PTSD. Of the total overseas forces in 1944, the rate of admissions for psychiatric reasons was 43 per 1000 men per year.
At the end of the war, Abram Kardiner published a revised version of a book he wrote on his psychiatric treatment of WWI veterans. Based on his experience with WWII soldiers, Kardiner wrote that psychiatric treatment at the frontlines was necessary to prevent chronic cases of the syndrome we now know as PTSD. He identified traumatic neurosis as having both physical and psychological symptoms.
The causes of chronic PTSD continued to be studied over the decades after the second world war, contributing to the understanding of the condition in the medical community. WWII PTSD statistics indicate that nearly 1 in 20 of the U.S.s 2.5 million World War II veterans developed PTSD.
Don’t Miss: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
Why Can It Be Difficult To Obtain A Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Diagnosis
- It can be difficult for someone who is suffering from PTSD to recognize that they have a problem, especially if the symptoms appear after a length of time following the traumatic event.
- PTSD is extremely isolating, making it even more difficult to get help.
- Individuals believe they can manage their symptoms and recover without outside help.
- Avoidance is a common symptom of PTSD, which makes it hard for someone to face his or her problems.
- People suffering from PTSD often feel misplaced guilt about the event. Since they bear a measure of blame, they believe their pain is a punishment.
- It can be impossible for someone suffering from PTSD to realize the connection of trauma and their symptoms if there is a delayed reaction to the trauma.
- Some traumatic events are embarrassing and people dont want to share painful events with others.
How Much Money Do You Get For Ptsd Disability
In 2018, there were nearly 65,000 new VA disability claims for PTSD, and over 800,000 veterans receive compensation from the VA due to some level of PTSD symptoms.Related ArticlesVeteran Affairs Schedule for Rating Disabilities Most Common VA DisabilitiesVASRD Subpart APTSD and Veterans Symptoms1 more row
You May Like: Pristiq Medication Side Effects
What Did They Call Ptsd After Vietnam
posttraumatic stress disorderThe term posttraumatic stress disorder has become a household name since its first appearance in 1980 in the third edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders published by the American Psychiatric Association, In the collective mind, this diagnosis is associated with the legacy
What Is The Historical Background Of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
The psychological problems of soldiers in World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War, along with the severe psychological impact of rape, fostered interest and research in the collection of symptoms that became known as posttraumatic stress disorder. PTSD was first included in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders in 1980 when DSM-III was published. The diagnostic criteria have undergone significant revisions with DSM-IV and DSM-5.
You May Like: How To Help People With Depression
The Meaning Of Alters Or Alternates
Although the alters described in DID are sometimes referred to as ego states, Watkins and Watkins draw a distinction between the two concepts. They define ego state as an organized system of behavior and experience whose elements are bound together by some common principle but that is separated from other such states by boundaries that are more or less permeable. Watkins and Watkins and others differentiate the concept of alters from that of ego states because the alters in DID have their own identities, involving a center of initiative and experience, they have a characteristic self representation, which may be different from how the patient is generally seen or perceived, have their own autobiographic memory, and distinguish what they understand to be their own actions and experiences from those done and experienced by other alters, and they have a sense of ownership of their own experiences, actions, and thoughts, and may lack a sense of ownership of and a sense of responsibility for the action, experiences, and thoughts of other alters.
Do Vietnam Vets Still Have Ptsd
A new study has found that some Vietnam veterans still have symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder decades after the end of that divisive war. According to a new study, 271,000 Vietnam veterans who served in the middle of the war zone currently have PTSD or meet some of the criteria for its diagnosis.
Read Also: Dikigorosophobia
The Dawn Of Modern Psychiatry
The psychiatrist Pinel is often depicted as freeing the insane from their chains in his treatise entitled Nosographie Philosophique , he described the case of the philosopher Pascal who almost drowned in the Seine when the horses drawing his carriage bolted. During the remaining eight years of his life, Pascal had recurring dreams of a precipice on his left side and would place a chair there to prevent falling off his bed. His personality changed, and he became more apprehensive, scrupulous, withdrawn, and depressive. From his experience with patients shocked by the events and wars of the French Revolution, Pinel wrote the first precise descriptions of war neuroses – which he called cardiorespiratory neurosis – and acute stuporous posttraumatic states – which he called idiotism.
Ptsd In Epics And Classics
Long before the dawn of modern psychiatry, people and situations depicting PTSD may have been recorded in early works of literature.
For example, in the Epic of Gilgamesh, the earliest surviving major work of literature , the main character Gilgamesh witnesses the death of his closest friend, Enkidu. Gilgamesh is tormented by the trauma of Enkidus death, experiencing recurrent and intrusive recollections and nightmares related to the event.
Later, in a 440-B.C. account of the battle of Marathon, Greek historian Herodotus describes how an Athenian named Epizelus was suddenly stricken with blindness while in the heat of battle after seeing his comrade killed in combat. This blindness, brought on by fright and not a physical wound, persisted over many years.
Other ancient works, such as those by Hippocrates, describe soldiers who experienced frightening battle dreams. And outside of Greco-Latin classics, similar recurrent nightmares also show up in Icelandic literature, such as Gísli Súrsson Saga.
In the Indian epic poem Ramayana, likely composed around 2,500 years ago, the demon Marrich experiences PTSD-like symptoms, including hyper-arousal, reliving trauma, and avoidance behavior, after nearly being killed by an arrow. Marrich also gave up his natural duty of harassing monks and became a meditating recluse.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Complex Ptsd Bpd And Personality Disorders
Recent research has produced detailed analysis of the symptoms of Complex PTSD, PTSD and Borderline Personality Disorder . Many people with BPD either have PTSD, or meet the proposed diagnostic criteria for Complex PTSD. Complex PTSD was shown to be a separate diagnosis from Borderline Personality Disorder because a significant number did not meet the diagnostic criteria for BPD . In 1992, when first proposing Complex PTSD, Judith Lewis-Herman stated:
Concepts of personality developed in ordinary circumstances are frequently applied to survivors, without an understanding of the deformations of personality which occur under conditions of coercive control. Thus, patients who suffer from the complex sequelae of chronictrauma commonly risk being misdiagnosed as having personality disorders. They may be described as “dependent,” “masochistic,” or “selfâdefeating.”Earlier concepts of masochism or repetition compulsion might be more useâ fully supplanted by the concept of a complex traumatic syndrome.:388
Ptsd In The Civil War

Nostalgia was a phenomenon noted throughout Europe and the disease reached American soil during the U.S. Civil War . In fact, nostalgia became a common medical diagnosis that spread throughout camps. But some military doctors viewed the illness as a sign of weakness and one that only affected men with a feeble willand public ridicule was sometimes the recommended cure for nostalgia.
While nostalgia described changes in veterans from a psychological perspective, other models took a physiological approach.
After the Civil War, U.S. doctor Jacob Mendez Da Costa studied veterans and found that many of them suffered from certain physical issues unrelated to wounds, such as palpitations, constricted breathing, and other cardiovascular symptoms. These symptoms were thought to arise from an overstimulation of the hearts nervous system, and the condition became known as soldiers heart,irritable heart, or Da Costas syndrome.
Interestingly, PTSD-like symptoms werent restricted to soldiers in the 1800s. During the Industrial Revolution, rail travel became more commonas did railway accidents.
Survivors of these accidents displayed various psychological symptoms , which collectively became known as railway spine and railway brain because autopsies suggested railway accidents caused microscopic lesions to the central nervous system.
Read Also: Which Of The Following Represents A Negative Symptom Of Schizophrenia
How Bad Was Ptsd After Ww2
Another prevalence rate, found in the 1950s, suggests that about 10% of WWII soldiers had PTSD at some point. While it is difficult to retroactively discern prevalence for PTSD in WWII soldiers, what is clear is that it is prevalent now more than ever due to the long-lasting effects of combat in World War II.
Criterion D: Negative Alterations In Mood
Negative alterations in cognition and mood that began or worsened after the traumatic event as evidenced by two or more of the following:
- Inability to recall key features of the traumatic event. This is usually dissociative amnesia, not due to head injury, alcohol, or drugs.
- Persistent, and often distorted negative beliefs and expectations about oneself or the world, such as “I am bad,” or “The world is completely dangerous.”
- Persistent distorted blame of self or others for causing the traumatic event or for the resulting consequences.
- Persistent negative emotions, including fear, horror, anger, guilt, or shame.
- Feeling alienated, detached or estranged from others.
- Persistent inability to experience positive emotions, such as happiness, love, and joy.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Meaning Of Phobia
Classification As A Disorder
The history of PTSD has seen several transformations from the designated terminology of its title to the criteria necessary for diagnosis, before finding its place among mental disorders. Post traumatic stress disorder was first classified as a disorder in 1980 in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
The DSM was developed by the American Psychiatric Association and is used by mental health professionals in the diagnosis of patients. Post traumatic stress disorder has evolved many times in the periodic revisions of the DSM. The DSM has also revised the definition of trauma in relation to PTSD.
In the DSM-III, trauma was seen as an event beyond the range of normal that would be distressing for anyone who experienced it. In the DSM-IV, trauma is viewed as an event that can cause serious injury, harm or death but not necessarily beyond the range of normal.
The DSM-IV was revised in 2000 and redefined trauma to include events that cause intense fear, helplessness and horror. The revision also states that exposure to a traumatic event can also cause post traumatic stress disorder.
Diagnostic And Statistical Manual
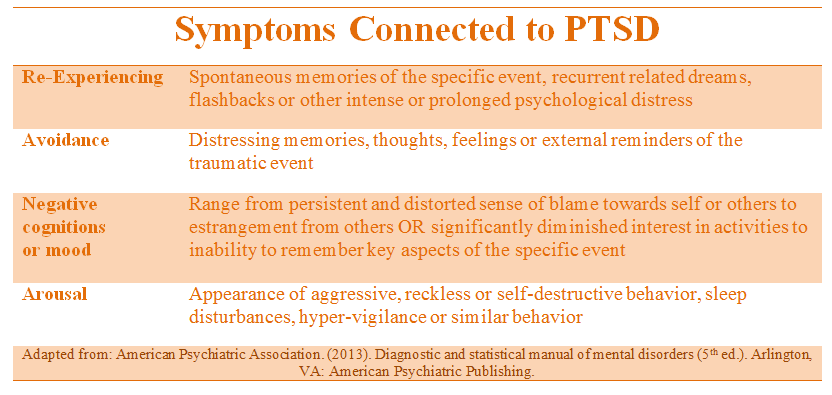
PTSD was classified as an anxiety disorder in the DSM-IV, but has since been reclassified as a “trauma- and stressor-related disorder” in the DSM-5. The DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for PTSD include four symptom clusters: re-experiencing, avoidance, negative alterations in cognition/mood, and alterations in arousal and reactivity.
Recommended Reading: Does Pristiq Help With Anxiety
Korean War Years: 1950
When To See A Professional
The debilitating symptoms of PTSD can make living, working, and interacting difficult. In fact, many people struggling with post traumatic stress disorder can turn to unhealthy coping skills like substance abuse or self-harm in an attempt to minimize or escape from their emotional distress.
If you have been experiencing symptoms for longer than a month, it could be helpful for you to talk with a professional. When you are dealing with nightmares, flashbacks, and a negative outlook about yourself and others, it can begin to feel like things will never change.
Finding a qualified professional to help can make all the difference, bringing back hope through the sharing of your experiences and helping you learn healthy, effective ways of coping.
PTSD Discussion Guide
Read Also: What Is The Phobia For Bees
Consider Malingered Or Factitious Ptsd
The next step is to determine whether observed PTSD-like symptoms are being volitionally produced. Patients feigning symptoms of PTSD will often give vague or non-specific answers to direct questions and will provide stereotypic or dramatic, heroic, or cinematic symptom depiction. It is important to determine if this is due to symptom avoidance, mistrust of the clinician, or exaggeration compensating for memory impairment.4,5,9,18,28,44 Patients attempting to portray PTSD often underestimate the body movement that typically occurs with PTSD nightmares, overestimate the frequency of flashbacks, and underappreciate the dissociative quality that typically accompanies them.4,18
Feigned PTSD is not necessarily a complete manufacturing of symptoms, and it is valuable to consider malingering patterns as described by Resnick: pure malingering is when the person feigns non-existing symptoms, partial malingering is when the person consciously exaggerates existing symptoms, and false imputation is when the individual consciously attributes existing symptoms to a cause not responsible for the symptoms .19 The motivation for malingering may be influenced by third parties, such as when patients are encouraged by legal representation to present for treatment for the sake of gaining a diagnostic report to bolster their case or for prolonged care to demonstrate refractory psychopathology to increase a potential financial settlement.9
Ptsd: A Systematic Approach To Diagnosis And Treatment

Current Psychiatry
Carol S. North, MD, MPEMedical DirectorThe Altshuler Center for Education and ResearchMetrocare ServicesThe Nancy and Ray L. Hunt Chair in Crisis PsychiatryProfessor of PsychiatryUniversity of Texas Southwestern Medical CenterDallas, Texas
Barry A. Hong, PhD, ABPPVice Chair of Clinical AffairsProfessor of PsychiatryWashington University School of MedicineChief Psychologist
Dana L. Downs, MA, MSWClinical Research CoordinatorWashington University School of MedicineSt. Louis, Missouri
DisclosuresThe authors report no financial relationships with any company whose products are mentioned in this article or with manufacturers of competing products.
Accurate diagnosis and management depends on proper application of DSM-5 criteria.
Read Also: Can Anxiety Cause You To Faint
Ptsd And The Civil War
The Civil War occurred before the age of modern psychiatry. At that time, the general consensus was that only weak-willed soldiers or persons with underlying health conditions suffered from PTSD. The horrific hand-to-hand combat was not considered a possible cause. Thus,Civil War PTSD was neither recognized nor treated at the time. However, detailed accounts of flashbacks, panic attacks, insomnia and suicidal thoughts were commonly documented among Civil War veterans.
Criterion E: Alterations In Arousal And Reactivity
Trauma-related alterations in arousal and reactivity that began or worsened after the traumatic event, including two or more of the following:
There are a few changes in the latest version of the DSM regarding PTSD diagnosis.
Key changes include:
- More clearly defining what kind of events are considered traumatic in Criterion A
- Adding a fourth type of exposure in Criterion A
- Increasing the number of symptom groups from three to four by separating avoidance symptoms into their own group
- Increasing the number of symptoms from 17 to 20
- Changing the wording of some of the symptoms from DSM-IV
- Adding a new set of criteria for children aged 6 or younger
- Eliminating the “acute” and “chronic” specifiers
- Introducing a new specifier “with dissociative symptoms“
The biggest change in the DSM-5 is removing PTSD from the category of anxiety disorders and putting it in a classification called “Trauma and Stressor-Related Disorders.”
You can review the rationale behind these changes, as well as look at other changes in the DSM-5, at the website for the American Psychiatric Association .
Recommended Reading: Can A Panic Attack Cause You To Faint