What To Do About Schizophrenia
Although it sounds scary, schizophrenia is the most common serious mental health condition and can be successfully treated.
If you think you are affected by schizophrenia, talk to someone straight away. Choose someone you like and trust, like a teacher, relative, counsellor or friend.
You should also see your GP. They may offer to refer you to Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services , an expert or a psychiatrist who can help you.
Early Warning Signs And Symptoms
Usually, a person with schizophrenia has gradual changes in their thoughts and perceptions. Families are often the first to see early signs of psychosis and schizophrenia in a loved one.
Before the first episode of psychosis, you go through what is known as a premorbid period. This is the 6 months before the first symptoms of psychosis. During this period, you might experience gradual changes.
Although sleep disturbances are not included in the diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia, people with the condition consistently report them.
Early warning signs include:
Differences In Brain Chemistry
Studies show that people can be more likely to experience schizophrenia if their brain development was disrupted during pregnancy or early childhood. Changes in brain structure do not appear in everyone with schizophrenia though.
Some chemicals also seem to behave differently in the brains of people who experience schizophrenia. These chemicals are thought to include dopamine, which helps to carry messages between brain cells.
Some research suggests that an imbalance between certain neurotransmitters, including dopamine and serotonin, may be one of the causes behind schizophrenia.
Antipsychotics, which are sometimes used to treat schizophrenia, can help to lower dopamine levels.
For more information see our pages on antipsychotics.
“More recently my physical health has deteriorated. I have become more agoraphobic and find group settings harder than before.”
Also Check: How To Help Panic Attacks Without Medication
The Age Of Onset In Men And Women
Its hard to pinpoint the exact onset of schizophrenia because people may have cognition problems or trouble in social relationships long before they are officially diagnosed. In general, schizophrenia is diagnosed in late adolescence through the early 30s.
Men are usually diagnosed between the late teens and early 20s, with a peak at 21-25 years of age. Women are diagnosed a few years later, at 25-30 or again after menopause.
The ages are just a guide. No matter when you notice any of the signs or symptoms of schizophrenia in yourself or a loved one, its important to get diagnosed and treated as soon as possible. Symptoms include confusion, disorganized speech, and hallucinations .
At Allied Psychiatry & Mental Health, board-certified psychiatrist Dr. Hadi Estakhri helps his patients live better quality lives through symptom management.
Hope For The Patient And Family
A diagnosis of schizophrenia is life-changing for those affected and everyone who loves them. But, with hard work and dedication, you can help your loved one enjoy a meaningful life.
People with schizophrenia can finish college, work jobs, get married, have families and enjoy a reasonably healthy life, stresses Dr. Bowers.
But it requires a combination of good medication, supportive counseling and being connected to community resources.
The National Alliance on Mental Illness offers support groups for the mentally ill and their families. And organizations like Recovery International and Emotions Anonymous are excellent resources for patients, she says.
Also Check: How To Be With Someone With Depression
What If I Am Not Happy With My Treatment
If you are not happy with your treatment you can:
- talk to your doctor about your treatment options,
- ask for a second opinion,
- get an advocate to help you speak to your doctor,
- contact Patient Advice and Liaison Service and see whether they can help, or
- make a complaint.
There is more information about these options below.
Treatment options
You should first speak to your doctor about your treatment. Explain why you are not happy with it. You could ask what other treatments you could try.
Tell your doctor if there is a type of treatment that you would like to try. Doctors should listen to your preference. If you are not given this treatment, ask your doctor to explain why it is not suitable for you.
Second opinion
A second opinion means that you would like a different doctor to give their opinion about what treatment you should have. You can also ask for a second opinion if you disagree with your diagnosis.
You dont have a right to a second opinion. But your doctor should listen to your reason for wanting a second opinion.
Advocacy
An advocate is independent from the mental health service. They are free to use. They can be useful if you find it difficult to get your views heard.
There are different types of advocates available. Community advocates can support you to get a health professional to listen to your concerns. And help you to get the treatment that you would like.
The Patient Advice and Liaison Service
Complaints
You can find out more about:
Final Thoughts: Getting Past The Stigma
Stories abound of individuals who have schizophrenia attempting to hide their condition from others. Despite research and mental health outreach efforts, the ignorance surrounding mental health issues is prevalent. This has led to a shameful social stigma attached to conditions like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and others.
As global citizens, we must do better. When people who are suffering feel support and encouragement, they are far more likely to seek potentially life-changing treatment.
If you or someone you love is suffering from a serious mental health disorder, please reach out for support. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration National Hotline can be reached at 1-800-662-HELP.
Read Also: How To Slow Heart Rate Panic Attack
When Should I See My Doctor
Some people with schizophrenia do not realise they have a problem or avoid health professionals if they have paranoid thoughts. Its important to get professional help to manage schizophrenia. If you or someone you know seems to be experiencing signs of schizophrenia, see your doctor as soon as possible.
It can be hard to recognise signs of schizophrenia at first, but over time the changes in someones thinking and behaviour may get worse.
See a doctor if you or someone you know:
- gets very preoccupied with something
- starts talking or writing very fast, or is talking much less than normal
- seems muddled, irrational or is hard to understand
- withdraws from normal activities
- is hyperactive or starts behaving recklessly
- laughs or cries inappropriately, or cannot laugh or cry or express happiness
- doesnt look after their personal hygiene
- develops depression or anxiety
Although the majority of people with schizophrenia are not violent, severe symptoms can cause some people to have thoughts of suicide or harming others. If you think someone may be at risk of suicide or violence, call triple zero .
Genetic Causes Of Schizophrenia
Many genes play a role in your odds of getting schizophrenia. A change to any of them can do it. But usually, itâs several small changes that add up and lead to a higher risk. Doctors arenât sure how genetic changes lead to schizophrenia. But theyâve found that people who have the disorder may be more likely to have problems in their genes that may interfere with brain development.
Don’t Miss: What To Do When You Feel A Panic Attack Starting
What Environmental Factors Increase The Risk Of Developing Schizophrenia
Environmental factors include everything the person experiences from being inside the womb, right the way through childhood and into adulthood.
There are considered to be many pregnancy-related schizophrenia risk factors. High levels of maternal stress can lead to an increased risk of schizophrenia later in life, and this includes bereavement, maternal depression, and any other situation that places the mother under stress. Infections such as rubella and toxoplasmosis caught during pregnancy can also increase the risk factor for schizophrenia. Complications during the birth have also been shown to increase the risk factor for schizophrenia. These include pre-eclampsia and Hypoxia.
The schizophrenia risk factors associated with children and adults are varied. Any child growing up in a dysfunctional family is at a higher risk of developing a mental illness , whereas a happy and stable childhood can significantly reduce the chances of developing schizophrenia later in life. In particular, there is a strong link between physical, sexual and emotional abuse during childhood and many serious mental health disorders, including schizophrenia.
Drug use, in particular cannabis, has been shown to significantly increase the chances of developing a mental illness such as schizophrenia. Other schizophrenia risk factors for children and adults include head injuries, social isolation during the formative years of childhood and early adulthood, and social stress.
Related Articles:
Early Intervention Programs For Young People
Schizophrenia most often develops for the first time between the late teens and early twenties. Identifying young people in the early stages of a psychotic illness and providing them with specialised support and treatment can make a huge difference to their future health.
Specialist Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services are also available across Australia talk to your GP about finding a service near you. You can also contact your local headspace or their online support service, eheadspace to enquire about early intervention for psychosis.
Your public hospital
The treatment available through a public community mental health team ranges from acute inpatient care, where you are admitted and stay in hospital, to outpatient treatment in the community. The type of service provided can differ a lot from state to state and hospital to hospital.
Your state or territory Department of Health can help you identify your local community mental health services, or you can use the National Health Services Directory.
Treatment in a private hospital
With private health insurance, its also possible to get treatment in a private hospital. To ensure your money is well spent, research the different types of cover available and the treatment programs offered by hospitals in your area.
Private therapists
Other services
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Anxiety Fast
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is more common among people with schizophrenia than in the general population, according to 2019 research. Some researchers think this could be because people with schizophrenia tend to smoke more often and for longer periods than the general population.
When you have COPD, your airways become blocked. This makes it more difficult to take deep breaths.
When To See A Healthcare Provider

As schizophrenia usually develops gradually, it can be difficult to pinpoint when changes in behavior start or know whether they are something to worry about. Identifying that you are experiencing a pattern of concerning behaviors can be a sign you should consult with a professional.
Symptoms may intensify in the run-up to an acute episode of psychosis in schizophrenia. The warning signs include:
- A worrying drop in grades or job performance
- New difficulty thinking clearly or concentrating
- Suspiciousness of or uneasiness with others
- Withdrawing socially, spending a lot more time alone than usual
- Unusual, overly intense new ideas, strange feelings, or having no feelings at all
- Difficulty telling reality from fantasy
- Confused speech or trouble communicating
While these changes might not be concerning by themselves, if you or a loved one are experiencing a number of these symptoms, you should contact a mental health professional. It can be difficult for those with schizophrenia to want to get help, especially if they are experiencing symptoms such as paranoia.
If you or your loved one is thinking of or talking about harming themselves, contact someone who can help right away. You can call the toll-free, 24-hour National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 800-237-8255.
If you require immediate emergency care, call 911 for emergency services or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
Don’t Miss: How Can You Get Schizophrenia
Managing Life With Schizophrenia
Some people living with schizophrenia find that the following strategies can help prevent episodes of psychosis, help them feel better in between episodes, or feel more in control:
- learning more about schizophrenia
- finding an individual definition of recovery, whether its reducing symptoms or working on other parts of life like relationships or employment
- looking after physical health including getting regular check-ups
- accessing peer support
- learning strategies to minimise stress
- developing a Relapse prevention plan including identifying early warning signs, what to do when these occur, and who to contact
- advance care planning may also be an option for times when a person doesnt have decision-making capacity. The nature of these statements varies between states.
Every person will need to find what works for them and its normal for this to take time. Check out our lived experience tips for managing life with schizophrenia.
What Are The Three Phases Of Schizophrenia
Research has identified schizophrenia to have three phases, these are as follows:
- Prodromal
- Acute / active
- Residual
It may sometimes seem as though schizophrenia suddenly develops out of nowhere, this, however, is not the case. There is no such thing as waking up one morning and have bouts of full-blown psychosis. The disease instead consists of psychotic symptoms that slowly start to appear, and the sufferer begins to show a way of thinking that is distorted and has difficulty relating to others.
The phases can be explained accordingly:
You May Like: How To Hide An Eating Disorder
Does Schizophrenia Get Better As You Get Older
Schizophrenia does not typically get better as you get older. The symptoms of schizophrenia may become worse over time, or they may remain the same for some people. Schizophrenia is a chronic illness that can be managed with medication and therapy, but it does not typically go away as you get older.
How Does Schizophrenia Affect Families
Schizophrenia takes an enormous toll on afflicted families. Many people with schizophrenia have difficulty maintaining a job or living independently, though it is important to recognize that treatment, especially at the onset of symptoms, allows individuals with a diagnosis of schizophrenia to lead meaningful, productive lives.
Recommended Reading: How Do Nutritionists Help With Eating Disorders
Negative Symptoms Of Schizophrenia: Things That Might Stop Happening
Negative symptoms refer to an absence or lack of normal mental function involving thinking, behavior, and perception. You might notice:
- Lack of pleasure. The person may not seem to enjoy anything anymore. A doctor will call this anhedonia.
- Trouble with speech. They might not talk much or show any feelings. Doctors call this alogia.
- Flattening: The person with schizophrenia might seem like they have a terrible case of the blahs. When they talk, their voice can sound flat, like they have no emotions. They may not smile normally or show usual facial emotions in response to conversations or things happening around them. A doctor might call this affective flattening.
- Withdrawal. This might include no longer making plans with friends or becoming a hermit. Talking to the person can feel like pulling teeth: If you want an answer, you have to really work to pry it out of them. Doctors call this apathy.
- Struggling with the basics of daily life. They may stop bathing or taking care of themselves.
- No follow-through. People with schizophrenia have trouble staying on schedule or finishing what they start. Sometimes they can’t get started at all. A doctor might call this avolition.
Depression has some of the same symptoms, too. They can be hard to spot, especially in teens, because even healthy teens can have big emotional swings between highs and lows.
What Causes Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia can have a range of causes. There is a lot that researchers still don’t know and it is likely to be caused by a combination of genetic, personal and environmental factors. These factors will be different for everybody but may include:
Highly stressful or life-changing events may sometimes trigger schizophrenia. These can include:
Sometimes stressful events like these are called trauma. For more information on how these experiences can affect your mental health see our pages on trauma.
“The onset of schizophrenia for me was sudden and dramatic, though it followed a period of depression and acute stress. A really compelling and powerful voice started to try to control me.”
You May Like: What Not To Say To Someone With Schizophrenia
When To Call A Doctor
If you notice symptoms like these, your teen needs to be checked by a doctor right away. That’s especially true if anyone on either side of their family has had schizophrenia.
The doctor will ask your teen questions about their thinking and behavior, possibly perform a brief physical exam, and give them blood or urine tests to make sure there isn’t another medical condition or drug abuse problem thatâs to blame.
For a schizophrenia diagnosis, the symptoms have to last for at least 6 months and donât seem to be due to another medical or psychiatric condition. Sometimes it takes longer than 6 months to make a confident diagnosis, based on how symptoms appear over time.
Your family doctor can refer you to a psychiatrist who works with teens. A psychiatrist has special training in how to diagnose and treat schizophrenia.
If your teen has the condition, a combination of treatments may work best. These might include medication and individual and family therapy.
The diagnosis can be tough news to hear. But with the right treatment, people with schizophrenia do go to college, hold jobs, and have a family life.
Show Sources
Brain And Body Risk Factors
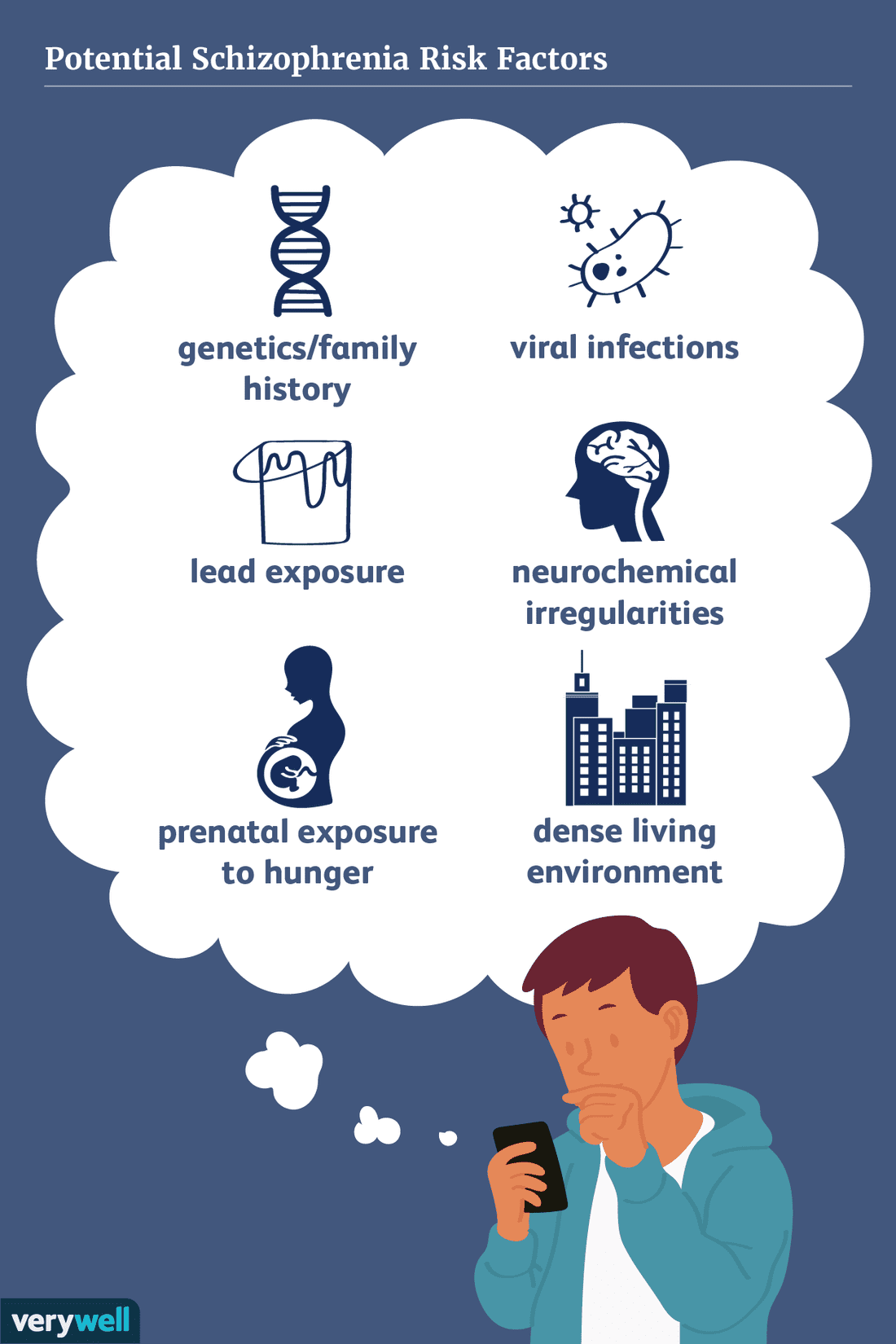
Developmental theories of schizophrenia suggest that something goes wrong when the brain is developing. Brain development, from the earliest stage of fetal development, the early years of life and through adolescence, is an extremely complicated process. Millions of neurons are formed, migrate to different regions of the forming brain, and specialize to perform different functions.
The something that goes wrong might be a viral infection, a hormonal imbalance, an error in genetic encoding, a nutritional stress, or something else. The common element in all developmental theories is that the causal event occurs during the brains development.
Even though these potential causes may be rooted in very early development, symptoms of schizophrenia typically emerge in late adolescence or early adulthood.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Leading Cause Of Ptsd