Mental Disorders And Gender
| Part of a series on |
Gender is correlated with the prevalence of certain mental disorders, including depression, anxiety and somatic complaints. For example, women are more likely to be diagnosed with major depression, while men are more likely to be diagnosed with substance abuse and antisocial personality disorder. There are no marked gender differences in the diagnosis rates of disorders like schizophrenia, borderline personality disorder, and bipolar disorder. Men are at risk to suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder due to past violent experiences such as accidents, wars and witnessing death, and women are diagnosed with PTSD at higher rates due to experiences with sexual assault, rape and child sexual abuse. Nonbinary or genderqueer identification describes people who do not identify as either male or female. People who identify as nonbinary or gender queer show increased risk for depression, anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder. People who identify as transgender demonstrate increased risk for depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Evaluation Of Women With Bipolar Disorder
A complete assessment of women with BD is an integral part of management that includes a psychiatric and medical history, family and social history, and mental status exam with a focus on mood, psychotic features, anxiety, substance use, and eating disorder signs and symptoms.
Because women with BD, particularly Bipolar II disorder, frequently present with depression, it is important to probe carefully for a history of hypomanic or manic symptoms, which may not be recognized as problematic by the patient. In all the women who present as a case of major depression, especially those who have an early age of onset and do not respond well to antidepressant monotherapy, there is the possibility of BD. The most well-known are MDQ other options include Hypomania checklist.
Using structured clinical interviews, such as the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV, may improve the identification of BD. The diagnosis of Bipolar II disorder, rapid cycling or mixed mania, which is more common in women, have an impact treatment options. The medical evaluation includes physical examination, weight and vital signs, laboratory tests , and toxicology screen. The assessment also includes the menstrual and reproductive history, and history of menstrual, pregnancy/postpartum, or menopausal-related mood or psychotic symptoms. The history of hormonal treatments and the effects of the treatment of mood are also important.
Women And Bipolar Disorder
- Women and people with bipolar II disorder are significantly more likely to experience periods of rapid cycling than men with the same condition. . Depression, anxiety and perceived stress in women with and without PCOS: A community-based study. Psychological Medicine, 49)
- Other research findings indicate that women with bipolar disorder may have more depressive episodes and more mixed episodes than do men with the illness.
Also Check: Feratraphobia
How Do Doctors Treat It
Although there’s no cure for bipolar disorder, treatment can help stabilize moods and help the person manage and control symptoms. Like other teens with long-lasting medical conditions , teens with bipolar disorder need to work closely with their doctors and other medical professionals to treat it.
This team of medical professionals, together with the teen and family, develop what is called a treatment plan. Teens with bipolar disorder will probably receive medication, such as a mood stabilizer, from a psychiatrist or other medical doctor. A psychologist or other type of counselor will provide counseling or psychotherapy for the teen and his or her family. Doctors will watch the symptoms closely and offer additional treatment advice if necessary.
Living With Bipolar Disorder
Teens normally face ups and downs with school, family, work, and friends. Dealing with bipolar disorder at the same time is a very difficult challenge. One 16-year-old reader who was diagnosed with bipolar disorder at 14 wrote to us about the experience:
“I had mood swings that were the worst anyone could have ever seen. My poor parents thought I hated them, but really I was sick and didn’t even realize it. But now I am on medications for my disorder and I live a pretty normal life. My family and friends support me, and they, along with my therapist, have helped me get to the point where I am today. I just want other teens to know that even though it is hard at times to be bipolar, things will get better.”
If you’ve been diagnosed with bipolar disorder, taking your medications as prescribed, reporting any changes in how you feel or function, and participating in therapy will be key to living a successful life. In addition to treatment, making a few lifestyle changes, such as reducing stress, eating well, and getting enough sleep and exercise can help someone who is living with the condition. And many teens find it helps to join a support network such as a local support group for people with bipolar disorder.
Recommended Reading: Aphobic Meaning
Sexual And Physical Abuse
Female patients of BD are more likely to report history of sexual abuse, which is associated with a worse course of this disorder, earlier age of onset, greater co-morbidity and a higher rate of suicidal attempts. Chandra et al., reported that Indian women with the psychiatric disorder also face sexual coercion and violence.
Social Media Pressures And Criticism
Social media is highly prevalent and influential among the current generation of adolescents and young adults. Approximately 90% of young adults in the United States have and use a social media platform on a regular basis. In terms of social media use and body image, boys experience social media as a higher positive influence on their body image than girls, who report social media causing more negative effects on their body image. Indeed, social media use has a connection to increased risk for eating disorders in women. Women receive greater amounts of pressure and criticism surrounding their physical appearance, making them more likely to internalize the body ideals that are glorified on social media.
Furthermore, Pro-anorexia communities are widespread among social media platforms which creates an environment that encourages disordered eating behaviors, and uses primarily photos of young women to spread unhealthy messages promoting thinness. Women are more likely to be involved with pro-anorexia communities.
Read Also: What Is The Fear Of Puke Called
Clinical And Demographic Correlates
There was a trend for a positive correlation between average PPI at the 60-ms and the 120-ms SOA in male and female controls , but not in BD. There was no correlation between average PPI and startle data in any of the four groups, or between average startle and any demographic or clinical variable. In all participants there were no significant correlations between PPI and demographic variables. In male BD participants there was a trend for a correlation between 60-ms average PPI and age of onset . Importantly, there were no significant correlations between PPI and symptoms or any medication . When all BD patients were combined, there was no difference in the effect of each medication on PPI, for either medication type.
To examine the effects of smoking on PPI, smoking status was added as a covariate to the PPI analyses. There was no significant effect of smoking, nor did it change the direction of our findings. The analyses were repeated comparing men and women in both groups for non-smokers only and the findings were similar to the whole-group results. Using Spearman’s rho correlation, we found that in female BD participants there was a negative correlation between 60-ms average PPI and cigarette smoking however, this does not explain the PPI effect that was observed in these participants at the 120-ms SOA.
How Do I Know If I Am Bipolar
Identifying bipolar disorder is very strategic because there are behavioral explanations that first need to be ruled out. Since the disorder is more commonly seen in teenage years than perhaps someone in their 40s, somebody might be inclined to gloss over symptoms as typical teenage behavior.
If the behavior of manic highs continues to be repeated over time with potentially dangerous consequences or depressed periods lasting longer than two weeks, a visit to a medical professional is in order. A routine physical including blood work can rule out other physical contributors and a full mental wellness evaluation can be performed.
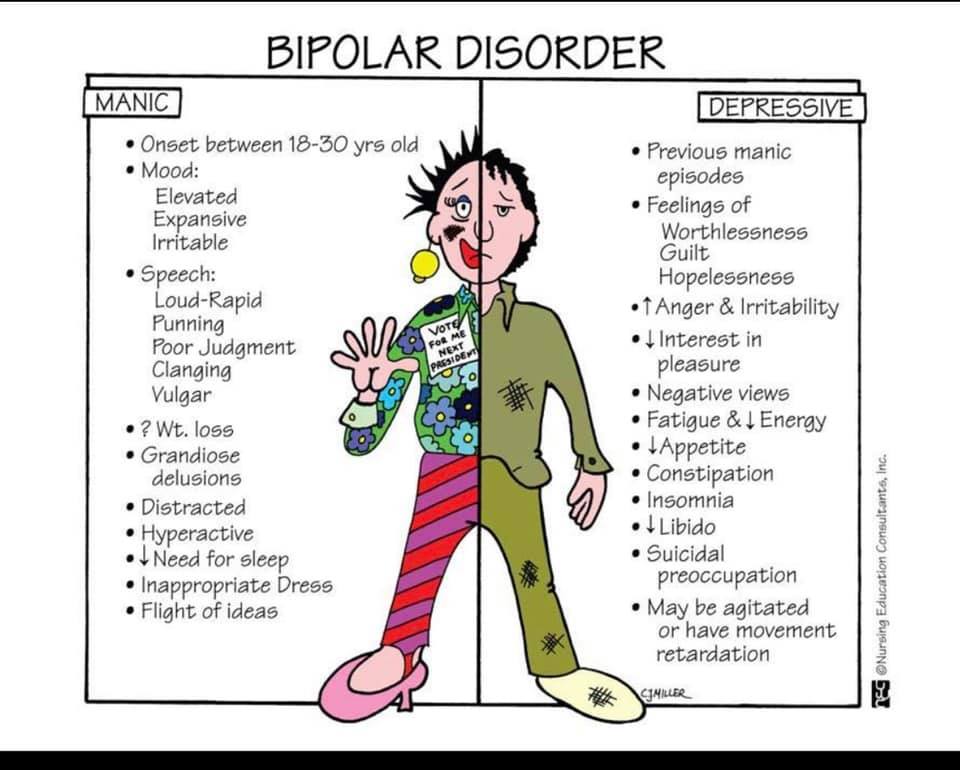
Common Signs & Symptoms of Mania
- Showing intense happiness or silliness for a long time
- Having a very short temper or seeming extremely irritable
- Talking very fast or having racing thoughts
- Having an inflated sense of ability, knowledge, and power
- Doing reckless things that show poor judgment
These symptoms may be more manic and an episode may require hospitalization until the person can be stabilized, as in bipolar I.
Common Signs & Symptoms of Depression
- Feeling very sad or hopeless
- Feeling lonely or isolating themselves from others
- Eating too much or too little
- Having little energy and no interest in usual activities
- Sleeping too much
You May Like: Can You Faint From Anxiety
Social Impact And Prejudice
Research confirms that the social, as well as the more clinical, effects of bipolar disorder can be different for females.
A concluded that females are more likely than males to face:
- stigma and isolation
- a loss of self-determination and a sense of a lack of control
- a lack of understanding from healthcare professionals and others
- pressure to appear normal or face consequences such as losing custody over children
Economic factors also influenced the experience of bipolar disorder among the study participants. Those who reported having a safe place to live and help with childcare and family responsibilities tended to manage better.
Participants with less privileged socioeconomic backgrounds and participants from marginalized groups, including Black Americans, were more likely to face abuse and experience other risk factors for psychosis. These participants were also more likely to work full-time and have full responsibility for caring for their families. A lack of support and safe living conditions, abuse, and other factors can increase the risk of severe symptoms of bipolar disorder and make the symptoms harder to manage.
Menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can influence how bipolar disorder affects females.
Risks Associated With Mood
The potential risks of medications during pregnancy include malformations, obstetrical, and neonatal complications and long-term neurobehavioral effects.
Neurobehavioral teratogenicity can result from medication exposure after the first trimester of pregnancy. Unfortunately, there is a dearth of long-term studies of children of women with BD exposed to medications during pregnancy. Maximizing safety requires familiarity with the impact of individual medications across these domains and interventional strategies to reduce risks.
Malformations associated with maternal drug use depend on the properties of the drug and the point of exposure: Up to 32 days postconception can affect neural tube development and closure days 2156 after conception may affect normal heart formation and during days 4263 may influence development of the lip and palate. Craniofacial anomalies can also occur after the first trimester.
Given that more than 50% of pregnancies are unplanned, by the time women and their clinicians are aware of the pregnancy, the period of susceptibility to these risks would have already occurred. Clinicians should provide maintenance treatments in anticipation of potential pregnancy and be aware of which medications pose the fewest risks.
Read Also: Topographic Depression Definition
Risk Factors And The Minority Stress Model
The minority stress model takes into account significant stressors that distinctly affect the mental health of those who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, or another non-conforming gender identity. Some risk factors that contribute to declining mental health are heteronormativity, discrimination, harassment, rejection , stigma, prejudice, denial of civil and human rights, lack of access to mental health resources, lack of access to gender-affirming spaces , and internalized homophobia. The structural circumstance where a non-heterosexual or gender non-conforming individual is embedded in significantly affects the potential sources of risk. The compounding of these everyday stressors increase poor mental health outcomes among individuals in the LGBTQ+ community. Evidence shows that there is a direct association between LGBTQ+ individuals’ development of severe mental illnesses and the exposure to discrimination.
In addition, there are a lack of access to mental health resources specific to LGBTQ+ individuals and a lack of awareness about mental health conditions within the LGBTQ+ community that restricts patients from seeking help.
Who Is At Risk Of Bipolar Disorder

More than 10 million Americans have bipolar disorder. Bipolar disorder affects men and women equally, as well as all races, ethnic groups, and socioeconomic classes.
Although men and women appear to be equally affected by bipolar disorder, rapid cycling is seen more often in women. Women also tend to experience more depressive and mixed state episodes than do men. A man’s first experience with bipolar disorder may be in a manic state women tend to first experience a depressive state.
Bipolar disorder can present itself at any age, but typically, onset occurs around age 25.
Also Check: Which Is Worse Bipolar Or Bpd
Can Lifestyle Habits Increase The Risk Of Bipolar Disorder
Lack of sleep increases the risk of having an episode of mania in someone with bipolar disorder. In addition, antidepressants, particularly when taken as the only medication, may also trigger a switch into a manic state.
Excessive use of alcohol or drugs can also trigger bipolar symptoms. Research has shown that about 50% of bipolar sufferers have a substance abuse or alcohol problem. Sufferers often use alcohol or drugs in an effort to reduce unpleasant feelings during low mood periods, or as part of the recklessness and impulsivity associated with manic highs.
Bipolar Disorder Treatments For Women
While theres no cure for bipolar disorder, there are many treatment options to help people manage their symptoms.
Finding the best treatments for you will likely take some trial and error not to mention good communication with your doctors.
The type of treatments you use will depend on many factors, including health history, symptoms, age, and reproductive phase.
Don’t Miss: Blurred Vision Panic Attack
Coping Mechanism Among The Lgbtq+ Community
Each individual has its own way to deal with difficult emotions and situations. Oftentimes, the coping mechanism adopted by a person, depending on whether they are safe or risky, will impact their mental health. These coping mechanisms tend to be developed during youth and early-adult life. Once a risky coping mechanism is adopted, it is often hard for the individual to get rid of it.
Safe coping-mechanisms, when it comes to mental disorders, involve communication with others, body and mental health caring, support and help seeking.
Because of the high stigmatization they often experience in school, public spaces and society in general, the LGBTQ+ community, and more especially the young people among them are less likely to express themselves and seek for help and support, because of the lack of resources and safe spaces available for them to do so. As a result, LGBTQ+ patients are more likely to adopt risky coping mechanisms then the rest of the population.
These risky mechanisms involve strategies such as self-harm, substance abuse, or risky sexual behavior for many reasons, including “attempting to get away from or not feel overwhelming emotions, gaining a sense of control, self-punishment, nonverbally communicating their struggles to others.” Once adopted, these coping mechanisms tend to stick to the person and therefore endanger even more the future mental health of LGBTQ+ patients, reinforcing their exposure to depression, extreme anxiety and suicide.
Bipolar Disorder And Gender Differences
Bipolar disorder affects men and women in about equal numbers, but in different ways.
Bipolar disorder develops in men and women in about equal numbers, but there are gender differences in the ways that the illness manifests itself. Women with the disorder tend to have more depressive and fewer manic episodes than men do. “The typical bipolar woman will start with a depressive episode, whereas a man will usually get a manic episode first,” says Michael First, M.D., professor of clinical psychiatry at Columbia University and editor of the latest edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, the American Psychiatric Association’s diagnostic guidelines. Women are also more likely to have bipolar II, which is a milder form of the disorder. However, women are more prone than men to rapid-cycling bipolar, which is characterized by four or more episodes of depression and mania in one year. Rapid-cycling bipolar appears to be more resistant to treatment than other forms of the illness.
Bipolar Disorder and Gender Differences: Women
Reproductive hormones may also play a role in bipolar disorder in women, since symptoms often worsen during perimenopause and menopause. “During perimenopause, women may be especially at risk for depressive episodes because of declining estrogen levels,” says Bearden.
Bipolar Disorder and Gender Differences: Men
You May Like: Late Onset Schizophrenia
Management Of Comorbid Disorders
The basic principle of management of comorbid disorders would be first to achieve mood regulation with the help of mood stabilizers. A mood stabilizer which can take care of both the bipolarity and comorbid disorder should be preferred such as valproate for panic disorder and alcohol dependence or migraine, carbamazepine for alcohol withdrawal, Topiramate in alcohol dependencies, obesity, migraine, binge eating, and gabapentin in social anxiety disorder.
Many comorbid psychiatric disorders like anxiety disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder, eating disorder etc., respond to antidepressants, but it would be prudent to use them along with mood stabilizers to avoid the risk of cycle acceleration. In case antidepressants have to be avoided, psychotherapic measures like cognitive behavioral therapy interpersonal therapy may be used.
Is Bipolar Disorder Treatment Different For Men And Women
In truth, the best bipolar treatment is different for each individual. Ideally, a treatment plan takes into account the persons history, symptoms, triggers, home and daily environment, available support, and personal goals and challenges. Those variables may be unique to each client.
Considering that there tend to be recognizable patterns of bipolar episodes that differ in men and women, this may inform the particulars of their clinical supervision. For example, because men tend to experience more frequent and severe episodes of mania, clinicians may place more emphasis on preparing male clients for the challenges related to mania. But, of course, this wouldnt make the depressive episodes any less serious. In fact, because men tend to be less likely to seek treatment, it is especially important that close attention is also paid to the lows that typically follow the highs.
On the other hand, women may experience more frequent depressive episodes and more rapid cycling of mania and depression. So, psychiatrists and therapists will aim to prepare female clients to cope with these personal challenges. They may also put in place treatment strategies to weather seasonal changes, as well as hormonal and phase-of-life changes that can affect bipolar women more intensely than men.
Also Check: Sesquipedalophobia Definition