Are Mental Health Disorders Considered Neurodivergent
So, where do mental health disorders fit in this movement? Its a little hard to know. Some articles about neurodiversity and neurodivergence include disorders like anxiety, schizophrenia, and PTSD, while others dont. As theres no standardized definition of neurodivergence, its a complex question.
Mental health disorders can affect your cognition, and they certainly impact the way you think and see the world. They are a difference in your brain that significantly impacts your life, just as is the case with neurological disorders.
People who are neurodivergent recognize that they face unique challenges based on those variations. This is true too of mental health disorders. One criterion for diagnosing any mental health disorder is that it affects your day-to-day functioning.
These points seem to suggest that mental health disorders are neurodivergent. One argument that could be made against this is that if we include more and more things under that umbrella, whats considered normal? But thats the point every brain is different, even among those who dont have neurological or mental health disorders.
Struggling with a mental health disorder, including addiction, is challenging, but it doesnt mean youre abnormal. In fact, according to the National Institute of Mental Health, nearly one in five adults live with a mental health disorder.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy
Learn more about how our TruHealing Centers team can support your mental health today.
A Quick Neurodivergent Definition
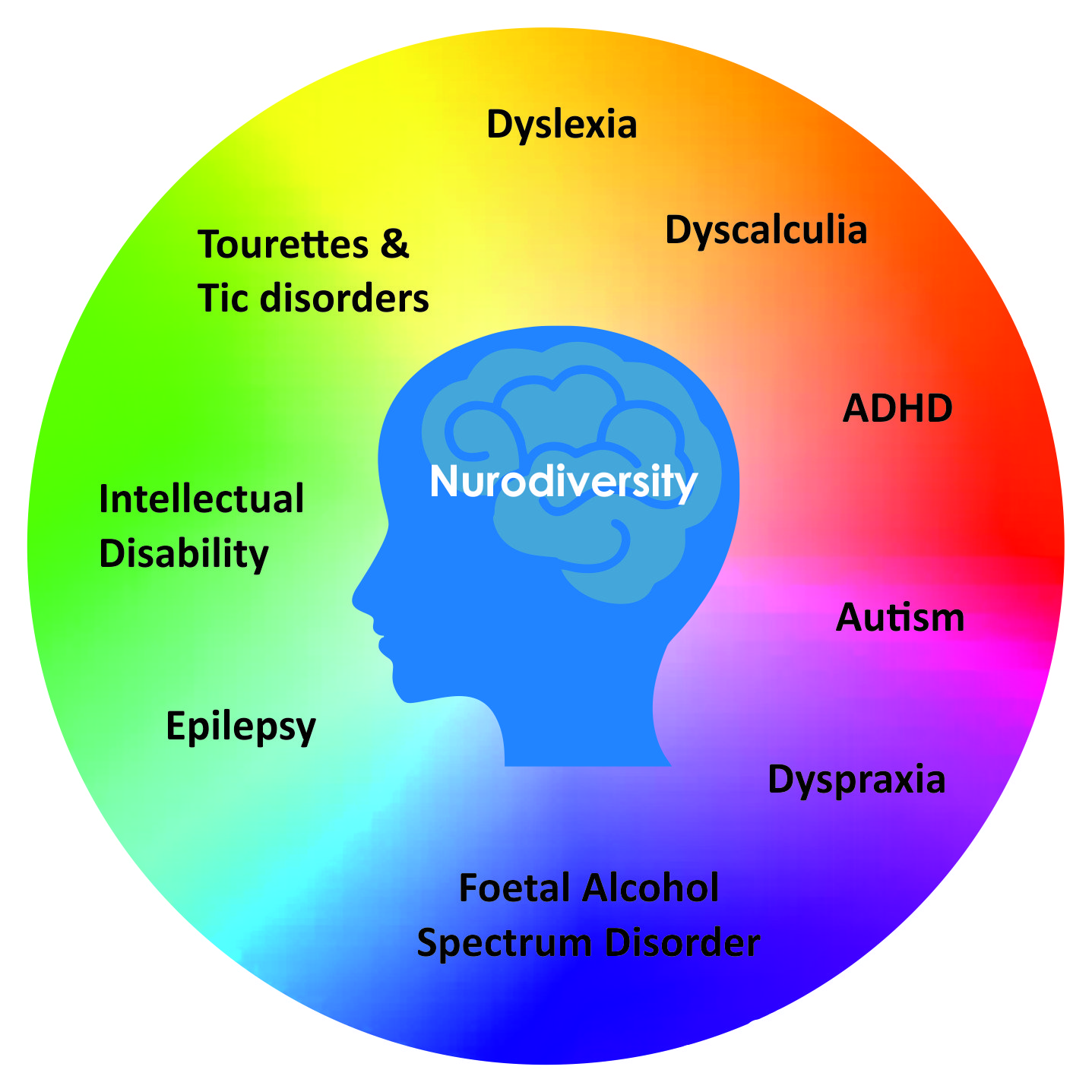
The term neurodivergent is used to describe a variety of conditions related to cognitive abilities, though more often people with these conditions prefer neurodiverse. It applies to conditions such as autism, dyslexia, dyscalculia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder , and obsessive compulsive disorder . Neurodiverse individuals often struggle with soft skills, especially ones that apply to social interactions. Unexpected physical behaviors like standing too close to someone or speaking too loudly occur for people on the autism spectrum, self soothing movements like rocking or irregular hand movement may also be present. In Tourettes sufferers, verbal and physical tics are the hallmark of the condition.
The term was coined by the sociologist Judy Singer, who goes into greater detail in her book, Disability Discourse:
For me, the key significance of the Autism Spectrum lies in its call for and anticipation of a politics of neurological diversity, or neurodiversity. The neurologically different represent a new addition to the familiar political categories of class/gender/race and will augment the insights of the social model of disability.
What Conditions Can A Neurodivergent Person Have
People who identify themselves as neurodivergent typically have one or more of the conditions or disorders listed below. However, since there arent any medical criteria or definitions of what it means to be neurodivergent, other conditions also can fall under this term as well. People with these conditions may also choose not to identify themselves as neurodivergent.
Some of the conditions that are most common among those who describe themselves as neurodivergent include:
Don’t Miss: Side Effects To Pristiq
Why The Term Neurodiversity Caught On
The term “neurodiversity” caught on quickly. This occurred for several reasons. For one, the number of people with diagnosed developmental disorders exploded in the early 2000s, making neurodiversity a much more common phenomenon.
In addition, because people don’t “grow out of” autism, ADHD, learning disabilities, or Tourette’s syndrome, neurodiverse children become neurodiverse adultsâmany of whom are very capable of self-advocacy.
Another important reason for the popularity of the concept of neurodiversity is that definitions of terms like autism spectrum, ADHD, and learning disabilities were and still are in a state of flux.
Many people grew up before certain disorders were given a label, but they always felt atypical. Today, many such people feel embraced by the neurodiversity movement.
Diagnostic labels are constantly changing, based largely on cultural norms and expectations. People who were neurotypical 50 years ago are no longer considered to be soâand vice versa.
For example, it was only in 1973 that homosexuality ceased to be listed as a pathological condition in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders . The DSM is the official handbook of the American Psychiatric Association on mental and developmental disorders.
In 2013, major changes were made that removed the disorder called Asperger’s syndrome from the DSM, changed the definitions of autism and ADHD, and added hoarding disorder (as a brand new diagnosable disorder.
Neurodiversity And The Brain
The advent of brain imaging has also lent credence to the concept of Neurodiversity. While the science is not definitive, scans have shown that some individuals with certain Neurodivergent traits have changes in their brain structures. In other words, these brains may process information differently because they are wired differently.
You May Like: Closed Depressions Are Shown By Closed Contours With Inward Pointing Hachures.
How To Navigate Neurodiversity Respectfully
“Being neurodivergent doesn’t mean that you have a disability,” says Mandell. “We tend to think about people in terms of what is ‘wrong’ with them, but people who are neurodivergent simply engage and interact with the world differently.”
If someone says they’re neurodivergent, then it’s typically okay to ask them if they’d be open to talking about it, but you should never make assumptions about their mental health or use of the label, notes Caudel. “If they’ve disclosed their neurodivergence, ask them questions about their perspective and what navigating life is like,” he says. “You have a golden opportunity to peer past the mask and see the real person inside.” This may help you to better understand how to communicate with them in the future.
If you notice that someone who you know to be neurodivergent seems to be stressed or struggling to understand what you’re trying to say, Mandell recommends offering your support. “It can be really helpful to ask, ‘What’s the best way for you to receive this information?’ or ‘What’s the best circumstances for us to communicate?'” he explains.
And it’s especially important to try to create a safe space for someone who is neurodivergent to be themselves. “They don’t often show that person for fear of being rejected and excluded, but there are a lot of wonderful, talented people out there who are excluded because they’re ‘weird’ or ‘different,'” says Caudel. “The better you understand someone, the better you can communicate.”
Neurotypical Vs Neurodivergent: Whats The Difference
The study of the human brain is a vast area with significant overlap between fields like neurology and psychiatry. The data can often be contradictory but significant inroads have been made in understanding how our brains affect our behaviors. Individuals on the autism spectrum in particular have benefited from a more holistic approach to treatment when it comes to ASD. New terminologies have also come into common usage to define the differences in how the world is perceived by different people. Two commonly used terms are neurodivergent and neurotypical.
Recommended Reading: Which Is Worse Bipolar Or Bpd
So Many Services And Support Agencies Have Been Affected By Covid
Dr. Fung: Indeed, services and support agencies are struggling financially in this economic downturn. However, many have adapted to the new normal, and are offering services virtually. For example, some service agencies are able to obtain funding from Department of Rehabilitation to run virtual pre-employment training for individuals on the spectrum. Children on the spectrum are receiving behavioral therapy sessions virtually as well.
What I worry about is the security of funding sources from state government. Many states have proposed budgets cuts on many areas, including funding for disabilities. A recent report by Turk et al. at SUNY Upstate Medical University examining about 30,000 COVID-19 patients found that the case-fatality rate was 1.6% among young patients with intellectual and developmental disabilities , substantially higher than the rate for patients without IDD . They also demonstrated higher case-fatality rate in adults with IDD than without IDD . These grim statistics really called for an increase in funding to support individuals with IDD, including autism.
Prevalence Of Anxiety Disorders
Overall, 51.6% of the FXS adolescents met criteria for any anxiety disorder, with 12.9% meeting criteria for multiple anxiety disorders. Similarly, 50.0% of adolescents with ASD met criteria for any anxiety disorder, and 30.0% met criteria for multiple anxiety disorders. No significant differences in the rates of overall anxiety diagnoses between the ASD and the FXS group were observed = 0.01, p> .05). Rates of specific anxiety diagnoses for each group can be found in Table 2.
Don’t Miss: Clown Phobia Definition
Do Neurotypical Disorders Relate To Neurodiversity
Neurotypical is a new form of classifying the different strengths and weaknesses of cognitive skills and behavioral patterns. Neurodiversity is defined as the range of differences in neurocognitive functioning within the general population. Neurodiversity embraces all facets of these developments.
Neurodiversity is an emerging term that references the differences between people, established by sociologist Judy Singer. That is to say, neurotypical behavior is different from neurodiverse behavior.
Someone neurotypical will consistently act within the bounds of accepted social norms while neurodiverse people , who are neuroatypical may behave in ways that appear odd or disturbing to neurotypicals.
Someone neurotypical can be characterized as:
- Not having cognitive or social difficulties that require coping mechanisms
- Not demonstrating issues with speech or certain motor impediments
- More consistent reading and interpreting social cues
- Very few sensory issues
- Hitting most developmental milestones without delay
What Is The Relationship Between Neurodivergence And Mental Illnesses
Image by Polina Zimmerman, Pexels.com
Like co-occurring neurodivergent diagnoses , mental health issues can also concur with neurodiversity.
There is a higher prevalence of mental health difficulties in individuals with autism while there are higher co-morbidity rates for those with dyslexia and ADHD.
A 2017 study has found that those with dyslexia who had more negative or uncomfortable emotions deriving from living with dyslexia experienced lower levels of total work self-efficacy and work competency.
An article, also from 2017, that looked at World Health Organisation data from mental health surveys has found that individuals with ADHD had a higher prevalence of anxiety. Overall individuals were less likely to seek support. If they did, it was more likely to be for their co-morbidities rather than their ADHD itself.
Neurodiverse individuals who suspect that they have a mental health issue may not want to disclose it due to a lack of understanding.
Also Check: Fainting And Anxiety
What Does It Mean To Be Neurodivergent
The term neurodiversity was first coined by sociologist Judy Singer in the late ’90s. David Mandell, professor at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, explains that it is the recognition that people’s brains operate in a variety of ways. The notion of neurodiversity states that all modes of thinking, behaving, and processing are normal and that there is no one “right” way to experience and interact with the world.
The term “neurotypical” refers to thinking, processing information, and behaving in ways that are considered “normal” or “average” by the overall public, according to Mandell. Neurotypical individuals do not necessarily identify as neurotypical, but they usually acknowledge it.
Neurodivergent individuals encompass everyone else. They often experience difficulties communicating with the neuro majority, and interacting with systems designed for the majority. This means neurodivergent individuals suffer because of their differences. For example, a person who is neurodivergent may be less productive than their coworkers due to certain processes in place. Something such as the need for regular in-person meetings or presentations may make the person feel uncomfortable.
There are many neurodivergent examples or types of neurodivergence, but if you’re especially wondering what is considered neurodivergent, these are some of the most common or familiar ways it manifests.
How To Know If You’re Neurodivergent
If you have ever been diagnosed with any of the above conditions, then you would be considered neurodivergent. On the other hand, if you have never been formally diagnosed, but you resonate strongly with the descriptors for one or more types of neurodivergence, then you might benefit from seeking a professional to find out for sure.
In all areas of life, having a formal diagnosis can bring you a deeper sense of understanding about why you function the way you do and how to best work with that.
If you have never been diagnosed with any of the above terms and you’ve never felt that you had any symptoms of them, then chances are you are neurotypical.
You May Like: Fear Of Spoons Phobia Name
Neurodivergence And Addiction Treatment
Seeking addiction treatment can be challenging for those who wish for a better alternative. Addiction treatment for those with neurodivergent qualities is often overlooked. For example, individuals with Autism spectrum disorder and Asperbergers can experience addiction.
This sensitive portion of the population deserves attention and comprehensive care in addiction treatment. Generally, it is reported that individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder are less likely to participate in drinking and drug use even those without an official diagnosis.
There hasnt been a dire need for programs such as these considering the low admissions. Although, this is a good reason to establish more programs suited for those with a neurotypical disorder.
The same treatment options within the continuum of care are available. Therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy have shown effectiveness in treating individuals with neurotypical disorders. Dual diagnosis treatment programs are emerging as a resource. For example, a patient with ADHD and a substance use disorder would be considered for dual diagnosis treatment.
According to Autistica, those with autism are 9 times more likely to commit suicide. Those with autism may not communicate these feelings in conventional forms, which can pose many obstacles. Dyslexics are at higher risk of self-harming and suicide.
What Does It Mean When A Person Is Neurodivergent
The term neurodivergent describes people whose brain differences affect how their brain works. That means they have different strengths and challenges from people whose brains dont have those differences. The possible differences include medical disorders, learning disabilities and other conditions. The possible strengths include better memory, being able to mentally picture three-dimensional objects easily, the ability to solve complex mathematical calculations in their head, and many more.
Neurodivergent isnt a medical term. Instead, its a way to describe people using words other than normal and abnormal. Thats important because theres no single definition of normal for how the human brain works.
The word for people who arent neurodivergent is neurotypical. That means their strengths and challenges aren’t affected by any kind of difference that changes how their brains work.
Read Also: Is Celine Dion Anorexic
We Know That Adults On The Spectrum With Valuable Skills Are Woefully Underemployed Leaving Them At Financial Risk With This Pandemic And Jobs Being Furloughed And Lost Are You Seeing The Impact In This Community And Has The Economic Fallout Stalled Hiring And Intern Programs In Companies Usually Proactive In Hiring The Neurodiverse
Dr. Fung: Before the pandemic, it was estimated that about 80% of adults on the spectrum are unemployed or under-employed in the United States. During this pandemic and the accompanying economic downturn, many people are losing their jobs, especially those in small to medium sized businesses. People with disabilities including autism are often the first to be let go, and the last to be hired. Without performing a study to assess the effects of the pandemic on employment in the neurodiverse community, we cannot tell the magnitude of the impact. However, from a previous study completed by Kaye during the 2008 recession, job losses among workers with disabilities far exceeded those of workers without disabilities.
The economic fallout has affected the entire economy. No sector is completely unaffected. Corporations with specialized employment programs for neurodiverse individuals are no different. I have not seen growth nor shrinkage of those programs. In the Stanford Neurodiversity Summit this October, leaders of these companies together with other small to medium-sized companies will participate in panel discussions. We hope that this forum can help with igniting the interest in the Neurodiversity at Work initiatives even during the toughest time during and after the pandemic.
New Routines Were Difficult While Working From Home
For Holmans, working from home throughout the pandemic means not having to deal with sensory overload, and other autistic people were similarly relieved by this aspect of quarantining. But for many, the jolt in routine also meant they now lacked access to their special interestsactivities pursued with intense passion and sometimes doubled as coping mechanisms. This was distressful for many autistic people who had special interests that required time spent away from home.
Many who struggle with sensory overload benefited from more time at home, but it was countered by a critical lack of structure, stability, and external support systems. Nirenberg notes that because neurodivergent people often live with social isolation, adding physical isolation can doubly impact mental health.
Adding in factors related to the shift in routine, lack of typical workplace or school accommodations, plus long hours and trauma exposure to essential workers while reducing the support systems available, will heighten difficulties.
Emilia Song, who has ADHD inattentive type, has always had challenges organizing and motivating herself she struggles with time-blindness. As a result, she often hyperfocuses, zeroing in on a specific task for an extended period of time. But without a structured setting, she falls into a boom-bust pattern, continually squeezing a lot of activity into a short amount of time, then requiring a prolonged recovery time after being productive.
Read Also: Does Anxiety Cause Blurry Vision
Traumatic Life Experiences Alter The Brain
These cases are physical damage to the brain. But what about experiences so horrific they change the way the brain functions. PTSD is a disorder that develops after a traumatic event. The sufferer feels intense anxiety when thinking about the incident and may have flashbacks. They can have nightmares and avoid people. It alters the way they see the world, and it also changes the way the brain functions causing it to be overactive. Treating it can be very difficult.
Much mental illness comes about from abuse sustained as a child, and the growing mind has to be different to handle strange and stressful situations in order to survive.
Those with these kinds of mental illness arent like those with ADHD or autism. Anxiety disorders can be cured successfully with the proper therapy. Cognitive-behavioural thearpy can change the connectivity and activity of the brain. In people with social anxiety, its success rate is about 70%.
Medical professionals dont consider it a natural state of the brain but rather an illness that needs to be treated. However, being afraid of exclusion from the group isnt something life-threatening now, but it meant certain death throughout human history.
When thinking about mental illness, should we try to consider that an unusual behaviour has a purpose. In this context, social anxiety sounds less like an illness and more like our minds way of making sure we stay alive.