Mri Assessment Of Brain Abnormalities In Ptsd And Trauma Spectrum Disorders
Findings of smaller hippocampal volume appear to be associated with a range of trauma related psychiatric disorders, as long as there is the presence of psychological trauma. We have used MRI to show smaller hippocampal volume in PTSD,144,145,149,196 depression,197 depression with early abuse,198 borderline personality disorder with early abuse,199 and Dissociative Identity Disorder with early abuse.200 The greatest magnitude of difference was seen in the DID patients, who had unusually severe early childhood sexual abuse histories. We did not find changes in hippocampal volume in patients with panic disorder without a history of abuse .201 We found smaller amygdala volume in BPD with early abuse199 and increased amygdala volume in depression.197,202 Patients with depression had smaller orbitofrontal cortex volume with no changes in anterior cingulate or medial prefrontal cortex .203 More recently, we found smaller anterior cingulate volume in women with abuse and PTSD relative to controls.204
Effects Of Pharmacotherapy On Brain Function And Structure In Ptsd
We have begun to assess the effects of pharmacotherapy on brain structure and function in PTSD.243 We recently assessed the effects of phenytoin on brain structure and function. Studies in animals show that phenytoin, which is used in the treatment of epilepsy and is known to modulate glutamatergic function, blocks the effects of stress on the hippocampus.67 We studied nine patients with PTSD in an open-label function before and after treatment with phenytoin. Phenytoin resulted in a significant improvement in PTSD symptoms.164 Phenytoin also resulted in increases in both right hippocampal volume and right hemisphere volume.165 These findings indicate that phenytoin has an effects on PTSD symptoms as well as brain structure in PTSD patients.
We have assessed the effects of open4abel paroxetine on memory and the hippocampus in PTSD. Male and female patients with symptoms of PTSD were medication-free for at least 4 weeks before participation in the study. Twenty-eight patients were found to be eligible and started the medication phase. Of the total patient sample five patients did not finish due to noncompliance 23 patients completed the study.
Before patients started the medication phase, neuropsychological tests were administered, including the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale – Revised, WAISR , two subtests of the Wechsler Memory ScaleRevised.WMS-R, including logical memory and figural memory and the verbal and visual components of the Selective Reminding Test, SRT.
Neuroscience Explains The Anxiety And Hypervigilance Of People With Ptsd
About 10 percent of women and 4 percent of men will develop Post-TraumaticStress Disorder over their lifetimes. Men and women who have experienced sexual trauma are at increased risk, especially if the trauma occurred at a young age or was repeated.
PTSD is a mental health condition that may involve disturbances in threat perception, threat sensitivity, self-image, and emotional functioning. It can cause serious disruption in the ability to have healthy, satisfying relationships or tolerate lifes uncertainties, failures, and rejections without excess distress. It can also cause phobias, sleep disturbance, negative mood, anxiety, and attention/concentration difficulties that interfere with academic or career success. Research in neuroscience suggests impaired functioning in brain areas responsible for threat detection/response and emotion regulation account for many PTSD symptoms.
Read Also: How Do People With Schizophrenia Act
A Brief Recap Of Post
Our body cascades many chemical reactions during a frightening event that set off the fight/flight/freeze response readying us to react quickly to the danger. Most peoples chemical responses will return to baseline, but others will maintain the chemical reactions long enough to cause damage.
Although most people believe PTSD to be a diagnosis that only forms in adults, t this is not true. Children also suffer incredibly traumatic events and will form the diagnosis of post-traumatic stress disorder.
According to Amen Clinics, the causes of post-traumatic stress disorder are too numerous and varied to list in this piece however, they may include:
- Military combat
- Witnessing someone getting hurt or killed
- Witnessing the death of a loved one
You may have noticed that pandemic made the list. With the onslaught of COVID-19, it is predicted the number of people affected by complex post-traumatic stress disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder will increase dramatically.
What Can I Do About My Ptsd

If you have PTSD, you may feel tempted to try and shove all of the negative memories and feelings away. After all, shoving all of your trauma into a box and hiding it in the back of your mind forever sounds like it must be better than enduring the struggles of flashbacks and constant stress.
Some even use substances, like alcohol or other drugs, to suppress that stress and escape their difficult thoughts and feelings. They may also develop abnormal sexual behaviors or eating habits, or throw themselves into other responsibilities such as work.
As common as these coping mechanisms are, they arenât healthy. Your health and self-esteem will become damaged in new ways. You could develop an eating disorder, a substance abuse disorder, an unhealthy relationship with intimacy, or new difficulties forming meaningful relationships.
In addition to being unhealthy, these coping mechanisms also arenât really effective, even if they feel like they work at first. Any short-term effectiveness you may see will be overridden in the long term, and your trauma will return â sometimes worse than before.
So avoidance doesnât work â but what will?
Mental health struggles are the same as physical health struggles â often, they need real medical attention before they get better. In the case of PTSD, this often means therapy.
You May Like: Which Is A Cardiac Complication Of An Eating Disorder
Neural Circuits In Ptsd
In summary, dysfunction of a circuit involving the medial prefrontal cortex, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, and possibly hippocampus and amygdala during exposure to traumatic reminders may underlie symptoms of PTSD. These studies have primarily assessed neural correlates of traumatic remembrance, while little has been done in the way of utilizing cognitive tasks as probes of specific regions, such as memory tasks as probes of hippocampal function.
The Brain’s Response To Trauma
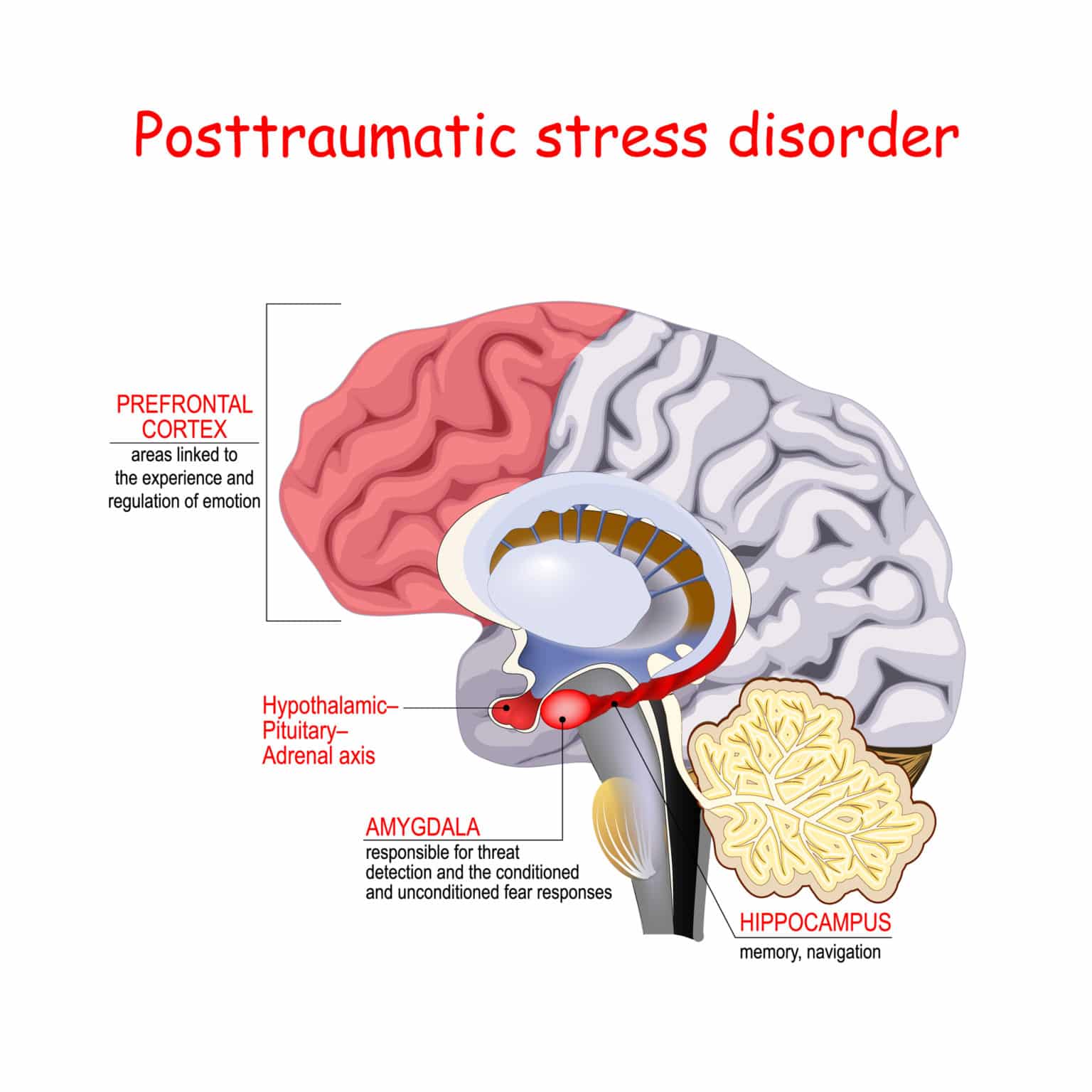
When your brain identifies some type of threat, the amygdala is responsible for initiating a fast, automatic reaction known as the fight-or-flight response. Think of the amygdala as the alarm that sounds when something poses a danger. This alarm prepares your body to respond, either by dealing with or getting away from the threat.
The amygdala also communicates with other areas of the brain, including the hypothalamus, which then releases the stress hormone cortisol. It is the brain’s prefrontal cortex that must then assess the source of the threat and determine if the body needs to stay on high alert to deal with the threat or if the brain needs to begin calming down the body.
The prefrontal cortex acts as a braking system that helps return your body to a normal state when you realize that the threat doesn’t pose a danger or after the threat has passed.
When people have symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder, the amygdala becomes hyperactive while the medial prefrontal cortex becomes hypoactive.
In other words, the part of the brain that triggers a fight-or-flight response responds too strongly, often in a way that is disproportionate to the danger posed by the threat. At the same time, the part of the brain responsible for calming this reaction does not work well enough.
Read Also: Why Do Bipolar Spend Money
How Is Ptsd Diagnosed
A doctor with experience in diagnosing mental illnesses, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist, can diagnose Post-traumatic stress disorder.To be diagnosed with PTSD, an adult must have all of the following for at least one month:
- At least one re-experiencing symptom.
- At least one avoidance symptom
- At least two arousal and reactivity symptoms
- At least two cognition and mood symptoms
PTSD symptoms must be severe enough to interfere with relationships or work. Some people recover within six months, while others have PTSD symptoms that come and go for decades.
Do Children React Differently Than Adults
Children and teens can have extreme reactions to trauma, but some of their symptoms may not be the same as adults. Symptoms sometimes seen in very young children , these symptoms can include:
- Wetting the bed after having learned to use the toilet
- Forgetting how to or being unable to talk
- Acting out the scary event during playtime
- Being unusually clingy with a parent or other adult
Older children and teens are more likely to show symptoms similar to those seen in adults. They may also develop disruptive, disrespectful, or destructive behaviors. Older children and teens may feel guilty for not preventing injury or deaths. They may also have thoughts of revenge.
Recommended Reading: Is Schizophrenia A Psychological Disorder
Ending Our Time Together
Traumatic events cause many chemical reactions and initiate the fight/flight/freeze response, but for some, these chemicals never return to baseline, causing damage to some regions of the brain.
60% of men and 50% of women will experience one or more traumatic events in their lifetime. These statistics mean that more research must happen to increase our knowledge and thus treatments for PTSD.
The brain areas affected by PTSD control memory, reasoning, and thought, causing the victim to experience difficulties remembering events, thinking, and learning new information.
Epigenetics, a new kid on the block of neuro-research about PTSD, has found that a persons genes are changed by trauma and that these changes can be passed to their progeny.
The next stage of research and learning about post-traumatic stress disorder will involve those who formed PTSD due to the COVID-19 pandemic as people emerge from isolation and face a new world.
Trauma is personal. It does not disappear if it is not validated. When it is ignored or invalidated, the silent screams continue internally heard only by the one held captive. When someone enters the pain and hears the screams, healing can begin. ~ Danielle Bernock
References
Bremner JD. Alterations in brain structure and function associated with post-traumatic stress disorder. Semin Clin Neuropsychiatry. 1999 Oct 4:249-55. DOI: 10.153/SCNP00400249. PMID: 10553030.
Epigenetics. Wikipedia. Retrieved from:
Your Reaction To Trauma Depends On You
While PTSD often manifests as a reliving of a traumatic event through nightmares and flashbacks, some people are affected more than others. “Some individuals may experience feelings of isolation, irritability, and guilt, and have difficulty sleeping and concentrating,” Nealon says.
And, although scientists have been able to define changes in brain structures, more research needs to be done to understand how some individuals end up with a diagnosis of PTSD and others don’t, despite being exposed to the same type of trauma, Cummins says.
“For example, some individuals in war combat will endure symptoms of PTSD throughout their life while others won’t,” Cummins says. “This can happen even if two individuals were on the same deployment and were exposed to the same traumas.”
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , a resource manual for mental health professionals, a person must have been exposed to “actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence” in order to be diagnosed with PTSD.
Besides that, though, there’s no threshold for whether something is traumatic enough to cause PTSD it depends more on the brain’s reaction to it, and how seriously a person is affected. PTSD can even be caused by witnessing or learning about a trauma that happened to someone else, or in rare cases, by looking at traumatic videos or photos.
You May Like: Is Binge Eating A Disorder
How Effective Are Magic Mushrooms For Ptsd
Traumatic events like war, accidents, and losing a loved one can alter the connection in our brains, leading to PTSD.
Our brains are essentially wired to have a flight-or-fight response, which is responsible for determining how we respond to extreme events. While the fight response allows us to face the danger, the flight response gives us the strength to withdraw from the danger.
With PTSD, the brain is stuck in flight-or-fight mode, which can lead to a cluster of symptoms:
This will ultimately mess around with the brain’s function and ability to respond to events less violently. People who suffer from PTSD often have a replay of their bad experiences or occurrences, thus requiring total brain rewiring via medications and other activities.
The psilocybin in magic mushrooms can help restore neuroplasticity. It does this by interacting with serotonergic receptors. Serotonin receptors are responsible for biological and neurological processes like
- Thermoregulation
They control how we respond to events. By interacting with these receptors, psilocybin and psilocin help to deal with anxiety, depression, PTSD, and addiction.
Several veterans have attested to the therapeutic activity of magic mushrooms in promoting mental balance. A 2022 study on army veterans suffering from trauma shows that all the participants who had used psilocybin reported immediate and long-term improvements in their symptoms.
Kruske had this to say about his magic mushroom trip:
Are There Effective Treatments
Many people recover from TBI without any formal treatment. Problems that linger may clear up in a few weeks. You may notice some problems more as you return to your normal routine. For example, you may not realize that you get tired more quickly until you return to your regular chores, work, or school. Even so, people usually get better after a head injury, not worse. Professional treatment for the symptoms that follow TBI usually involves rehabilitation to improve functioning.
The good news is that effective treatments for PTSD also work well for those who have suffered mTBI. This includes two forms of therapy: Cognitive Processing Therapy and Prolonged Exposure . Learn more about Treatment Basics for PTSD.
You May Like: How To Tell If A Bipolar Man Loves You
Physical Causes Of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
Brain structures and brain chemicals have both been implicated in the causes of PTSD. Research shows that exposure to trauma can cause “fear conditioning” of the brain. Fear conditioning is where the person learns to predict traumas and the predicted traumas cause parts of the brain to activate. With posttraumatic stress disorder, fear conditioning causes the brain to anticipate danger where none exists, causing PTSD symptoms.2
Additionally, the parts of the brain that are designed to dampen this fear response seem less capable of doing so in those with PTSD. This may be caused by stress-induced atrophy of the brain structures in that area.
The Science And Biology Of Ptsd
PTSD isnt all in the mind or something you can just get over or move on from. No matter how much reasoning and coaxing you do, someone with PTSD may find it impossible to achieve sustainable recovery without professional treatment.
Thats because post-traumatic stress disorder is a form of injury to the brain. Bringing with it physical as well as mental symptoms and changes.
We feel its really important to understand how the brain can change with PTSD and C-PTSD. Brain scans show that PTSD symptoms and behaviours are caused by biological changes in the brain, NOT by some personal failure. Understanding the changes can also help friends and families gain a better understanding that their loved ones PTSD symptoms are not their fault. This can promote forgiveness and encourages families to become more involved in the healing process.
Modern science has enabled us to get a far clearer picture of the brain and in fact the whole neurological systems structure and activities. It has become possible to map and measure the different development paths that each human brain follows. Our age and the things that happen to us each day naturally dictate microscopic changes to our brains structure.
This article looks at the parts of the brain affected by PTSD.
As a starting point, heres an important definition. The things that affect our body are referred to as physiological. When its our emotions and mental capabilities that are impacted, the word used is psychological.
Read Also: How To Treat Ptsd With Medication
How Trauma And Ptsd Impact The Brain
- Addiction BlogHow Trauma and PTSD Impact the Brain
- Drug Addiction Treatment
After a stressful event, its typical for people to have an emotional response. Many people experience trauma after serving in combat or living through a mass shooting or natural disaster. People can be traumatized after an event that only affects them, such as a car accident or sexual assault.
Following a traumatic event, some people develop post-traumatic stress disorder. While more than half the population is likely to experience a traumatic event at some point, only 7 to 8% of people go on to have PTSD. PTSDs effects are long-lasting and disruptive, making it challenging for people to feel safe. Many people living with PTSD also develop substance use, depression or anxiety disorders.
Understanding how traumatic events can affect you and how PTSD can change the brain allows you to get the help you need to get your life back following a traumatic situation.
Ptsd Causes: Causes Of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
The causes of post-traumatic stress disorder are not well known or understood. Posttraumatic stress disorder is an anxiety disorder that occurs after being involved in a traumatic event involving harm, or threats of harm to the self or others. Even learning about an event has the possibility of causing PTSD in some people.
Prior to the third edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders in 1980, PTSD was not recognized, and those who exhibited the symptoms were considered to be having an exaggerated stress reaction . This reaction was attributed to a character flaw or personal weakness. We now know that character does not cause PTSD and there are physical, genetic and other causes of PTSD at work.
While one could think of the trauma as the cause of PTSD, some people can undergo trauma and not develop posttraumatic stress disorder. Posttraumatic stress disorder is initiated by trauma, but the causes of PTSD are related to the brain and risk factors for developing an anxiety disorder.
The events most likely to cause post-traumatic stress disorder are:1
- Physical attack
- Being threatened with a weapon
However, any kind of event perceived as traumatic can trigger PTSD .
Also Check: What Is Considered An Eating Disorder