Many People With Bipolar Disorder Are Misdiagnosed As Depressed
Up to 25 percent of people with bipolar disorder are wrongly diagnosed with depression initially, which may have to do with the fact that they only seek treatment when theyre trapped in the desperate pit of clinical depression. Later on, when the medical professional learns of the episodes of mania or hypomania in the patients life, they are more often able to correctly identify bipolar disorder.
Theres another side to the misdiagnosis, though. Many people think of bipolar as a way to describe extreme mood swings and it tends to be overdiagnosed, especially in teenage populations, Aman tells Bustle. But the phases of mania or hypomania differ distinctly from mood swings, both in their duration and how they interfere with peoples everyday lives. Individuals with bipolar disorder, versus those with severe mood swings or clinical depression, are more likely to suffer from substance abuse, eating disorders, and metabolic issues.
This also means treatment will vary for each person. Aman says she cannot prescribe a single way of helping someone through a manic stage, as everyone responds differently. She does point out, though, that every person with bipolar disorder, no matter what type they have or how often they fall into a clinical depression, needs loads of support from friends and family. They often forget the fact that theyre loved, so keep encouraging them, even if you feel like you dont quite get what theyre going through.
Images: Fotolia Unsplash
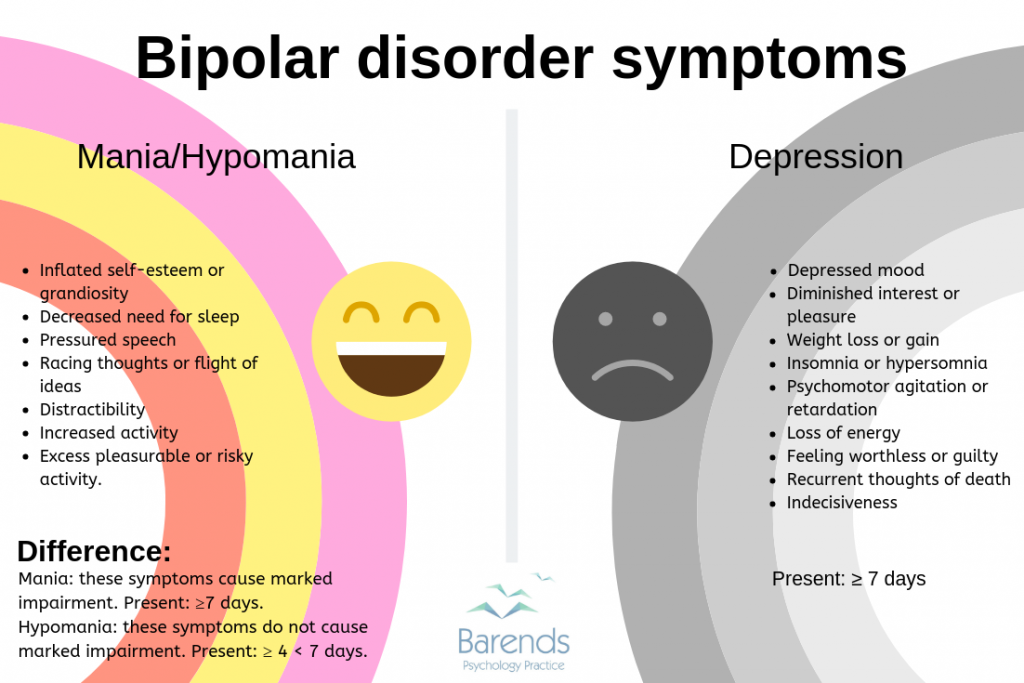
What Are The Symptoms Of Bipolar Disorder
The changing mood states do not always follow a set pattern, and depression does not always follow manic phases. A person may also experience the same mood state several times before experiencing the opposite mood. Mood changes can happen over a period of weeks, months, and sometimes even years.
An important aspect of the mood changes are that they are a departure from the persons regular self and that the mood change is sustained for a long period of time. It may be many days or weeks in the case of mania and many weeks or months in the case of depression. Shorter periods of mania or depression may be an indicator of more severe episodes in the future but are usually not enough to diagnose a person with bipolar disorder.
The severity of the depressive and manic phases can differ from person to person and in the same person at different times. Symptoms of mania include:
- Excessive happiness, hopefulness, and excitement
- Sudden changes from being joyful to being irritable, angry, and hostile
- Restlessness
- Rapid speech and poor concentration
- Increased energy and less need for sleep
- High sex drive
Patients with depression can also become psychotic and hear things or have delusions.
What You Can Do
People can often manage the symptoms of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia with medication and therapy. Having a support system in place will increase your chances of successfully managing your symptoms. A support system may include family, friends, and the people in your workplace.
If you have either bipolar disorder or schizophrenia, you have an increased risk of suicide. See your doctor if you have thoughts of suicide. They can provide treatment. Support groups can help to reduce the risk of suicide. You should also avoid alcohol and drugs to further reduce your risk.
If you have bipolar disorder, you should do the following:
- Follow a relatively stable lifestyle.
- Get an adequate amount of sleep.
- Maintain a healthy diet.
Don’t Miss: Type 2 Diabetes And Anxiety
What Risks And Complications Can Bipolar Disorder Cause
There can be complications and risks for people who live with bipolar disorder. But these risks can be lessened with the right support and treatment.
What about suicide and self-harm?
You might have an illness where you experience psychosis, such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Your risk of suicide is estimated to be between 5% and 6% higher than the general population.
You are more likely to try to take your own life if you have a history of attempted suicide and depression. It is important that you get the right treatment for your symptoms of depression and have an up to date crisis plan.
There is also research that suggests you are 30% 40% more likely to self-harm if you live with bipolar disorder.
What about financial risk?
If you have mania or hypomania you may struggle to manage your finances. You may spend lots of money without thinking about the effect that it may have on your life.
You could make a Lasting Power of Attorney. This is a legal process. This means that you pick someone that you trust to manage your finances if you lack mental capacity to manage them by yourself.
You can work with your carer and mental health team. You can form an action plan. This can say what they can do if you have a period of mania or hypomania and you start to make poor financial decisions.
What about physical health risk?
What about alcohol and drugs risk?
If you want advice or help with alcohol or drug use contact your GP.
What about driving risk?
What Is Rapid Cycling

Some people with bipolar disorder develop rapid cycling where they experience four or more episodes of mania or depression within a 12-month period. Mood swings can occur very quickly, like a rollercoaster randomly moving from high to low and back again over a period of days or even hours. Rapid cycling can leave you feeling dangerously out of control and most commonly occurs if your bipolar disorder symptoms are not being adequately treated.
The different faces of bipolar disorder
Bipolar I Disorder This is the classic manic-depressive form of the illness, characterized by at least one manic episode or mixed episode. Usuallybut not alwaysBipolar I Disorder also involves at least one episode of depression.
Bipolar II Disorder In Bipolar II disorder, you dont experience full-blown manic episodes. Instead, the illness involves episodes of hypomania and severe depression.
Cyclothymia Cyclothymia is a milder form of bipolar disorder that consists of cyclical mood swings. However, the symptoms are less severe than full-blown mania or depression.
You May Like: Phobia Definition
Potential Causes And Risk Factors
Experts do not know exactly what causes bipolar disorder, although they believe that several factors play a role. These include:
- Genetics. People with bipolar disorder seem to have variations in genes that may have increased their risk of developing the condition. However, it is unclear exactly how these variations lead to the onset of the disorder.
- Family history. If a sibling or parent has bipolar disorder, a person is more likely to develop it themselves.
- Environmental factors. Experiencing periods of high stress, such as bereavement, can trigger bipolar symptoms. A traumatic head injury or abusing alcohol or drugs may also increase the risk.
Most likely, a combination of heredity and environmental factors plays a role in bipolar development.
Setting The Record Straight
Continuing the topic of spreading accurate information on the topic of bipolar disorder, there is another important item to note regarding what symptoms are needed to meet the criteria for bipolar disorder. Bipolar disorder is the appropriate diagnosis when someone experiences periods of significant depression and periods of significant manic or hypomanic symptoms. These episodes are separated by days, weeks, or months.
A depressive episode needs to be a period of at least two weeks where the person is experiencing symptoms of depression more often than not. These symptoms include:
- Having low energy and fatigue.
- Having low motivation.
- Changes in diet or weight.
- Feeling excessively guilty or worthless.
- Thinking about death.
- Feeling slowed down or sped up.
- Poor concentration and decision-making.
A hypomanic/manic episode will present much differently. Hypomania is typically less severe than a manic episode based on intensity and duration. Manic symptoms include:
- Reduced need for sleep.
- Increased energy.
- Feeling driven to complete certain behaviors.
- A string of poor decisions involving sexual promiscuity, overspending money, drug use, and other risky behaviors.
These behaviors will last for at least four consecutive days but can last for much longer with consistency.
It is time to put this myth to bed: manic depression and bipolar disorder are not two separate conditions. They are one and the same.
Recommended Reading: Apiphobia Definition
Is Bipolar More Serious Than Depression
Both are serious mental illnesses than can affect a persons quality of life. And both can lead to serious consequences if left untreated, including suicide, self-harm, reckless behavior, and impairment at work, home, or school. Both bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder, however, can be treated to lessen the risk of these dangerous symptoms.
How Does Bipolar Disorder Affect Women
Women and men are equally likely to have bipolar I disorder, but women are more likely to have bipolar II disorder and may experience more rapid cycling between highs and lows.1
Women with bipolar disorder are also more likely than men with bipolar disorder to have other physical and mental health conditions, including problems with alcohol use, depression caused by bipolar disorder, thyroid disease, obesity caused by medicines that treat bipolar disorder, and migraine headaches.1
Changing hormones during the menstrual cycle and menopause can also affect how severe a womans bipolar disorder is, but they do not cause bipolar disorder.2
Also Check: Fear Of Large Words
How Does Pregnancy Affect Bipolar Disorder
Women who have bipolar disorder are at risk for experiencing an episode after giving birth, especially a depressive episode.7,1 Women who experience a depressive or manic episode after giving birth are also more likely to have episodes after other pregnancies.2 Women with bipolar disorder are at high risk of developing postpartum psychosis, which is a medical emergency.
Talk to your doctor or nurse if you are trying to get pregnant or are pregnant. Some medicines are not safe to take during pregnancy.
How Do Doctors Treat It
Although there’s no cure for bipolar disorder, treatment can help stabilize moods and help the person manage and control symptoms. Like other teens with long-lasting medical conditions , teens with bipolar disorder need to work closely with their doctors and other medical professionals to treat it.
This team of medical professionals, together with the teen and family, develop what is called a treatment plan. Teens with bipolar disorder will probably receive medication, such as a mood stabilizer, from a psychiatrist or other medical doctor. A psychologist or other type of counselor will provide counseling or psychotherapy for the teen and his or her family. Doctors will watch the symptoms closely and offer additional treatment advice if necessary.
Read Also: Fear Of Really Long Words
What Are The Depression Symptoms Of Bipolar Disorder
The clinical depression symptoms seen with bipolar disorder are the same as those seen in major depressive disorder and include:
- Decreased appetite and/or weight loss, or overeating and weight gain
- Difficulty concentrating, remembering, and making decisions
- Fatigue, decreased energy, being “slowed down”
- Feelings of guilt, worthlessness, helplessness
- Feelings of hopelessness, pessimism
- Poor judgment and risk taking
- A decreased need for sleep due to high energy
Now We Know The Difference Where To Now
For people living with bipolar recovery is possible. Combining medication with a healthy lifestyle and support from community services and health professionals is an effective way to manage and respond to symptoms.
Charlotte is a SANE Speaker who was diagnosed with bipolar disorder ten years ago. She says shes made mistakes, but has learnt and continues to refine the management of her symptoms.
After the confusion, relief, blaming and identity crisis, I knew I had to sort myself out with help from doctors, medication, therapy, and family understanding, she says.
I kept going and Ive become a better human being. I know my own vulnerabilities and accept them. I know my stress triggers, how to step back, take a breath, regroup my feelings and then I can deal with it.
Yes, Ive stuffed up occasionally, but Ive learnt. Having bipolar disorder doesnt define me, but its helped me to teach my mind to be clearer.
For information about mental illness, including bipolar disorder, visit SANE Facts & Guides, or contact the SANE Help Centre on 1800 18 7263 .
You May Like: How Is A Depression Shown On A Contour Map
Risk Factors For Depression And Bipolar Disorder
Anyone can have depression. You may be at an increased for it if you have another serious illness or if theres a family history of depression. Environmental and psychological factors may also increase your risk.
The exact cause of bipolar disorder is unknown. However, youre more likely to have it if someone else in you family does. The symptoms usually become noticeable during adolescence or early adulthood, but it can appear later in life.
If you have bipolar disorder, youre at increased risk of:
- substance abuse
Know The Difference Between Bipolar And Manic Depressive Disorder
Many people are confused about the difference between the terms bipolar, depression, and manic depression. All of these terms refer to mental illnesses, but bipolar and manic depression refer to the same illness.
Bipolar and Manic Depression
The field of psychiatry changed the term for manic depression to bipolar many years ago to distinguish manic depression from clinical depression. Clinical depression is a mental illness characterized by the following symptoms:
Feeling sad and unhappy for an uninterrupted period of at least two weeks Crying for no reason Losing interest in pleasurable activities
Bipolar is characterized by alternating moods of mania and depression. What is a manic episode?
Feeling overly happy, excited, or confident Feeling extremely irritable or aggressive Having racing thoughts or speech Thoughts of being overly important, gifted, or special Making poor judgments with respect to money or relationships Engaging in risky behavior
RELATED ARTICLE: 7 Things Everyone Gets Wrong About Bipolar Disorder
Hypomania is a lesser form of mania where you might experience only a few of these symptoms or experience them with a low intensity. People with the more severe form of the illness are diagnosed with Type 1 Bipolar Disorder. Those who have hypomanic instead of full blown manic episodes are said to have Type 2 Bipolar Disorder.
Treatments for the Two Disorders
Bipolar and ADHD
Causes of Bipolar Disorder
Genetic Factors in Bipolar Disorder
You May Like: Definition Phobia
Is It Possible To Be Hypomanic And Depressed At The Same Time
Certainly! Some studies, the most common mood state in bipolar disorder is a mixture of hypomanic/manic and depressed symptoms. In fact, the classic picture of bipolar disorder having a course alternating between the poles of high and low moods is an over-simplification. The very name, bipolar disorder is probably less accurate than the older term, manic-depressive disorder. How can this be?
Although bipolar disorder has been classified as a mood disorder, ample research shows that the core symptom of hypomania and mania is not high mood, but rather hyperactivation. The mood, as many people have experienced, can either be elevated or irritable. But what always appears in manic or hypomanic episodes is a sense of being sped up physically and/or mentally. Racing thoughts, pressured speech, decreased need for sleep, starting lots of projects, and impulsive decision-making all derive from being overly activated, overly driven. Many times this sense of hyperactivation is pleasantwhen one is feeling particularly on my game the person is self-confident, more likely to act decisively, and often more likely to take risks. However, sometimes being hyperactivated simply is a sense that ones motor cannot be turned off. This can lead to restless irritability, especially if one is confronted by reality or other individuals that do not match expectations. Thus what is common in mania or hypomania is the sense of hyperactivation, or being driven, but the mood can be variable.
Beyond Treatment: Things You Can Do
Regular Exercise: Regular aerobic exercise, such as jogging, brisk walking, swimming, or bicycling, helps with depression and anxiety, promotes better sleep, and is healthy for your heart and brain. There is also some evidence that anaerobic exercise such as weightlifting, yoga, and Pilates can be helpful. Check with your health care provider before you start a new exercise regimen.
Keeping a Life Chart: Even with proper treatment, mood changes can occur. Treatment is more effective when a patient and health care provider work together and talk openly about concerns and choices. Keeping a life chart that records daily mood symptoms, treatments, sleep patterns, and life events can help patients and health care providers track and treat bipolar disorder over time. Patients can easily share data collected via smartphone apps including self-reports, self- ratings, and activity data with their health care providers and therapists.
Don’t Miss: Phobia Means
Is Bipolar Depression Worse Than Unipolar Depression
Some research has found that people with bipolar disorder, when not in a depressed phase, are worse at regulating happy and sad emotions than are those with depression.2 Also, bipolar disorder features more phases than does major depressive disorder, including mania, hypomania and depression.
But in terms of severity, neither disorder is worse, or better, than the other.
American Psychological Association, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, American Psychiatric Publishing, Washington, D.C., 2013.
FAQ Sources:
What Is The Difference Between Bipolar 1 And Bipolar 2
The main difference between bipolar 1 and 2 is the intensity of manic episodes. Bipolar 1 involves periods of severe mania whereas bipolar 2 involves periods of less severe hypomania.
A manic episode lasts for at least one week, and its effects are intense and debilitating, affecting someones personal life and ability to work.
Symptoms include erratic behavior like talking too rapidly and loudly, breaking the law, and driving or spending money recklessly. A manic episode may also cause someone to have overblown feelings of self-importance or to experience hallucinations and delusions. There must be at least one episode of mania for a diagnosis of bipolar 1.
Meanwhile, those with bipolar 2 experience similar, but less intense symptoms in a hypomanic episode. They may feel euphoric and excited for a few days. They may be extremely physically active, appear agitated, and have difficulty sleeping.
Not everyone who has hypomanic episodes has bipolar disorder. It is possible for someone to be diagnosed as having bipolar 2, and then to have an episode of mania that changes their diagnosis to bipolar 1.
Prevalence of depressive episodes is another difference between bipolar 1 and 2. A bipolar 2 diagnosis requires a patient to experience one or more depressive episodes. Although those with bipolar 1 may also experience a major depressive episode, it is not a diagnostic requirement.
Also Check: Celine Dion Anorexia