The Case For A Soft Landing
Despite the dire warnings, there are plenty who believe a “soft landing” – a moderate economic slowdown, instead of a full-on recession – is still possible. Under such a scenario, you might see slower growth without the upheaval associated with a full-blown downturn.
Driving that optimism is America’s strong job market. Employers added 315,000 new workers in August. That’s hardly a sign of a sputtering economy, according to US Federal Reserve Governor Christopher Waller.
In a recent speech in Vienna, he dismissed recession fears, saying: “The robust US labour market is giving us the flexibility to be aggressive in our fight against inflation.”
The Fed has said it won’t hesitate to keep interest rates high, for as long as it takes to drive down inflation. With the US central bank preparing to show it won’t flinch in its resolve to lower prices, the process is unlikely to be smooth. If it raises rates by too much, the economy could plunge into recession. Raise them by too little and inflation continues to soar.
The Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta President Raphael Bostic acknowledged it was a difficult high-wire act to pull off, saying recently that a soft landing is “a very hard thing to do”.
The Stagflation Recession Part I: January 1980 To July 1980
Following the turbulent 1970s, U.S. inflation peaked at 22% in 1980. Fed chair Paul Volcker famously promised to kill inflation by massively raising interest rates to curb ballooning prices.
Volckerâs plan led to an economic slowdown and a brief recession. During this time, unemployment reached 7.8% and GDP fell by 0.2%.
Economic Trends Preceding The 1890s
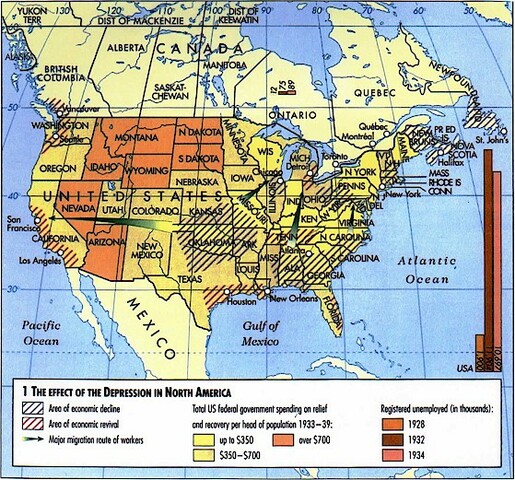
Between 1870 and 1890 the number of farms in the United States rose by nearly 80 percent, to 4.5 million, and increased by another 25 percent by the end of the century. Farm property value grew by 75 percent, to $16.5 billion, and by 1900 had increased by another 25 percent. The advancing checkerboard of tilled fields in the nations heartland represented a vast indebtedness. Nationwide about 29% of farmers were encumbered by mortgages. One contemporary observer estimated 2.3 million farm mortgages nationwide in 1890 worth over $2.2 billion. But farmers in the plains were much more likely to be in debt. Kansas croplands were mortgaged to 45 percent of their true value, those in South Dakota to 46 percent, in Minnesota to 44, in Montana 41, and in Colorado 34 percent. Debt covered a comparable proportion of all farmlands in those states. Under favorable conditions the millions of dollars of annual charges on farm mortgages could be borne, but a declining economy brought foreclosures and tax sales.
Railroad construction was an important spur to economic growth. Expansion peaked between 1879 and 1883, when eight thousand miles a year, on average, were built including the Southern Pacific, Northern Pacific and Santa Fe. An even higher peak was reached in the late 1880s, and the roads provided important markets for lumber, coal, iron, steel, and rolling stock.
Don’t Miss: How To Relax During A Panic Attack
The Investment Bust Recession: August 1957april 1958
- Duration: Eight months
- GDP decline: 3.7%
- Peak unemployment rate: 7.4%
- Reasons and causes: The end of the Korean War unleashed a global investment boom marked by a surge in exports of U.S. capital goods. The Fed responded by tightening monetary policy as the inflation rate rose from 0.4% in March 1956 to 3.7% a year later. Fiscal policy focused on limiting budget deficits produced a surplus of 0.7% of GDP in 1957. The 1957 Asian Flu pandemic killed 70,000 to 100,000 Americans in 1957, and industrial production slumped late that year and early in 1958. The dramatic drop in domestic demand and evolving consumer expectations led to the failure of the Ford Edsel, the beginning of the end for Detroit’s auto industry dominance. The sharp worldwide recession contributed to a foreign trade deficit. The recession ended after policymakers eased fiscal and monetary constraints on growth.
The New Deal: A Road To Recovery
Among the programs and institutions of the New Deal that aided in recovery from the Great Depression was the Tennessee Valley Authority , which built dams and hydroelectric projects to control flooding and provide electric power to the impoverished Tennessee Valley region, and the Works Progress Administration , a permanent jobs program that employed 8.5 million people from 1935 to 1943.
When the Great Depression began, the United States was the only industrialized country in the world without some form of unemployment insurance or social security. In 1935, Congress passed the Social Security Act, which for the first time provided Americans with unemployment, disability and pensions for old age.
After showing early signs of recovery beginning in the spring of 1933, the economy continued to improve throughout the next three years, during which real GDP grew at an average rate of 9 percent per year.
A sharp recession hit in 1937, caused in part by the Federal Reserves decision to increase its requirements for money in reserve. Though the economy began improving again in 1938, this second severe contraction reversed many of the gains in production and employment and prolonged the effects of the Great Depression through the end of the decade.
Recommended Reading: Does Donald Duck Have Ptsd
List Of Economic Expansions In The United States
| This article is missing information about pre1945 content.. Please expand the article to include this information. Further details may exist on the talk page. |
| This article is part of a series on the |
|
|
In the United States the unofficial beginning and ending dates of national economic expansions have been defined by an American private non-profit research organization known as the National Bureau of Economic Research . The NBER defines an expansion as a period when economic activity rises substantially, spreads across the economy, and typically lasts for several years.
During the 19th century, the United States experienced frequent boom and bust cycles. This period was characterized by short, frequent periods of expansion, typically punctuated by periods of sharp recession. This cyclical pattern continued through the Great Depression. Economic growth since 1945 has been more stable with fewer recessions when compared to previous eras.
The Stagflation Recession Part Ii: July 1981 To November 1982
According to the Fed, the 1981-1982 recession was the worst economic downturn in the U.S. since the Great Depression. During this time, unemployment reached nearly 11% and GDP fell by 1.8%.
The recession was triggered by the Fedâs tight monetary policy plan to fight inflation in 1980. The resulting recession was inflamed by a global energy crisis, triggered by Iran decreasing its oil output, which inflated global oil prices.
Also Check: How To Talk To Someone With An Eating Disorder
What Is A Recession Anyway
In a growing economy, a country’s citizens become slightly richer on average as the value of the goods and services they produce – its Gross Domestic Product – increases.
But sometimes that value falls, and a recession is usually defined as when this happens for two three-month periods – or quarters – in a row.
Typically it’s a sign the economy is doing badly and can mean that, in the short term, businesses have more layoffs.
What Caused The Great Depression
Throughout the 1920s, the U.S. economy expanded rapidly, and the nations total wealth more than doubled between 1920 and 1929, a period dubbed the Roaring Twenties.
The stock market, centered at the New York Stock Exchange on Wall Street in New York City, was the scene of reckless speculation, where everyone from millionaire tycoons to cooks and janitors poured their savings into stocks. As a result, the stock market underwent rapid expansion, reaching its peak in August 1929.
The American economy entered a mild recession during the summer of 1929, as consumer spending slowed and unsold goods began to pile up, which in turn slowed factory production. Nonetheless, stock prices continued to rise, and by the fall of that year had reached stratospheric levels that could not be justified by expected future earnings.
You May Like: How Do Eating Disorders Affect The Brain
Do You Have Depression
If you think you may have depression, its important to not wait and take action as soon as possible.
However, for many people, they are unsure whether or not what they have is temporary and will pass with time or show signs of something more serious that needs treatment.
Getting a diagnosis for major depression will require an assessment from your doctor or mental health professional. Still, if you want to feel a bit more certain about what youre experiencing, you can try taking this free depression test beforehand.
For many people, this gives patients the confidence and drive to act now and start getting the help they need to start living happier and healthier lives.
Additionally, you can also find more tests on various mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders, which tend to coexist with major depression.
So Is America In Recession
US GDP has fallen for two consecutive quarters – 1.6% during the first quarter of 2022, and 0.6% the next. In most countries, that’s a recession. Just not in the US.
The official recession call is made by the Business Cycle Dating Committee – a little-known group of eight economists chosen by the National Bureau of Economic Research, a non-profit organisation. And so far, the committee has refused to use the R word.
You May Like: Is Seroquel Used For Bipolar Disorder
Who Is To Blame For The Great Recession Of 2008
The Biggest Culprit: The Lenders Most of the blame is on the mortgage originators or the lenders. Thats because they were responsible for creating these problems. After all, the lenders were the ones who advanced loans to people with poor credit and a high risk of default. 7 Heres why that happened.
What Is An Economic Depression
It is first essential to define what a recession is in the economy. This is when the gross domestic product experiences two back-to-back quarters of contraction. A depression can be summarized as being more intense than a recession. While there is no standard definition for a depression, it is commonly accepted that it is defined using two metrics: a decline in the GDP by 10% and a recession that lasts two or more years.
Economists also use a joke to describe the difference between these economic cycles: When your neighbor loses their job, its a recession. When you lose your job, thats a depression!
Put simply, recessions and depressions have the same start dates but different durations and ending times.
Recommended Reading: What To Expect In Eating Disorder Recovery
The Current Financial Landscape
Between 1929 and 1939, President Franklin D. Roosevelt passed numerous pieces of legislation aimed at stabilizing the economy. He established the FDIC to protect consumers’ bank accounts. The SEC was created to regulate the stock market, and the Social Security Act guaranteed pensions to Americans and set up an unemployment insurance program.
The programs and reforms put in place in response to the Great Depression were established in hopes that an economic downturn of parallel magnitude would unlikely be repeated. Yet, the economy took a tumble as a result of the pandemic. In July 2020, the US GDP fell a historic 33% annualized rate in the second quarter of 2020, with no other downturn in history causing a sharp decline in the economy.
So could we be heading into another depression? Well, no. Barring any major unseen circumstances, a recession that impacts the economy so deeply that it’s widely considered a depression is unlikely. However, the turbulence that rising inflation and soaring interest rates have stirred up also carry whispers of an upcoming recession.
That said, unemployment has settled back to pre-Covid levels, hovering at approximately 3.6%, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, which is below the unemployment rate right before the Great Recession. Meanwhile, retail sales in April of 2022 were up 0.9%. Experts say that if we see a recession, which we won’t see until 2023, it will be fairly mild.
What Is The Difference Between A Recession And A Depression
An economic depression lasts longer than a recession, and it causes greater damage to an economy. The Great Depression ravaged the economy over a matter of years, while recessions are typically measured in months.
Correction – Oct. 19, 2022: This article has been updated to correct the Fed’s policy on the fed funds rate after it lowered it to basically 0% in 2020.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can A Bipolar Episode Last
What Is A Depression
An economic depression is typically understood as an extreme downturn in economic activity lasting several years, but the exact definition and specifications of a depression are less clear.
“The way people think about it is a depression is a more widespread and severe recession,” Ullrich says, “but there is no clear-cut moment where we can say ‘we hit X unemployment rate or Y GDP growth we’re now officially in a depression.'”
The NBER notes that economists differ on the period of time that designates a depression. Some experts believe a depression lasts only when economic activity is declining, while the more common understanding is that a depression extends until economic activity has returned to close to normal levels.
November 1948 To October 1: Post
When wartime rations and restrictions were lifted after WWII, American consumers rushed to catch up on years of pent-up purchases. From 1945 to 1949, American households bought 20 million refrigerators, 21.4 million cars, and 5.5 million stoves.
When the consumer spending boom began to level off in 1948, it triggered a mild 11-month recession in which GDP shrunk by only 2 percent. Unemployment was up considerably, though, with all former GIs back in the job market. At its peak, unemployment reached 7.9 percent in October 1949.
Read Also: Which Assessment Finding Is Associated With Depression
Causes Length Gdp And Unemployment Rates For Every Us Recession
Kimberly Amadeo is an expert on U.S. and world economies and investing, with over 20 years of experience in economic analysis and business strategy. She is the President of the economic website World Money Watch. As a writer for The Balance, Kimberly provides insight on the state of the present-day economy, as well as past events that have had a lasting impact.
Erika Rasure, is the Founder of Crypto Goddess, the first learning community curated for women to learn how to invest their moneyand themselvesin crypto, blockchain, and the future of finance and digital assets. She is a financial therapist and is globally-recognized as a leading personal finance and cryptocurrency subject matter expert and educator.
Sturtus / Getty Images
The history of recessions in the United States shows that they are a natural, though painful, part of the business cycle. The National Bureau of Economic Research determines when a recession starts and ends.
The Bureau of Economic Analysis measures the gross domestic product that defines recessions. The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports on the unemployment rate. Unemployment often peaks after a recession ends because it is a lagging economic indicator. Most employers wait until they are sure the economy is back on its feet again before hiring permanent employees.
There have been 19 noteworthy recessions throughout U.S. history.
How Many People Are Depressed Worldwide
While the previous section regarding U.S. depression statistics shows that it is certainly a significant problem, major depression is truly a global issue.
According to the World Health Organization, approximately 264 million people worldwide experience depression across all ages. Out of the world nearly 8 billion people, this accounts for just over 3 percent of individuals with depression.
However, this percentage of people with depression may be inaccurate, and this figure is expected to be significantly higher than the value suggests
Although we know that China, India, and the United States are two of the leading countries with depression, most likely due to population alone, others may not be accounted for several reasons, which can affect the global depression rate.
Depression can go unreported in countries, especially in those with a lack of mental health resources and education and where mental disorders and getting treatment for them is a stigma.
Stigmatization can be self-imposed or based on society. It can involve different beliefs such as it being a character flaw, weakness, a form of incompetence, or a sign that someone is dangerous. Unfortunately, this can lead to prejudice and discrimination from others.
Don’t Miss: How To Help A Child Having A Panic Attack
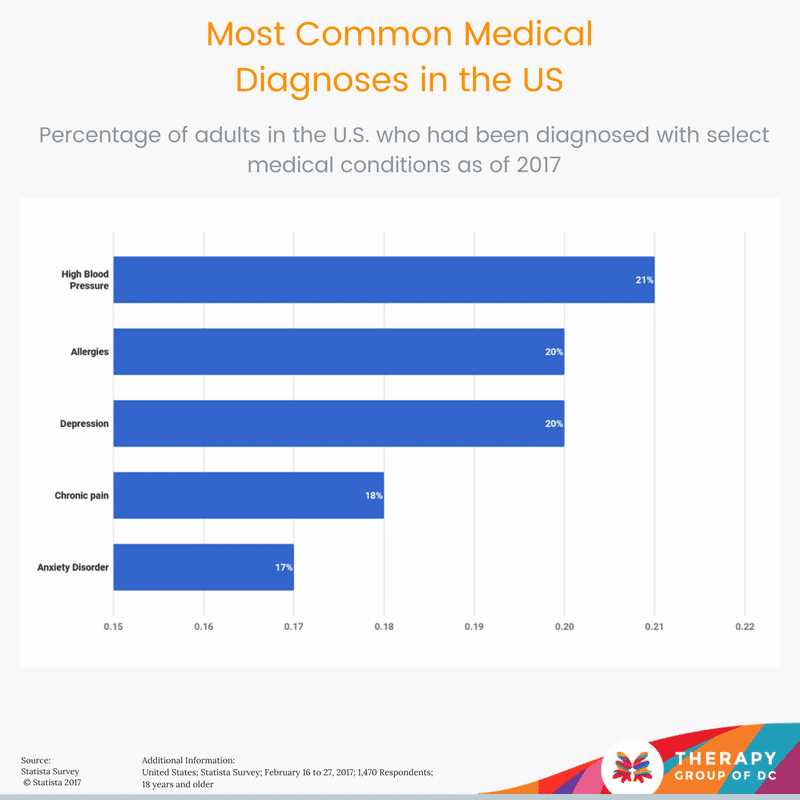
Prevalence Of Major Depressive Episode Among Adolescents
- Figure 2 shows the past year prevalence of major depressive episode among U.S. adolescents in 2020.
- An estimated 4.1 million adolescents aged 12 to 17 in the United States had at least one major depressive episode. This number represented 17.0% of the U.S. population aged 12 to 17.
- The prevalence of major depressive episode was higher among adolescent females compared to males .
- The prevalence of major depressive episode was highest among adolescents reporting two or more races .
Figure 2
| Demographic | |
|---|---|
| 2 or more Races | 29.9 |
*Persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race all other racial/ethnic groups are non-Hispanic. Note: Estimates for Native Hawaiian / Other Pacific Islander and American Indian / Alaskan Native groups are not reported in the above figure due to low precision of data collection in 2020.
Great Depression Ends And World War Ii Begins
With Roosevelts decision to support Britain and France in the struggle against Germany and the other Axis Powers, defense manufacturing geared up, producing more and more private-sector jobs.
The Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in December 1941 led to Americas entry into World War II, and the nations factories went back in full production mode.
This expanding industrial production, as well as widespread conscription beginning in 1942, reduced the unemployment rate to below its pre-Depression level. The Great Depression had ended at last, and the United States turned its attention to the global conflict of World War II.
You May Like: How To Date Someone With Bipolar